Tryngolza: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: olezarsen sodium
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Miscellaneous antihyperlipidemic agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Feb 9, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TRYNGOLZA (olezarsen) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024
Indications and Usage for Tryngolza
TRYNGOLZA is an APOC-III-directed antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglycerides in adults with familial chylomicronemia syndrome (FCS). ( 1)
Tryngolza Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 80 mg/0.8 mL in a single-dose autoinjector. ( 3)
Contraindications
History of serious hypersensitivity reactions to olezarsen or any of the excipients in TRYNGOLZA. ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients treated with olezarsen. Advise patients on the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct patients to promptly seek medical attention and discontinue use of TRYNGOLZA if hypersensitivity reactions occur. ( 5.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >5% of TRYNGOLZA-treated patients and >3% higher frequency than placebo) were injection site reactions, decreased platelet count, and arthralgia. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc. at toll free number 1-833-644-6647 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2024
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tryngolza
TRYNGOLZA is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglycerides in adults with familial chylomicronemia syndrome (FCS).
2. Tryngolza Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TRYNGOLZA is 80 mg administered subcutaneously once monthly [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] .
2.2 Administration Instructions
Prior to initiation, train patients and/or caregivers on proper preparation and administration of TRYNGOLZA [see Instructions for Use] .
Remove the single-dose autoinjector from the refrigerator 30 minutes prior to the injection and allow to warm to room temperature. Do not use other warming methods.
Inspect TRYNGOLZA visually for particulate matter prior to administration. The solution should be clear and colorless to yellow. Do notuse if cloudiness, particulate matter, or discoloration is observed prior to administration.
Maintain a low-fat diet (≤20g fat per day) in conjunction with TRYNGOLZA.
Inject TRYNGOLZA subcutaneously into the abdomen or front of the thigh. The back of the upper arm can also be used as an injection site if a healthcare provider or caregiver administers the injection.
Administer TRYNGOLZA as soon as possible after a missed dose. Resume dosing at monthly intervals from the date of the most recently administered dose.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 80 mg/0.8 mL of olezarsen as a clear, colorless to yellow solution in a single-dose autoinjector.
4. Contraindications
TRYNGOLZA is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity to olezarsen or any of the excipients in TRYNGOLZA. Hypersensitivity reactions, including symptoms of bronchospasm, diffuse erythema, facial swelling, urticaria, chills, and myalgias, requiring medical treatment have occurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (including symptoms of bronchospasm, diffuse erythema, facial swelling, urticaria, chills, and myalgias) have been reported in patients treated with TRYNGOLZA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Advise patients on the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct patients to promptly seek medical attention and discontinue use of TRYNGOLZA if hypersensitivity reactions occur.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of TRYNGOLZA cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of TRYNGOLZA was evaluated in 66 patients with FCS enrolled in Trial 1 (NCT #04568434) [see Clinical Studies (14)] . In this trial, 43 patients received at least one dose of TRYNGOLZA, 50 mg (N=21) or 80 mg (N=22) and 23 patients received placebo. TRYNGOLZA 50 mg is not an approved dosing regimen for FCS [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Across treatment groups, the mean age was 45 years and 42% of patients were male. Eighty-five percent (85%) of patients were White, 9% were Asian and 6% were reported as other races; 11% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Forty-three (43) patients were exposed to TRYNGOLZA for a median of 52 weeks; 22 patients were treated with TRYNGOLZA 80 mg every 4 weeks for a median of 52 weeks.
Adverse reactions led to discontinuation of treatment in 7% of TRYNGOLZA-treated patients and 0% of placebo-treated patients. The most common reasons for TRYNGOLZA treatment discontinuation were hypersensitivity reactions. Adverse reactions (>5% of patients treated with TRYNGOLZA and at >3% higher frequency than placebo) are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions That Occurred in >5% of Patients Treated with TRYNGOLZA and at >3% Higher Frequency than Placebo (Trial 1)
|
||
| Adverse Reaction * |
Total
| Placebo
(N = 23) |
| Injection site reactions | 8 (19%) | 2 (9%) |
| Decreased platelet count | 5 (12%) | 1 (4%) |
| Arthralgia | 4 (9%) | 0 |
Laboratory Tests
Decrease in Platelet Count:TRYNGOLZA can cause reductions in platelet count. In Trial 1, the mean platelet count in the TRYNGOLZA 80 mg group was 188,000 mm
3at baseline, and the mean percent change in platelet count was -10% at Week 53. In comparison, the mean platelet count in the placebo group was 215,000/mm
3at baseline, and the mean percent change in platelet count was 22% at Week 53. No TRYNGOLZA-treated patient with FCS had a platelet count <50,000/mm
3. There were no major bleeding events associated with a low platelet count. Overall, the proportion of patients experiencing a bleeding adverse event was similar across the TRYNGOLZA and placebo treatment groups.
