Crohn Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is Crohn disease?
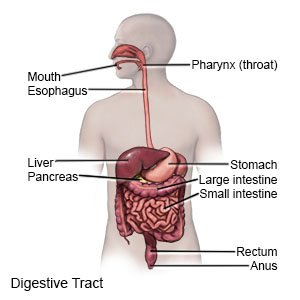
Crohn disease is an inflammatory disease of the digestive system. Crohn disease causes the lining of your intestines to become inflamed. The lining of your mouth, esophagus, or stomach may also be affected.
 |
What increases my risk for Crohn disease?
The cause of Crohn disease is not known. Any of the following may increase your risk:
- A family history of Crohn disease
- Smoking cigarettes
- Immune system that overreacts to bacteria or viruses
- Too much sugar or animal fat and protein, such as too much beef, chicken, or fish
- An infection, such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, or Clostridium difficile
- Certain medicines such as NSAIDs
What are the signs and symptoms of Crohn disease?
You may have different symptoms at different times. Your symptoms may come and go with remission (no symptoms) and active (flare-up) periods. Over time, active periods may occur more often and symptoms may be more severe. The most common signs and symptoms include the following:
- Cramping pain on the lower right side of your abdomen
- Diarrhea that may be dark or tar-colored, or blood in your bowel movements
- Fever
- More mentally and physically tired than usual (fatigue)
- Nausea, loss of appetite, or weight loss without trying
- Slow growth or failure to thrive in children
How is Crohn disease diagnosed?
- Blood tests may be needed to check for infection or health problems caused by Crohn disease, such as low iron levels. Inflammation levels may also be checked.
- A bowel movement sample may show if bacteria are causing your illness.
- A colonoscopy is a test that is done to look at your colon. A tube with a light on the end will be put into your anus, and then moved forward into your colon.
- A barium enema is an x-ray of the colon. A tube is put into your anus, and a liquid called barium is put through the tube. Barium is used so that your healthcare provider can see your colon better.
- A barium swallow is an x-ray of your throat and esophagus. This test may also be called a barium esophagram. You will drink a thick liquid called barium. Barium helps your esophagus and stomach show up better on x-rays. Follow the instructions of your healthcare provider before and after the test.
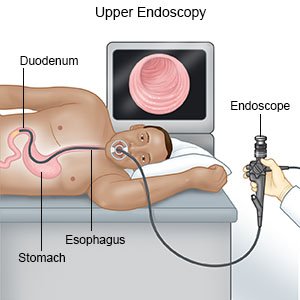
- An endoscopy is a test that uses a scope to see the inside of your digestive tract, including the esophagus and stomach. Samples may be taken from your digestive tract and sent to a lab for tests. Bleeding may also be treated during an endoscopy.
- MRI or CT pictures may be taken of your digestive system and other organs. You may be given contrast liquid to help the pictures show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. The MRI machine contains a powerful magnet. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- An ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to look at pictures of your digestive system.
Related medications
How is Crohn disease treated?
- Medicines may be used to decrease inflammation in your digestive tract. You may need antibiotics to treat or prevent an infection and antidiarrheal medicine to decrease diarrhea. Immunosuppressants may also be given to slow your immune system.
- Surgery may be needed to decrease your symptoms or to correct problems such as blockage or bleeding. Your healthcare provider may remove the diseased part of your intestines and reconnect the healthy parts. You may also need to have a colostomy.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage Crohn disease?
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can make it harder to manage Crohn disease and increase your risk for a flare-up. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
- Take your medicines exactly as directed. This may help to keep your disease in remission.
- Keep a record of everything you eat and drink. Include any symptoms the food or drink causes or makes worse. You may need to avoid certain foods. Dairy, alcohol, hot spices, and high-fiber foods are common examples of foods that may worsen your symptoms. Your provider may recommend that you take vitamins or minerals. Always ask your provider before you take vitamins or nutritional supplements.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You suddenly have trouble breathing.
- You have a fast heart rate, fast breathing, or are too dizzy to stand.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You vomit blood, or your vomit looks like coffee grounds.
- You have severe pain in your stomach.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have tar-colored bowel movements or you see blood in your bowel movements.
- You have a fever or chills.
- The pain in your abdomen does not go away or gets worse after you take medicine.
- Your abdomen is swollen.
- You are losing weight without trying.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Crohn Disease
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
