Panic Disorder in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Panic disorder
is an anxiety disorder that causes your child to have sudden panic attacks. A panic attack is a strong feeling of fear or discomfort. The attack starts suddenly, is worst 10 minutes after it starts, and stops within 20 minutes. The attack may have a trigger, or it may happen for no reason. Panic disorder means your child had at least 2 panic attacks that had no trigger. The attacks caused your child to worry over the next month that he or she would have more attacks. The attacks or worry about future attacks also change your child's behavior. For example, he or she stops going out with friends from fear of an attack.
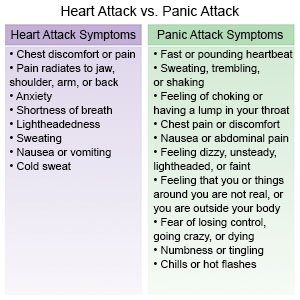
Common signs and symptoms of a panic attack:
- Chest pain or discomfort, or fast or irregular heartbeats
- Sweating, trembling, lightheartedness, or fainting
- Hyperventilation (breathing so quickly your child become dizzy, lightheaded, or faint)
- Shortness of breath, trouble breathing, or a feeling of choking or smothering
- Pale or cold skin, chills, or hot flashes
- Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain
- A feeling that your child is separate from his or her body
 |
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
Your child has any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in his or her chest
- and any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in his or her back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Xanax
Xanax (alprazolam) is a benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety and panic disorders ...
Cymbalta
Cymbalta (duloxetine) is used to treat major depressive disorder, general anxiety disorder and ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Lexapro
Lexapro is used to treat anxiety and major depressive disorder. Learn about side effects ...
Zoloft
Zoloft is an antidepressant used to treat major depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic ...
Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine is used to treat depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder in adults. Learn about side ...
Prozac
Prozac (fluoxetine) is an SSRI antidepressant used to treat depression, OCD, panic disorder ...
Ativan
Ativan is a benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety disorders or anxiety associated with depression ...
Buspirone
Buspirone is used to treat symptoms of anxiety, such as fear, tension, irritability and dizziness ...
Sertraline
Sertraline (Zoloft) is an SSRI used to treat depression, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and PMDD by increasing ...
Call your child's pediatrician or therapist if:
- Your child has new or worsening symptoms.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Treatment
may include any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to make your child feel more relaxed or to reduce anxiety that causes a panic attack. Some medicines are taken only when your child is having a panic attack. Other medicines can be taken to prevent panic attacks. Medicines are usually used along with therapy or other treatments.
- A behavior therapist can help your child learn to control how his or her body responds to stressful situations. The therapist may also teach your child ways to relax muscles and slow breathing during a panic attack. The therapist may teach your child ways to know that the panic attack will not get worse. Your child may also learn ways to prevent or stop hyperventilation.
- Exposure therapy is used to help your child change his or her reaction to triggers. Your child is exposed to triggers in small amounts. The amount of exposure is slowly increased until it no longer triggers a panic attack.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Help your child manage panic disorder:
- Keep a record of your child's panic attacks. The record should include each panic attack, how long it lasted, and anything that helped stop it. Bring the record with you every time you see your child's healthcare providers.
- Help your child manage stress. Stress can trigger a panic attack. Help your child talk about the stress he or she feels. Offer support and encouragement. Your child may need help finding a solution to a problem. He or she may also just need to talk.
- Encourage your child to be physically active. Physical activity, such as exercise, can reduce stress and help your child sleep better. Children and adolescents should get at least 60 minutes of physical activity every day. Your child's healthcare provider can help you create an exercise plan.

- Set a sleep schedule. Too little sleep can increase anxiety. Have your child go to bed at the same time each night and wake up at the same time each morning. Keep your child's room quiet and free from distractions, such as a television or computer.
- Offer your child a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish, and beans. Limit sugar. Sugar can increase your child's symptoms.

- Do not let your child have foods or drinks that contain caffeine. These include coffee, tea, soda, energy drinks, and chocolate. Caffeine can make anxiety worse or trigger a panic attack.
- Talk to your adolescent about not smoking. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can increase anxiety. Ask your adolescent's healthcare provider for information if he or she currently smokes and needs help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your adolescent's healthcare provider before he or she uses these products.
Follow up with your child's pediatrician or therapist as directed:
Your child's healthcare providers will ask if medicine is helping to reduce his or her symptoms. Tell them about any side effects or problems your child has with the medicine. Sometimes the type or amount of medicine may need to be changed. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Panic Disorder
- Antidepressants: Options, Advantages, and Precautions
- Anxiety Medications and Alcohol Interactions
- Benzodiazepines: Overview and Use
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