Increase in Glucose:Small increases in average values in fasting glucose (≤17 mg/dL) and HbA1c (<0.2 percentage points) were observed over time with TRYNGOLZA treatment in the FCS population in Trial 1. The incidence of hyperglycemia (defined as adverse events, new antidiabetic medication, or laboratory values) was higher in olezarsen-treated patients without a medical history of diabetes at baseline (52%) compared to placebo-treated patients (35%).
Increase in Liver Enzymes:Increases from baseline in liver enzymes within the normal range were observed with olezarsen treatment in the FCS population. These increases occurred within the first 3 months of treatment and stabilized. Liver enzymes returned towards baseline with discontinuation of olezarsen.
Increase in LDL-cholesterol:Increases in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and total apolipoprotein B (apoB) were observed in the FCS population treated with TRYNGOLZA compared to those treated with placebo [see Clinical Studies (14)] . Despite increases in LDL-C, the maximum LDL-C value remained low for most patients (i.e., <70 mg/dL for 74% of patients treated with TRYNGOLZA).
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on TRYNGOLZA use in pregnant women to inform drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Patients with FCS are at risk for pancreatitis during pregnancy because of defects in lipid metabolism and increased triglyceride levels (see Clinical Considerations) .
In animal reproduction studies conducted with the unconjugated antisense oligonucleotide (lacking GalNAc) in rabbits and mice, no adverse effects on development or pregnancy were observed at doses 21 times or 20 times, respectively, the maximum recommended clinical dose.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20% respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo-Fetal Risk
During pregnancy, triglyceride levels increase during the third trimester of pregnancy. In patients with underlying defects in lipid metabolism, such as FCS, severe gestational hypertriglyceridemia may occur, increasing the risk of acute pancreatitis during pregnancy.
Data
Animal Data
Olezarsen was not evaluated for potential effects on embryofetal development (EFD). However, effects of the administration of the unconjugated antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), which shares the same nucleotide sequence but lacks the N-acetyl galactosamine [GalNAc] moiety [see Description (11)] , were evaluated.
In a combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study in mice, the unconjugated ASO was administered to male and female mice by subcutaneous injection at doses of 10.5, 35, and 87.5 mg/kg/week prior to mating and through to the completion of organogenesis (gestation day 15). No adverse developmental outcomes occurred at doses up to 87.5 mg/kg/week (approximately 21-times the monthly maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on a body surface area (BSA) comparison of the unconjugated ASO).
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits, the unconjugated ASO was administered by subcutaneous injection at doses of 10.5, 21, and 52.5 mg/kg/week during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 to 18). No adverse developmental effects were observed at doses up to 21 mg/kg/week (approximately 20-times the monthly MRHD based on a BSA comparison of the unconjugated ASO).
In a pre-/postnatal toxicity study in mice, the unconjugated ASO was administered at 10.5, 35, or 87.5 mg/kg/week during the period of organogenesis and continuing until weaning (gestation day 6 through lactation day 21). Offspring body weights at 87.5 mg/kg/week (21-times the monthly MRHD based on BSA) were lower throughout their lives and were associated with slight delays in the attainment of morphological and developmental landmarks. No adverse effects on offspring were observed at 35 mg/kg/week (approximately 9-times the monthly MRHD based on a BSA comparison of the unconjugated ASO).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of olezarsen in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, the unconjugated antisense ASO, which shares the same nucleotide sequence but lacks GalNAc, was present in the milk of lactating mice at low levels. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. Oligonucleotide-based products typically have poor oral bioavailability; therefore, it is considered unlikely that low levels present in milk will lead to clinically relevant levels in breastfed infants. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for TRYNGOLZA and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed infant from TRYNGOLZA or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TRYNGOLZA in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No dose adjustment is recommended in patients aged 65 years and older [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . In clinical studies, 111 (38%) patients treated with TRYNGOLZA were ≥65 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of TRYNGOLZA have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] ≥30 to <90 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . TRYNGOLZA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . TRYNGOLZA has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment.
