Photosensitivity
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is photosensitivity?
Photosensitivity is a skin reaction caused or worsened by sunlight.
What increases my risk for photosensitivity?
- Certain medicines, such as antibiotics, birth control pills, or diuretics
- Certain chemicals, such as those in perfume, dye, or disinfecting cleaning products
- A family history of photosensitivity
- An autoimmune disease, such as lupus or Sjögren syndrome
What are the signs and symptoms of photosensitivity?
Your signs and symptoms may start within minutes to 5 days after sun exposure. They may go away within 24 hours or last 1 week or more. You may have any of the following:
- Itchy or painful, red rash on skin exposed to the sun
- Red bumps on your skin
- Hives
- Blisters or swelling
How is photosensitivity diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and examine your skin. Tell your provider about medicines you take or perfume, dye, or disinfecting cleaning products you use. You may need any of the following:
- Phototesting and photopatch testing are procedures that expose an area of your skin to artificial light. These tests may show if your symptoms were caused by light alone or by light and a chemical.
- A blood or urine test may show a medical condition that is causing your symptoms.
- A skin biopsy may show a skin condition such as rosacea that is causing your symptoms.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Dupixent
Dupixent is used to treat eczema, eosinophilic or oral-corticosteroid-dependent asthma, chronic ...
Elidel
Elidel cream is used on the skin to treat mild to moderate eczema (atopic dermatitis). Learn about ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Elocon
Elocon is a topical steroid used to treat inflammation and itching caused by allergic reactions and ...
Cortizone-10
Cortizone-10 is used for atopic dermatitis, dermatitis, eczema, intertrigo, pruritus, psoriasis ...
Pimecrolimus topical
Pimecrolimus topical is used for atopic dermatitis, eczema, perioral dermatitis
Methotrexate
Methotrexate is used to treat certain types of cancer of the breast, skin, head and neck, or lung ...
Prednisone
Prednisone is used to treat allergic disorders, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis and arthritis. Learn ...
Desonide topical
Desonide topical is used for allergies, atopic dermatitis, dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis
Fluocinonide topical
Fluocinonide is a high to super-high potency topical corticosteroid that may be used to reduce ...
How is photosensitivity treated?
- Steroids may help decrease itching and inflammation.
- Antihistamines may help decrease itching.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Phototherapy is used to expose your skin to doses of ultraviolet light. This may help your skin adjust to the sunlight and help prevent skin reactions.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage or prevent a skin reaction?
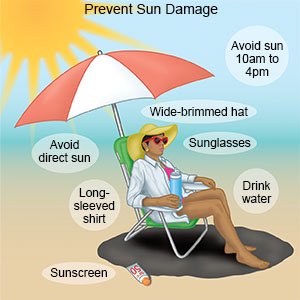 |
- Soothe your skin. Apply a cool, damp cloth to the rash area. This may also help relieve itching. Use lukewarm water when you bathe. Pat your skin dry. Do not rub your skin with a towel. Use detergents, soaps, and shampoos made for sensitive skin.
- Apply sunscreen before you go outside. Use a broad spectrum, waterproof sunscreen with an SPF of at least 50. Apply sunscreen even on cloudy or cool days. Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours.
- Avoid direct sunlight between 10 am and 3 pm. This is when ultraviolet light is strongest. Sit in the shade, if possible. Wear long sleeves, pants, or long skirts when you must be in the sun. Cover your skin as much as possible if no shade is available.
- Wear sunglasses and a hat when you are outside. Wear a hat with a wide brim all the way around to protect your face, ears, and neck. Sunglasses with UVA/UVB protection can help protect your eyes and the skin around your eyes.
- Do not use tanning beds or other artificial light devices. These are not safer than direct sunlight and may cause a reaction.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe pain.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- Your rash spreads and covers large parts of your body.
- Your rash starts to turn into blisters.
- Your symptoms do not get better, or get worse, even after treatment.
- You have a rash on your cheeks and nose that looks like a butterfly.
- Your skin bruises easily.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Photosensitivity
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
