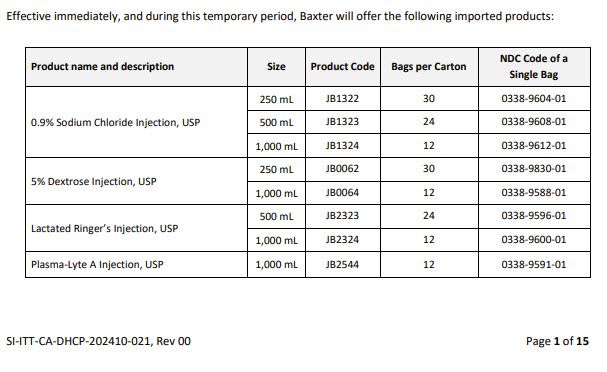
Lactated Ringers: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: sodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, calcium chloride
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Intravenous nutritional products
J Code (medical billing code): J7120 (1000 mL, injection)
Health Care Professional Letter
Reportin Adverse Events or Product Quality Issues
To report adverse events associated with these imported products, please call Baxter at 1-866-888-2472, or fax: 1-800-759-1801. Adverse events or quality problems experienced with the use of these imported products may also be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program either online, or by regulary mail or by fax:
- •
- Complete and submit the report Online: https://www.fda.gov/safety/medwatch-fda-safety-information-and-adverse-event-reporting-program
- •
- Regular mail or Fax: Download form https://www.fda.gov/safety/medical-product-safety-information/medwatch-forms-fda-safety-reporting or call 1-800-332-1088 to request a reporting form, then complete and return to the address on the pre-addressed form, or submit by fax to 1-800-FDA-0178 (1-800-332-0178)
To report product quality issues associated with these imported products, please contact Baxter Product Surveillance through Baxter – Product Feedback Portal (https://productfeedback.baxter.com/).
Please refer to the FDA-approved prescribing information for each drug product as follows:
- •
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP (click DailyMed - DEXTROSE- dextrose monohydrate injection, solution)
- •
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP (click DailyMed - SODIUM CHLORIDE injection, solution)
- •
- Lactated Ringers Injection, USP (click DailyMed - LACTATED RINGERS- sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium lactate and calcium chloride injection, solution)
- •
- Plasma-Lyte Injection, USP (click DailyMed - PLASMA-LYTE A- sodium chloride, sodium gluconate, sodium acetate, potassium chloride and magnesium chloride injection, solution)
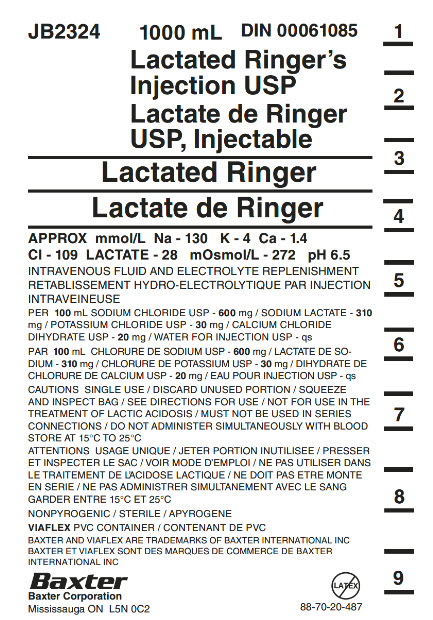
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Container Label
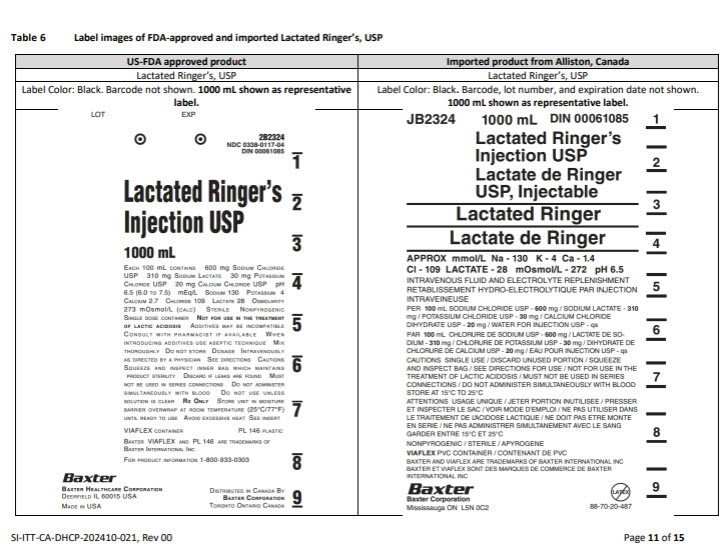
JB2324
1000 mL
DIN 00061085
Lactated Ringer’s
Injection USP
Lactate de Ringer
USP, Injectable
Lactated Ringer
Lactate de Ringer
APPROX mmol/L Na – 130 K – 4 Ca – 1.4
CI – 109 LACTATE – 28 mOsmol/L – 272 pH 6.5
INTRAVENOUS FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE REPLENISHMENT
RETABLISSEMENT HYDRO-ELECTROLYTIQUE PAR INJECTION
INTRAVENIEUSE
PER 100 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE USP – 600 mg / SODIUM LACTATE – 310
mg / POTASSIUM CHLORIDE USP – 30 mg / CALCIUM CHLORIDE
DIHYDRATE USP – 20 mg / WATER FOR INJECTION USP – qs
PAR 100 mL CHLORURE DE SODIUM USP – 600 mg / LACTATE DE SO-
DIUM – 310 mg/ CHLORURE DE POTASSIUM USP – 30 mg / DIHYDRATE DE
CHLORURE DE CALCIUM USP – 20 mg / EAU POUR INJECTION USP – qs
CAUTIONS SINGLE USE / DISCARD UNUSED PORTION / SQUEEZE
AND INSPECT BAG / SEE DIRECTIONS FOR USE / NOT FOR USE IN THE