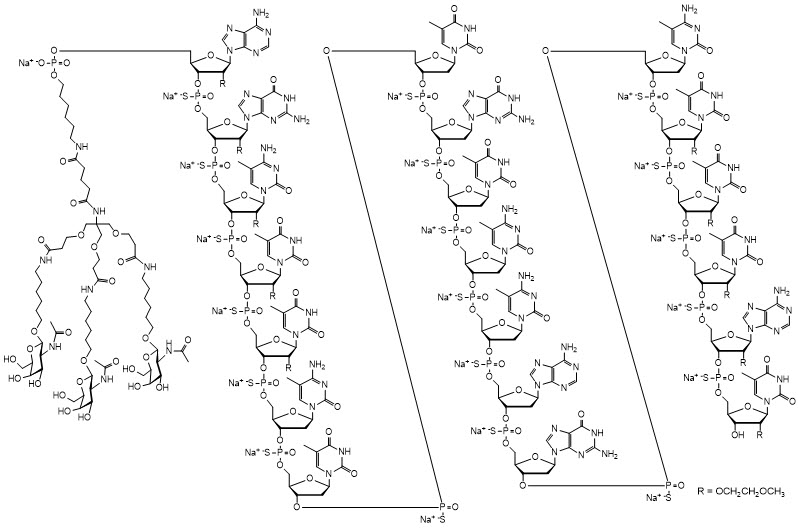
11. Tryngolza Description
Olezarsen is an ASO directed inhibitor of Apolipoprotein C-III (apoC-III) mRNA, conjugated to a ligand containing three N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc) residues to enable delivery of the ASO to hepatocytes.
TRYNGOLZA contains olezarsen sodium as the active ingredient. Olezarsen sodium is a white to yellow solid and it is freely soluble in water and in phosphate buffer. The molecular formula of olezarsen sodium is C 296H 419N 71O 154P 20S 19Na 20and the molecular weight is 9124.48 daltons. The chemical name of olezarsen sodium is DNA, d(P-thio) ([2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] rA-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] rG-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] m5rC-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] m5rU-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] m5rU-m5C-T-T-G-T-m5C-m5C-A-G-m5C-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] m5rU-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] m5rU-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] m5rU-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)] rA-[2'- O-(2-methoxyethyl)]m5rU), 5'-[26-[[2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-β-D-galactopyranosyl]oxy]-14,14-bis[[3-[[6-[[2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-β-D-galactopyranosyl]oxy]hexyl]amino]-3-oxopropoxy]methyl]-8,12,19-trioxo-16-oxa-7,13,20-triazahexacos-1-yl hydrogen phosphate], sodium salt (1:20).
The structure of olezarsen sodium is presented below:
TRYNGOLZA is a sterile, preservative-free solution for subcutaneous injection. Each single-dose autoinjector contains 80 mg olezarsen (equivalent to 84 mg of olezarsen sodium) in 0.8 mL of solution. The solution also contains the following inactive ingredients: disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate to maintain pH and provide tonicity, and water for injection. The solution may include hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment between 6.9 to 7.9. Each dose of TRYNGOLZA injection contains 6 mg of phosphorous and 5 mg of sodium.
12. Tryngolza - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Olezarsen is an ASO-GalNAc 3conjugate that binds to apoC-III mRNA leading to mRNA degradation and resulting in a reduction of serum apoC-III protein. Reduction of apoC-III protein leads to increased clearance of plasma TG and VLDL.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Fasting apoC-III
Olezarsen decreased fasting apoC-III following administration of TRYNGOLZA 80 mg dosage every 4 weeks to patients with FCS
[See
Clinical Studies (14)]
. The placebo-corrected percent change in fasting apoC-III from baseline was -57% at 1 month, -69% at 3 months, -72% at 6 months, and -80% at 12 months.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Olezarsen steady state mean (SD) maximum concentrations (C max) is 883 (662) ng/mL and area under the curve (AUC τ) is 7440 (3880) ng*h/mL at the approved recommended dosage in patients with FCS. Olezarsen C maxand AUC increase dose-proportionally following single subcutaneous doses ranging from 10 to 120 mg (i.e., 0.13- to 1.5-times the approved recommended dose) in healthy volunteers. No olezarsen accumulation occurs with repeat dosing.
