Sepsis in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
Sepsis is a condition that develops when your child's immune system reacts too strongly to an infection. The immune system normally fights germs causing an infection. Sepsis develops when the immune system stops attacking germs and starts attacking healthy cells throughout your child's body. This causes a low blood pressure (BP) and inflammation. Sepsis is considered severe if the inflammation affects how one or more of your child's organs work. Sepsis must be treated immediately to prevent septic shock. Septic shock is life-threatening low BP that leads to organ failure.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has trouble breathing, or his or her lips and fingernails are pale or turning blue.
- Your child passes out or has a seizure.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child is coughing hard or coughing up blood.
- Your child has a high-pitched cry.
- Your child's bowel movement or vomit has blood in it.
- Your child looks very tired or weak, or is more fussy or sleeping more than usual.
- Your child is not able to eat, suck, or drink, or is urinating less or not at all.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Vancocin
Vancocin is used for bacteremia, bacterial endocarditis prevention, bacterial infection, bone ...
Ceftin
Ceftin (cefuroxime) is an antibiotic used to treat many kinds of bacterial infections. Includes ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Zinacef
Zinacef is used for bacterial infection, bladder infection, bone infection, bronchitis ...
Vancocin HCl
Vancocin HCl is used for bacteremia, bacterial endocarditis prevention, bacterial infection, bone ...
Claforan
Claforan is used for bacteremia, bone infection, cesarean section, CNS Infection, endometritis ...
Fortaz
Fortaz is used for bacteremia, bladder infection, bone infection, endocarditis, endometritis ...
Tazicef
Tazicef is used for bacteremia, bladder infection, bone infection, endocarditis, endometritis ...
Vancocin HCl Pulvules
Vancocin HCl Pulvules is used for bacteremia, bacterial endocarditis prevention, bacterial ...
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child's symptoms return.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to help treat an infection or decrease your child's symptoms.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Prevent sepsis:
- Wash your hands and your child's hands often. This can help decrease your child's risk for infections. Have your child wash his or her hands before he or she eats. Also have your child wash his or her hands after he or she uses the bathroom. Wash your hands before you prepare your child's meal. Also wash your hands after you use the bathroom. You and your child should use soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.

- Care for your child's wounds and incisions as directed. Keep your child's wounds and incisions clean and dry. Change your child's bandages when they get wet or dirty. Tell your child's healthcare provider immediately if you see signs of a wound infection. Signs include redness, warmth, swelling, or pus.
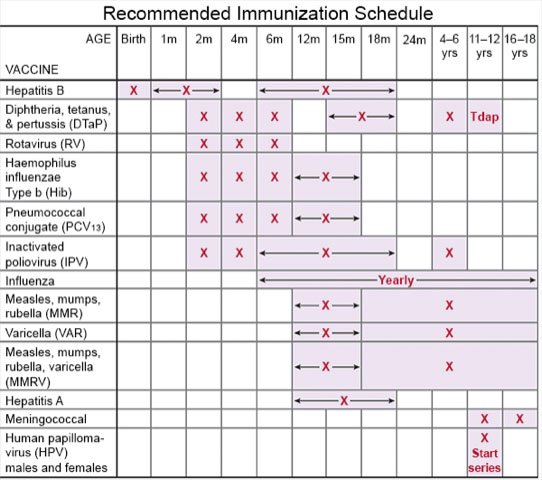
- Ask about vaccines your child may need. Vaccines can help prevent some infections that may lead to sepsis. Have your child get a flu vaccine every year as soon as recommended, usually in September or October. Children 6 months or older should get a COVID-19 vaccine and recommended boosters. Your child's healthcare provider can tell you if your child also needs other vaccines, and when to get them.
- Prevent the spread of germs. Keep your child home from school or daycare if others are sick. Try to keep your child away from people who have a cold or the flu. If your child is sick, keep him or her away from others as much as possible.
 |
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Sepsis
Treatment options
- Medications for Infection
- Medications for Sepsis
- Medications for Septicemia
- Medications for Streptococcemia
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
