Eczema in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is eczema?
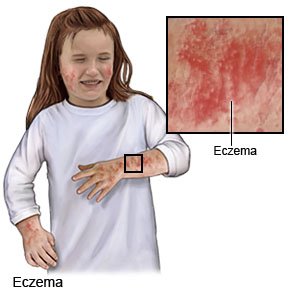
Eczema is an itchy, red, scaly skin rash. Eczema is common in children between the ages of 2 months and 5 years. Your child is more likely to have eczema if he or she also has asthma or allergies. Your child's symptoms may improve as he or she gets older. However, your child may have flare-ups from time to time for the rest of his or her life.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of eczema?
- Patches of dry, red, itchy skin
- Bumps or blisters that crust over or ooze clear fluid
- Areas of skin that are thick, scaly, or hard and leather-like
- Being irritable or having trouble sleeping because of itching
What triggers eczema?
Anything that increases dryness or makes your child want to scratch is a trigger. Triggers can cause eczema to flare up. The following are common triggers:
- Frequent hot baths or showers can lead to dry, itchy skin. Soaps and skin cleansers with dyes or fragrances can also make eczema worse.
- Sudden temperature changes , such as cold air, dries out your child's skin. Heat can increase sweating. Both can make your child itch.
- Allergens such as dust mites and pet dander can make your child's symptoms worse. Pollen, mold, and cigarette smoke may also irritate his or her skin.
- Stress, anxiety, or depression may cause your child's eczema to get worse.
How is eczema diagnosed?
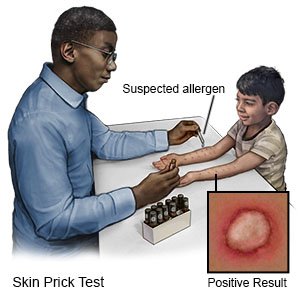
Your child's healthcare provider will examine your child's skin. Tell the provider if you know what triggers your child's rash. Tell the provider if you have tried any treatments that have helped. Your child's provider may want to know if anyone in your family has allergies, asthma, or eczema. Your child's provider may test your child for allergies to find out if they trigger his or her eczema. A skin biopsy may confirm the diagnosis.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Solarcaine First Aid Medicated Spray
Solarcaine First Aid Medicated Spray is used for burns, external, pain, sunburn
Dupixent
Dupixent is used to treat eczema, eosinophilic or oral-corticosteroid-dependent asthma, chronic ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Elidel
Elidel cream is used on the skin to treat mild to moderate eczema (atopic dermatitis). Learn about ...
Bactine
Bactine is used for burns, external, local anesthesia, pain, pruritus, sunburn
Elocon
Elocon is a topical steroid used to treat inflammation and itching caused by allergic reactions and ...
Prednisone
Prednisone is used to treat allergic disorders, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis and arthritis. Learn ...
Desonide topical
Desonide topical is used for allergies, atopic dermatitis, dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis
Fluocinonide topical
Fluocinonide is a high to super-high potency topical corticosteroid that may be used to reduce ...
Lidocaine topical
Lidocaine topical is used for anal itching, anesthesia, burns, external, gastrointestinal surgery ...
How is eczema treated?
The goal of treatment is to reduce your child's itching and pain and add moisture to his or her skin. This helps repair your child's skin barrier. The skin barrier is the outer layer of the skin. It protects the skin from outside conditions and helps prevent water loss from the body. Your child's symptoms should improve within several weeks of treatment. He or she may need the following:
- Medicines may help reduce itching, redness, pain, and swelling. They may be given as an emollient (thick) cream, pill, or injection under the skin. Your child may also receive antibiotics if he or she has a skin infection.
- Phototherapy , or light therapy, may help heal your child's skin.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I care for my child's skin?
- Pat or press on your child's skin to relieve itching. Remind your child not to scratch. Trim your child's fingernails. Put cotton gloves or mittens on your child's hands while he or she sleeps.
- Keep your child's skin moist. Rub gentle or sensitive skin lotion, cream, or ointment on your child's skin many times throughout the day. Ask your child's healthcare provider what to use and how often to use it. Use moist bandages if directed. Do not use products that contain alcohol, dyes, or fragrances.
- Give your child warm water baths or showers for 10 minutes or less. Use mild soap. Apply moisturizer to your child's skin when it is damp, right after the bath or shower. Teach your child how to gently pat his or her skin dry.
- Choose cotton clothes. Dress your child in loose-fitting clothes made from cotton or cotton blends. Avoid wool, polyester, or other scratchy material.
- Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air in your home.
- Help your child avoid changes in temperature. For example, activities that cause him or her to sweat a lot. Sweat can cause itching. Remove blankets from your child's bed if he or she gets hot while sleeping.
- Avoid allergens, dust, and skin irritants. Use mild soap, shampoo, and detergent. Do not use fabric softener.
- Ask your child's healthcare provider about allergy testing. Allergy testing may help identify allergens that irritate your child's skin.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child develops a fever.
- Your child has red streaks going up his or her arm or leg.
- Your child's rash gets more swollen, red, or hot.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Most of your child's skin is red, swollen, painful, and covered with scales.
- Your child develops bloody, painful crusts.
- Your child's skin blisters and oozes white or yellow pus.
- Your child has trouble sleeping because of itching.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Eczema
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