Absorption
Olezarsen time to C max(T max) is approximately 2 hours following subcutaneous administration.
Distribution
The population estimates for the apparent central volume of distribution is 91.9 L and the apparent peripheral volume of distribution is 2960 L for olezarsen. Olezarsen is greater than 99% bound to plasma proteins, in vitro.
Olezarsen distributes primarily to the liver and kidney after subcutaneous dosing.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of olezarsen were observed based on age (< 65 to ≥ 75 years), body weight, sex, race (White, Black or African American, Asian, Japanese, American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander), mild-to-moderate renal impairment (eGFR ≥30 to <90 mL/min) [CKD-EPI], or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN; , or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5 x ULN and any AST, National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group criteria). The effect of severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min), end-stage renal disease, moderate or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 x ULN with any AST) on olezarsen pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
CYP450 Enzymes:Olezarsen is not an inhibitor or inducer of CYP450 enzymes.
Transporter Systems: Olezarsen is not a substrate or inhibitor of OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, MATE1, MATE2-K, BCRP, P-gp, and BSEP.
Protein Binding:Olezarsen does not displace warfarin and ibuprofen from plasma protein binding sites.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of ADAs in the study described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of olezarsen.
In Trial 1, with duration of treatment up to 53 weeks, 18 out of 43 (42%) patients treated with TRYNGOLZA developed treatment-emergent ADAs. The presence of ADAs did not affect olezarsen plasma C max, but increased C trough. Although ADA development was not found to affect the pharmacodynamics, safety, or efficacy of TRYNGOLZA in these patients, the available data are limited to make definitive conclusions.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No long-term carcinogenicity studies were conducted with olezarsen in animals. However, the unconjugated antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) lacking GalNAc was administered weekly in mice and rats at subcutaneous doses of 0, 6, 25, 40 mg/kg/week (along with a mouse-specific surrogate ASO at 25 mg/kg/week) and 0, 0.2, 1, 5 mg/kg/week, respectively, for 2 years. In male mice, there were statistically significant increases in the incidences of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas at ≥25 mg/kg/week and hemangiomas and hemangiosarcomas at all doses. In female mice, there were statistically significant increases in the incidences of histiocytic sarcomas at all doses (including the mouse-specific surrogate) and pituitary gland adenomas at 25 mg/kg/week. In rats, the incidence of malignant fibrous histiocytoma at the injection site was increased in both sexes at doses ≥1 mg/kg/week. These tumors are considered a response to chronic tissue irritation and inflammation caused by repeated subcutaneous injection. The clinical significance of these findings is uncertain.
Mutagenesis
Olezarsen was negative for genotoxicity in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation assay and chromosome aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung cells) and in vivo (mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay).
Impairment of Fertility
Olezarsen was administered at doses of 0, 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg given every other week to male and female mice prior to mating, followed by every other day dosing after mating and until gestation day 6 in females. There was no effect on fertility in mice administered olezarsen at doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 2-times the monthly maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of TRYNGOLZA was demonstrated in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial in adult patients with genetically identified FCS and fasting triglyceride (TG) levels ≥880 mg/dL (Trial 1; NCT04568434). After a ≥4-week run-in period where patients continued to follow a low-fat diet with ≤20 grams fat per day, patients were randomly assigned to receive doses every 4 weeks of TRYNGOLZA 80 mg (n=22) or matching volume of placebo (n=23) via subcutaneous injection over a 53 week treatment period.
Patient demographic and baseline characteristics were generally similar across the treatment groups [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . The proportion of patients with diabetes at enrollment was 32% in the TRYNGOLZA 80 mg group compared with 26% in the placebo group. Patients in the TRYNGOLZA 80 mg and placebo groups were treated with statins (27%), omega-3 fatty acids (42%), fibrates (49%), or other lipid lowering therapies (13%) at study entry. Seventy-one percent (71%) of patients in the TRYNGOLZA 80 mg and placebo groups combined had a history of documented acute pancreatitis in the prior 10 years. Mean (SD) and median fasting TG levels at baseline were 2,604 (1,364) mg/dL and 2,303 mg/dL, respectively (range of 334 to 6,898 mg/dL).