TREATEMENT OF LACTIC ACIDOSIS / MUST NOT BE USED IN SERIES
CONNECTIONS / DO NOT ADMINSTER SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH BLOOD
STORE AT 15°C TO 25°C
ATTENTIONS USAGE UNIQUE / JETER PORTION INUTILISEE / PRESSER
ET INSPECTER LE SAC / VOIR MODE D’EMPLOI / NE PAS UTILISER DANS
LE TRAITEMENT DE L’ACIDOSE LACTIQUE / NE DOIT PAS ETRE MONTE
EN SERIE / NE PAS ADMINISTRER SIMULTANEMENT AVEC LE SANG
GARDER ENTRE 15°C ET 25°C
NONPYROGENIC / STERILE / APYROGENE
VIAFLEX PVC CONTAINER / CONTENANT DE PVC
BAXTER AND VIAFLEX ARE TRADEMARKS OF BAXTER INTERNATIONAL INC
BAXTER ET VIAFLEX SONT DES MARQUES DE COMMERCE DE BAXTER
INTERNATIONAL INC
Baxter Logo
Baxter Corporation
Mississauga ON L5N 0C2
No Latex Label
88-70-20-487
1
_
2
_
3
_
4
_
5
_
6
_
7
_
8
_
9
Container Label
JB2323
500 mL
DIN 00061085
Lactated Ringer’s Injection
USP
Lactate de Ringer USP,
Injectable
Lactated Ringer
Lactate de Ringer
APPROX mmol/L Na – 130 K – 4 Ca – 1.4 CI
109 LACTATE – 28 mOsmol/L – 272 pH 6.5
INTRAVENOUS FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE REPLENISHMENT / RETABLISSE-
MENT HYDRO-ELECTROLYTIQUE PAR INJECTION INTRAVENIEUSE
PER100 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE USP – 600mg / SODIUM LACTATE – 310mb / PO-
TASSIUM CHLORIDE USP – 30mg / CALCIUM CHLORIDE DIHYDRATE USP – 20mg /
WATER FOR INJECTION USP – qs
PAR100 mL CHLORURE DE SODIUM USP – 600mg / LACTATE DE SODIUM –
310mg/ CHLORURE DE POTASSIUM USP – 30mg / DIHYDRATE DECHLORURE DE
CALCIUM USP – 20mg / EAU POUR INJECTION USP – qs
CAUTIONS SINGLE USE / DISCARD UNUSED PORTION / SQUEEZE AND INSPECT
BAG / SEE DIRECTIONS FOR USE / NOT FOR USE IN THE TREATEMENT OF LACTIC
ACIDOSIS / MUST NOT BE USED IN SERIES CONNECTIONS / DO NOT ADMINSTER
SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH BLOOD STORE AT 15°C TO 25°C
ATTENTIONS USAGE UNIQUE / JETER PORTION INUTILISEE / PRESSER ET INSPECT-
ER LE SAC / VOIR MODE D’EMPLOI / NE PAS UTILISER DANS LE TRAITEMENT DE
L’ACIDOSE LACTIQUE / NE DOIT PAS ETRE MONTE EN SERIE / NE PAS ADMINISTRER
SIMULTANEMENT AVEC LE SANG GARDER ENTRE 15°C ET 25°C
NONPYROGENIC / STERILE / APYROGENE
VIAFLEX PVC CONTAINER / CONTENANT DE PVC
BAXTER AND VIAFLEX ARE TRADEMARKS OF BAXTER INTERNATIONAL INC
BAXTER ET VIAFLEX SONT DES MARQUES DE COMMERCE DE BAXTER
INTERNATIONAL INC
Baxter Logo
Baxter Corporation
Mississauga ON L5N 0C2
No Latex Label
07-25-77-062
-1-
_
-2-
_
-3-
_
-4-
| LACTATED RINGERS
sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium lactate and calcium chloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| LACTATED RINGERS
sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium lactate and calcium chloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Baxter Healthcare Company (005083209) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baxter Corporation | 205087968 | ANALYSIS(0338-9600, 0338-9596) , LABEL(0338-9600, 0338-9596) , MANUFACTURE(0338-9600, 0338-9596) , STERILIZE(0338-9600, 0338-9596) , PACK(0338-9600, 0338-9596) | |
More about lvp solution
Patient resources
Professional resources
Other brands
Lactated Ringers Injection, Normosol-R, Extraneal, Delflex, ... +3 more