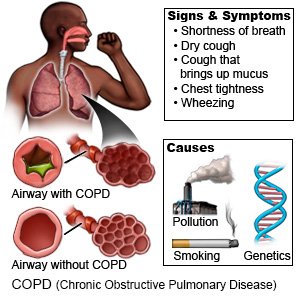
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) can get worse quickly. Your healthcare providers will help you create a care plan to use at home. The plan will give directions on how to prevent or manage shortness of breath. Your family members or anyone who cares for you will also get directions to help you.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Medicines:
- Bronchodilators open your airway so you can breathe easier. They are most often given through an inhaler or nebulizer.
- Mucolytics thin and loosen the mucus in your lungs so you can cough it out.
- Steroids help decrease swelling in your airway.
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection. Antibiotics may be given for up to 5 days during an exacerbation.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. You may bleed or bruise more easily while you are taking this medicine.
Monitoring:
- A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood. A cord with a clip or sticky strip is placed on your finger, ear, or toe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine.
- An EKG records your heart rhythm and how fast your heart beats.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Symbicort
Symbicort (budesonide and formoterol) is used to prevent bronchospasm in people with asthma or ...
Trelegy Ellipta
Trelegy Ellipta is an inhalation powder used to improve symptoms and prevent bronchospasm in adults ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Breztri Aerosphere
Breztri (budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate) is a combination inhaler that may be used ...
Nucala
Nucala is used to treat severe eosinophilic asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps ...
Anoro Ellipta
Anoro (umeclidinium and vilanterol inhalation powder) is used to treat chronic obstructive ...
Budesonide/formoterol/glycopyrrolate
A budesonide, glycopyrrolate, and formoterol inhaler (Breztri Aerosphere) combines 3 medicines into ...
Budesonide
Budesonide systemic is used for asthma, asthma, maintenance, autoimmune hepatitis, crohn's disease ...
Mepolizumab
Mepolizumab (Nucala) is a prescription medication FDA-approved for several eosinophil-related ...
Montelukast
Montelukast is a daily oral medication used to prevent asthma attacks, exercise-induced ...
Tests:
- Lung function tests are used to find how well your lungs work. Spirometry measures the airflow into and out of your lungs. A lung volume test measures the amount of air your lungs can hold. The amount of oxygen that gets into your blood when you breathe may also be measured.
- Blood tests check for infection and measure oxygen levels in your blood. Blood tests may also be used to find if you have alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. This is a genetic condition that can increase your risk for COPD. Blood tests may also show if you have any nutrition problems, such as low vitamin levels.
- A mucus sample is collected in a cup when you cough. The sample is tested for bacteria to find out if you need antibiotic treatment.
- A chest x-ray is done to check for other lung problems.
Treatment:
- Pulmonary rehabilitation (rehab) is a program run by specialists who help you learn to manage COPD. Examples include a pulmonologist (lung specialist), dietitian, and exercise therapist. You may start rehab in the hospital and continue after you return home. You will get directions on how to continue rehab if this is recommended.
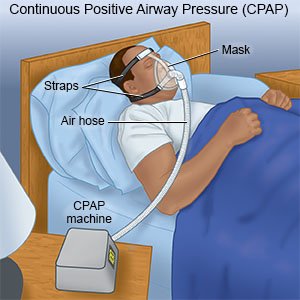
- Oxygen may help you breathe easier and feel more alert. You may receive oxygen through a ventilator or a CPAP machine.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
COPD raises your risk for diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Without treatment, COPD can become life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about COPD
Treatment options
Care guides
- Asthma
- Asthma in Children
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Chronic Bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Moderate and Severe Persistent Asthma
- Reactive Airways Disease
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