The primary endpoint was percent change in fasting triglycerides from baseline to Month 6 (average of Weeks 23, 25, and 27) compared to placebo. The difference between TRYNGOLZA 80 mg group and the placebo group in percent change in fasting triglycerides from baseline to Month 6 was -42.5% (95% CI: -74.1%, -10.9%; p=0.0084). For additional results see Table 2.
Table 2. Mean Baseline (BL) and Mean Percent (%) Changes from Baseline in Lipid/ Lipoprotein Parameters in Patients with FCS at Month 6 in Trial 1
| Abbreviations: apoB = apolipoprotein B; non-HDL-C = non high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Note: Analyses results were based on an analysis of covariance model with treatment, the two randomization stratification factors, prior history of pancreatitis within 10 years prior to Screening (yes vs. no), previous treatment with the unconjugated ASO (yes vs. no) as the fixed effects and log-transformed Baseline value as a covariate. Missing data was imputed using placebo washout imputation. The 95% CIs of treatment differences were calculated using a robust variance estimator. For triglycerides and non-HDL, a test of residual normality did not indicate significant departure from normal distribution. |
|||||
| Parameter
(mg/dL) | TRYNGOLZA
80 mg N = 22 | Placebo
N = 23 |
TRYNGOLZA
|
||
| BL |
% change Month 6 | BL |
% change Month 6 |
Treatment Difference % change (95% CI) at Month 6 |
|
| Triglycerides | 2613.1 | -30 | 2595.7 | +12 | -42.5
*
(-74.1, -10.9) |
| Non-HDL-C | 262.9 | -18 | 271.3 | +5.7 | -23.4
(-45.3, -1.5) |
| LDL-C | 22.8 | +64 | 16.7 | +9 | +55.0
†
(0.7, 109.4) |
| Total ApoB | 58.4 | +20 | 59.7 | +9 | +11.7
(-12.6, 35.9) |
| ApoB-48 | 11.6 | -51 | 14.2 | +25 | -75.9
(-149.8, -2.0) |
Median percent change from baseline (Figure 2) and median absolute TG values (Figure 3) over time demonstrated a consistent lowering effect during the 12-month treatment period.
Figure 2. Percent Change in Fasting Triglyceride (mg/dL) Over Time
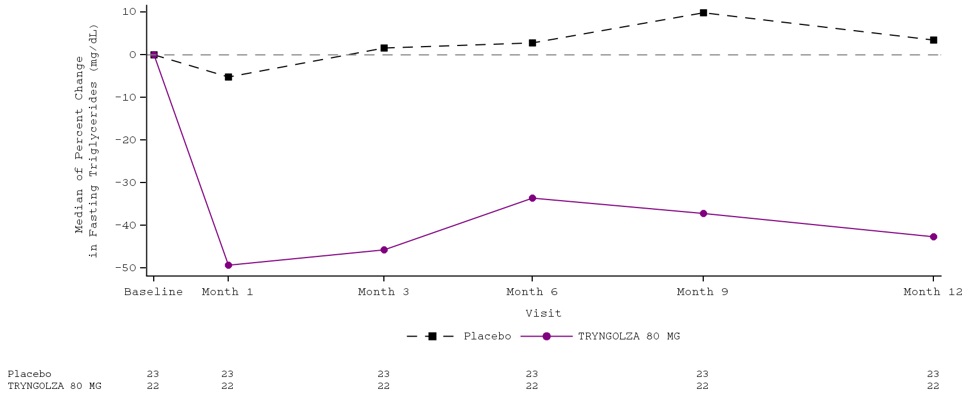
Figure 3. Fasting Triglyceride (mg/dL) Over Time
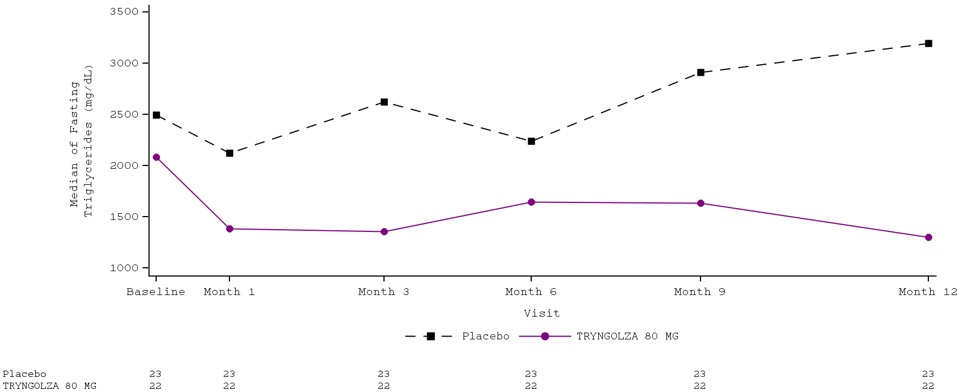
Over the 12-month treatment period, the numerical incidence of acute pancreatitis in patients treated with TRYNGOLZA 80 mg was lower compared with placebo [1 (5%) patient in the TRYNGOLZA 80 mg group compared with 7 (30%) patients in the placebo group]; all of these patients had a prior history of pancreatitis within 10 years prior to screening.
