Sepsis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is sepsis?
Sepsis is a condition that develops when your immune system reacts too strongly to an infection. Your immune system normally fights the germs causing an infection. Sepsis develops when your immune system stops attacking the germs and starts attacking healthy cells throughout your body. This causes a low blood pressure (BP) and inflammation. Sepsis is considered severe if the inflammation affects how one or more of your organs work. Sepsis must be treated immediately to prevent septic shock. Septic shock is sepsis with a life-threatening low BP that leads to organ failure.
What increases my risk for sepsis?
- An infection anywhere in your body, especially your lungs, blood, or urinary tract
- Treatment in a hospital for a serious illness, or having an implanted catheter
- Age older than 65
- Chronic conditions such as COPD, heart failure, or diabetes
- A weak immune system caused by medicines or a condition such as cancer
- Severe injuries, such as large burns
- A recent surgery
- Use of certain medicines
What are the signs and symptoms of sepsis?
- Fast and shallow breathing
- Confusion, loss of consciousness, or a seizure
- Fever or very low body temperature with chills or shivering
- Severe pain
- Cold, pale, or clammy skin
- Extreme weakness
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Urinating very little or not at all
How is sepsis diagnosed?
- Measurement of your vital signs may show an abnormal temperature, heart rate, or blood pressure. Healthcare providers may use certain tests or checklists to track measurements. They may also track your level of consciousness, signs of organ damage, or problems with blood clotting.
- Blood and urine tests may show signs of infection or organ function. The tests may also show which germ is causing the infection.
How is sepsis treated?
Several treatments may be needed if sepsis causes one or more organs to stop working correctly. Treatments are often started in the emergency room and continued in an intensive care or critical care unit of a hospital. You may need any of the following:
- Medicines will be given to treat the infection. Medicines may be given to increase your blood pressure and blood flow to your organs. Medicines may also be given to control your blood sugar level, or to prevent stomach ulcers or blood clots.
- Oxygen may be needed if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be.
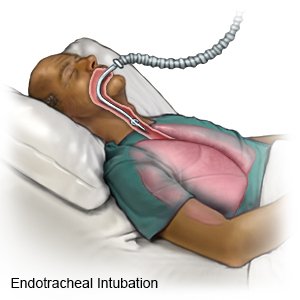
- A ventilator is a machine that gives you oxygen and breathes for you when you cannot breathe well on your own. An endotracheal (ET) tube is put into your mouth or nose and attached to the ventilator.
- A blood transfusion may be needed if bleeding occurs or platelet levels drop. This can happen in severe sepsis.
- Removal or change of a catheter or drain may be needed to get rid of the infection.
- Dialysis may be needed if your kidneys stop working correctly or are damaged during sepsis. Dialysis is a procedure to remove chemicals, wastes, and extra fluid from your blood.
- Surgery or other procedures may be needed to treat problems causing sepsis. This may include draining an abscess or removing infected tissue.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to prevent sepsis?
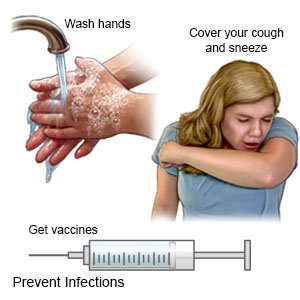
- Wash your hands often with soap and water. Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a child's diapers, or sneeze. Do not touch your eyes, nose, or mouth unless you have washed your hands first. Wash your hands before you prepare or eat food. Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available.

- Care for wounds and incisions as directed. Keep wounds and incisions clean and dry. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty. Tell your healthcare provider immediately if you have signs of a wound infection. Signs include redness, warmth, swelling, or pus.
- Prevent the spread of germs. Try to stay away from people who have a cold or the flu. If you are sick, stay away from others as much as possible.
- Ask your healthcare provider about vaccines you may need. Vaccines can help prevent some infections that may lead to sepsis. Get a flu vaccine every year as soon as recommended, usually in September or October. Get a COVID-19 vaccine and recommended boosters. You may also need a pneumonia vaccine. Your provider can tell you if you also need other vaccines, and when to get them.
- Care for a drain or IV catheter to help prevent an infection. Care instructions will include keeping the device area clean and dry.
 |
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Related medications
Learn more about Sepsis
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
