Sunburn
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is a sunburn?
A sunburn is when your skin is damaged by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV radiation comes from sunlight and devices such as tanning beds.
What increases my risk for sunburn?
- Certain medicines may make you more sensitive to sunlight. Talk to your provider to learn more about medicines that may increase your risk for sunburn.
- Exposure to UV rays for long periods increases your risk. The longer your skin is under UV rays, the higher your risk for sunburn.
- Skin tone that is very light or pale increases your risk for sunburn.
- The time of day can increase your risk. Between 10 AM and 3 PM, the sun is hotter and puts out more UV radiation.
- Skin that is not protected burns more easily. Your risk increases if you do not protect your skin with sunscreen or clothing.
What are the signs and symptoms of a sunburn?
Your signs and symptoms may appear while you are under the UV rays. They may also appear a few hours after your exposure. Your symptoms may become worse 12 to 24 hours later. You may have any of the following:
- Red skin
- Pain or a burning feeling
- Swelling, and a feeling of tightness
- Blisters
- Itchiness
- Peeling and flaking
How is a sunburn diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and examine you. He or she may ask how often and how long you stay under the sun or inside tanning beds. Your provider may also ask if you wear sunscreen or clothing to protect your skin. He or she may ask if anyone in your family sunburns easily or if anyone has a history of skin cancer. Tell your provider if you are taking any medicines, or have any other health conditions.
How is a sunburn treated?
You will need to stay out of the sun and tanning beds. Treatment may decrease symptoms:
- Apply a cool compress. A cool compress or wet towel can help soothe your skin.
- Take short baths or showers. Bathe or shower in lukewarm water. Add oatmeal, baking soda, or cornstarch to the bath water to help reduce skin irritation.
- Use lotions or gels to keep your skin moist. These include products such as aloe vera, petroleum jelly, or ointments. These may help cool your skin and decrease pain and redness. Ask which products are best for you.
- Drink liquids as directed. This will help prevent dehydration. Ask which liquids are best for you and how much liquid to drink each day.
- Medicines:
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Steroids decrease redness, pain, and swelling. This medicine may be given as a pill, or used as a lotion to rub on sunburned areas.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I prevent a sunburn?
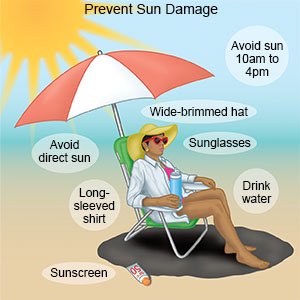 |
- Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher. Put sunscreen on 15 to 30 minutes before you go outside, and again every 2 hours. You will need to put sunscreen on again after you swim, sweat, or dry yourself with a towel.
- Wear clothing that will block UV rays. This includes dark, loose clothing made of a tight weave fabric. Pants, long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses also help block UV rays.
- Stay indoors between 10 AM and 3 PM. This will help you avoid the highest concentrations of UV rays.
- Limit exposure. Do not stay outdoors or in tanning beds for long periods.
- Ask about vitamin supplements. Vitamins A, C, and E may help protect your skin against UV radiation.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Solarcaine First Aid Medicated Spray
Solarcaine First Aid Medicated Spray is used for burns, external, pain, sunburn
Bactine
Bactine is used for burns, external, local anesthesia, pain, pruritus, sunburn
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
AneCream
AneCream is used for anal itching, burns, external, hemorrhoids, local anesthesia, pain, pruritus ...
Xylocaine Topical
Xylocaine Topical is used for anal itching, anesthesia, burns, external, hemorrhoids, local ...
Dermoplast
Dermoplast is used to reduce pain or discomfort caused by insect bites, minor burns, minor cuts ...
DermacinRx Lido V Pak
DermacinRx Lido V Pak is used for anesthesia, burns, external, gastrointestinal tract examination ...
Zionodil
Zionodil is used for anal itching, anesthesia, burns, external, hemorrhoids, local anesthesia ...
CidalEaze
CidalEaze is used for anal itching, anesthesia, burns, external, hemorrhoids, local anesthesia ...
Benzocaine topical
Benzocaine topical is used for anal itching, anesthesia, aphthous ulcer, burns, external, cold ...
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your skin has many blisters, which break or bleed.
- You feel dizzy, weak, or faint.
- You have new headaches that do not go away with medicine.
- You have problems thinking or remembering things.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- You have a fever.
- Your skin is red and itchy from the sunscreen.
- You have a new mole, or one that has changed color, shape, or size.
- Your skin and mouth are dry, and you feel very thirsty.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Sunburn
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