16. How is Tryngolza supplied
16.1 How Supplied
TRYNGOLZA injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear, colorless to yellow solution supplied in a single-dose autoinjector. Each autoinjector of TRYNGOLZA is filled to deliver 0.8 mL of solution containing 80 mg of olezarsen.
TRYNGOLZA is available in cartons containing one 80 mg single-dose autoinjector each.
(NDC 71860-101-01).
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store the TRYNGOLZA autoinjector in the refrigerator between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F) in the original carton.
Once taken out of the refrigerator, the TRYNGOLZA autoinjector can be stored at room temperature between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) in the original carton for up to 6 weeks. If not used within the 6 weeks stored at room temperature, discard TRYNGOLZA.
Do notfreeze. Do notexpose to heat .Protect from light.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions, including bronchospasm, diffuse erythema, facial swelling, urticaria, chills, and myalgia, have been reported in patients treated with TRYNGOLZA. Advise patients on the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct them to stop taking TRYNGOLZA and seek medical advice promptly if such symptoms occur. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Adherence to Diet
Advise patients with FCS that use of lipid-regulating agents does not reduce the importance of adhering to a low-fat diet [see Dosage and Administration (2)] .
Missed Dose
Instruct patients to take TRYNGOLZA as prescribed. If a dose is missed, instruct patients to take it as soon as they remember. Resume dosing at monthly intervals from the date of the most recently administered dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
Distributed by: Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc., Carlsbad, CA 92010
TRYNGOLZA is a trademark of Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2024 IONIS Pharmaceuticals Inc.
| PATIENT INFORMATION
TRYNGOLZA ™ [trin-GOLE-zah] (olezarsen) injection, for subcutaneous use |
|
|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Approved: 12/2024 |
| What is TRYNGOLZA? | |
| TRYNGOLZA is a prescription medicine used along with diet to reduce triglycerides (fat in the blood) in the treatment of adults with a condition that keeps the body from breaking down fats called familial chylomicronemia syndrome (FCS). | |
| It is not known if TRYNGOLZA is safe and effective in children. | |
Do not use TRYNGOLZA if:
|
|
Before using TRYNGOLZA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | |
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | |
How should I use TRYNGOLZA?
|
|
What are the possible side effects of TRYNGOLZA?
|
|
|
The most common side effects of TRYNGOLZA include:
|
|
| These are not all the possible side effects of TRYNGOLZA. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away while taking TRYNGOLZA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |
How should I store TRYNGOLZA?
|
|
| Keep TRYNGOLZA and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
| General information about the safe and effective use of TRYNGOLZA. | |
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use TRYNGOLZA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TRYNGOLZA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TRYNGOLZA that is written for health professionals. | |
| What are the ingredients in TRYNGOLZA? | |
| Active ingredient:olezarsen sodium. | |
| Inactive ingredients: disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate to maintain pH and provide tonicity and water for injection. The solution may include hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. | |
| Distributed by: Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc. Carlsbad, CA 92010 | |
| TRYNGOLZA is a trademark of Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. | |
| For more information, go to www.TRYNGOLZA.com or call 1-833-644-6647. If you still have questions, contact your healthcare provider. | |
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
TRYNGOLZA ™[trin-GOLE-zah] (olezarsen) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose autoinjector 80 mg/0.8 mL |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Approved: 12/2024 | ||
| This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject TRYNGOLZA™using the autoinjector. | |||
|
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using your TRYNGOLZA autoinjector and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Your healthcare provider should show you or your caregiver how to use the TRYNGOLZAautoinjector the right way. If you or your caregiver have any questions, talk to your healthcare provider. |
|||
 |
|||
Important information:
|
|||
|
Storage information:
|
|||
| Keep TRYNGOLZA and all medicine out of the reach of children. | |||
| Parts of your TRYNGOLZA autoinjector | |||
| Single-dose autoinjector | 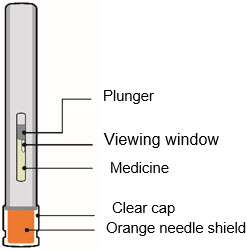 |
||
| Other supplies (not included) |
|  Sharps container |
|
|
|  Small bandage |
||
| Preparing to inject TRYNGOLZA | |||
| Step 1 Remove from the refrigerator
a) Remove the autoinjector from the refrigerator. | 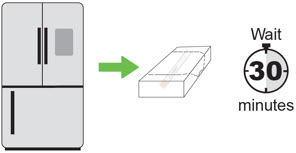 |
||
| b) Keep the autoinjector in the original carton andlet the autoinjector come to room temperature for 30 minutes before injecting. | |||
| Do nottry to speed up the warming process using other heat sources, such as a microwave or hot water. | |||
| Step 2 Check the medicine | |||
| a)Check the expiration (EXP) date. | 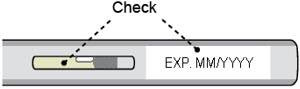 |
||
| b)Check the medicine through the viewing window. The TRYNGOLZAmedicine should be clear and colorless to yellow. There should be no particles. It is normal to see air bubbles in the solution. | |||
Do not use the autoinjector if the:
|
|||
| Step 3 Choose the injection site | 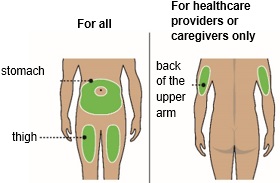 |
||
| a)Choose an injection site on the stomach or the front of the thigh. | |||
| b)Only your healthcare provider or caregivers may choose the back of upper arm. | |||
Do not inject:
|
|||
| Step 4 Wash hands and clean the injection site | 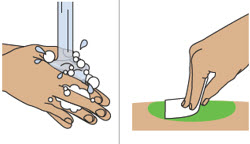 |
||
| a)Wash your hands with soap and water. | |||
| b)Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe in a circular motion. Let the skin air dry. | |||
| Do nottouch the cleaned skin before injecting. | |||
| Injecting TRYNGOLZA | |||
| Step 5 Remove and throw away the clear cap | |||
| a)Hold the autoinjector by the middle with the clear cap facing away from you. | 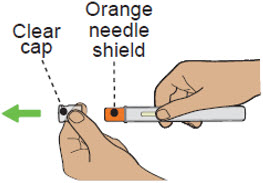 |
||
| b)Remove the clear cap by pulling it straight off. Do nottwist it off. The needle is inside the orange needle shield. | |||
| c)Throw away the clear cap in the trash or sharps container. | |||
|
|||
| Step 6 Begin injection | |||
| a)Hold the autoinjector in 1 hand. Place the orange needle shield at a 90-degree angle against your skin. Make sure you can see the viewing window. | 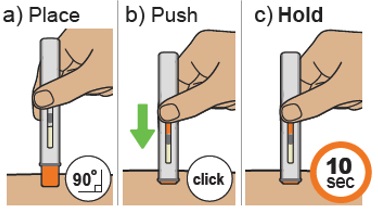 |
||
| b)Push firmly and hold the autoinjector straight against the skin. You will hear a click as the injection starts. | |||
| You may hear a second click. This is normal. The procedure is not finished. | |||
| c)Hold the autoinjector against the skin for 10 seconds to make sure the full dose has been given. | |||
| Do notmove, turn, or change the angle of the autoinjector during the injection. | |||
| Step 7 Finish injection | |||
a)Check that the orange plunger rod has moved down to fill the entire viewing window.
| 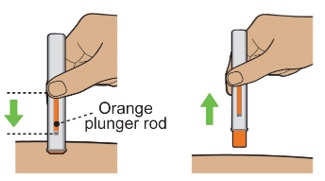 |
||
| b)Remove the autoinjector by lifting it straight up. After removal from the skin, the orange needle shield locks into place and covers the needle. | |||
| c)There may be a small amount of blood or liquid where you injected. This is normal. | |||
| If needed, press a cotton ball or gauze on the area and apply a small bandage. | |||
| Do notreuse the autoinjector. | |||
| Throwing away TRYNGOLZA | |||
| Step 8 Throw away autoinjector |  |
||
| a)Put the used autoinjector in a sharps container right away after use. | |||
| Do notthrow away the autoinjector in your household trash.
Do notrecycle your used sharps disposal container. Do notreuse the autoinjector or clear cap. |
|||
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps container, you may use a household container that is:
|
|||
| When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used autoinjectors. | |||
| For more information about safe sharps disposal, and specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal. | |||
| Do notthrow away your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do notrecycle your used sharps disposal container. | |||
| For more information, go to https://www.TRYNGOLZA.com or call 1-833-644-6647. If you still have questions, contact your healthcare provider. | |||
| Distributed by: Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Carlsbad, CA 92010 | |||
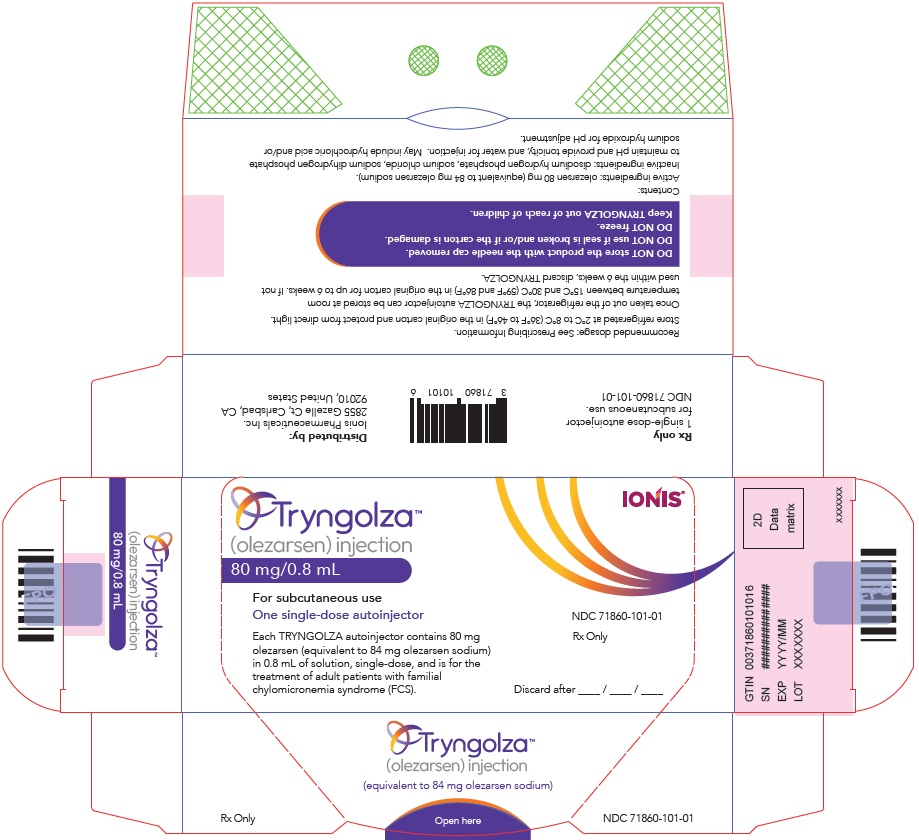
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 80 mg/0.8 mL Autoinjector Carton
Tryngolza™
(olezarsen) injection
80 mg/0.8 mL
For subcutaneous use
One single-dose autoinjector
Each TRYNGOLZA autoinjector contains 80 mg
olezarsen (equivalent to 84 mg olezarsen sodium)
in 0.8 mL of solution, single-dose, and is for the
treatment of adult patients with familial
chylomicronemia syndrome (FCS).
IONIS ®
NDC 71860-101-01
Rx Only
Discard after ____ / ____ / ____
| TRYNGOLZA
olezarsen sodium injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (011829916) |
More about Tryngolza (olezarsen)
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: miscellaneous antihyperlipidemic agents
- En español