Jivi: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: antihemophilic factor (recombinant) pegylated-aucl
Dosage form: injection
Drug class: Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
J Code (medical billing code): J7208 (Per unit, injection)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 2, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
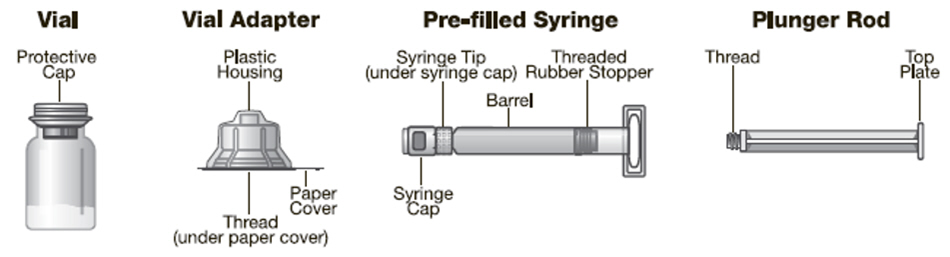
JIVI® [antihemophilic factor (recombinant), PEGylated-aucl] lyophilized powder for solution, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Jivi
JIVI, is a recombinant DNA-derived, Factor VIII concentrate indicated for use in previously treated adults and pediatric patients 7 years of age and older with hemophilia A (congenital Factor VIII deficiency) for:
- On-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes
- Perioperative management of bleeding
- Routine prophylaxis to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes (1)
Limitations of use
JIVI is not indicated for use in:
Jivi Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use after reconstitution only.
Control of bleeding episodes and perioperative management
- Expected recovery: one unit per kilogram body weight of JIVI will increase the Factor VIII level by 2 international units per deciliter (IU/dL). Each vial of JIVI contains the labeled amount of recombinant Factor VIII in IU. (2.1)
- Required dose (IU) = body weight (kg) × desired Factor VIII rise (% of normal or IU/dL) × reciprocal of expected recovery (or observed recovery, if available). (2.1)
- Estimated Increment of Factor VIII (IU/dL or % of normal) = [Total Dose (IU)/body weight (kg)] × 2 (IU/dL per IU/kg). (2.1)
Routine prophylaxis
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older):
- The recommended initial dosage regimen is 30–40 IU/kg twice weekly. (2.1)
- Based on the bleeding episodes:
- The regimen may be adjusted to 45–60 IU/kg every 5 days.
- A regimen may be further individually adjusted to less or more frequent dosing. (2.1)
Children (7 to <12 years of age):
Dosage Forms and Strengths
JIVI is available as lyophilized powder in single-dose vials containing nominally 500, 1000, 2000, 3000, or 4000 IU. (3)
Contraindications
Do not use in patients who have a history of hypersensitivity reactions to the active substance, polyethylene glycol (PEG), mouse or hamster proteins, or other constituents of the product. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including severe allergic reactions, have occurred. Monitor patients for hypersensitivity symptoms. Should hypersensitivity symptoms occur, discontinue treatment with JIVI and administer appropriate treatment. Hypersensitivity reactions may also be related to antibodies against polyethylene glycol (PEG). (5.1, 5.3)
- Development of Factor VIII neutralizing antibodies have occurred. If expected plasma Factor VIII activity levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled as expected with the administered dose, then perform an assay that measures Factor VIII inhibitor concentration. (5.2, 5.3)
- Immune response to PEG, manifested as symptoms of acute hypersensitivity and/or loss of drug effect, has occurred following JIVI administration. Discontinue JIVI and switch patients to a different anti-hemophilic product. (5.3, 6.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5%) were headache, fever, cough, and abdominal pain. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer at 1-888-842-2937 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Pediatric Use: Higher clearance, a shorter half-life and lower incremental recovery of Factor VIII has been observed in children <12 years of age. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 5/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Jivi
JIVI, is indicated for use in previously treated adults and pediatric patients 7 years of age and older with hemophilia A (congenital Factor VIII deficiency) for:
- On-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes
- Perioperative management of bleeding
- Routine prophylaxis to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes
Limitations of Use
JIVI is not indicated for use in:
- Children < 7 years of age due to greater risk for hypersensitivity reactions and/or loss of efficacy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
- Previously untreated patients (PUPs)
- Treatment of von Willebrand disease
2. Jivi Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use after reconstitution only.
2.1 Recommended Dosage
- Each vial label of JIVI states the Factor VIII potency in international units (IU). One IU is defined by the current WHO (World Health Organization) international standard for Factor VIII concentrate.
- Dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the Factor VIII deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. Careful control of replacement therapy is especially important in cases of major surgery or life-threatening bleeding episodes.
- Potency assignment for JIVI is determined using a chromogenic substrate assay.
- Monitor the Factor VIII activity of JIVI in plasma using either a validated chromogenic substrate assay or a validated one-stage clotting assay [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Calculation of the required dose of Factor VIII is based on the empirical finding that 1 IU of Factor VIII per kilogram body weight increases the plasma Factor VIII level by 2 IU/dL.
- Estimate the required dose for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding and perioperative management using the following formula:
Required dose (IU) = body weight (kg) × desired Factor VIII rise (% of normal or IU/dL) × reciprocal of expected recovery (or observed recovery, if available) (e.g., 0.5 for a recovery of 2 IU/dL per IU/kg)
Estimate the expected in vivo peak increase using the following formula:
Estimated increment of Factor VIII (IU/dL or % of normal) = [Total dose (IU)/body weight (kg)] × 2 (IU/dL per IU/kg) - Adjust dose and frequency to the patient's clinical response. Patients may vary in their pharmacokinetic [e.g., half-life, incremental recovery and AUC (area under the curve)] and clinical responses to JIVI.
- The total recommended maximum dose per infusion is approximately 6000 IU (rounded to vial size) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
On-demand Treatment and Control of Bleeding Episodes
A guide for dosing JIVI for the on-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes is provided in Table 1. The goal of treatment is to maintain a plasma Factor VIII activity level at or above the plasma levels (in % of normal or in IU/dL) outlined in Table 1.
| Degree of Bleeding Hemorrhage/Hemorrhagic Event | Factor VIII Level Required (IU/dL or % of normal) | Dose (IU/kg) | Frequency of Doses (hours) | Duration of Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor (e.g., early hemarthrosis, minor muscle bleeding, oral bleeds) | 20–40 | 10–20 | Repeat every 24–48 hours | Until bleeding is resolved |
| Moderate (e.g., more extensive hemarthrosis, muscle bleeding, or hematoma) | 30–60 | 15–30 | Repeat every 24–48 hours | Until bleeding is resolved |
| Major (e.g., intracranial, intra-abdominal or intrathoracic hemorrhages, gastrointestinal bleeding, central nervous system bleeding, bleeding in the retropharyngeal or retroperitoneal spaces, or iliopsoas sheath, life- or limb- threatening hemorrhage) | 60–100 | 30–50 | Repeat every 8–24 hours | Until bleeding is resolved |
Perioperative Management of Bleeding
A guide for dosing JIVI during surgery (perioperative management) is provided in Table 2. The goal of treatment is to maintain a plasma Factor VIII activity level at or above the plasma level (in % of normal or in IU/dL) outlined in Table 2. During major surgery, monitoring with appropriate laboratory tests, including serial Factor VIII activity assays, is highly recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
| Type of Surgery | Factor VIII Level Required (IU/dL or % of normal) | Dose (IU/kg) | Frequency of Doses (hours) | Duration of Treatment (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor (e.g., tooth extraction) | 30–60 (pre- and post-operative) | 15–30 | Repeat every 24 hours | At least 1 day until healing is achieved |
| Major (e.g., intracranial, intra-abdominal, intrathoracic, or joint replacement surgery) | 80–100 (pre- and post-operative) | 40–50 | Repeat every 12–24 hours | Until adequate wound healing is complete, then continue therapy for at least another 7 days to maintain Factor VIII activity of 30–60% (IU/dL) |
Routine Prophylaxis
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older):
- The recommended initial dosage regimen is 30–40 IU/kg twice weekly.
- Based on the bleeding episodes:
- The regimen may be adjusted to 45–60 IU/kg every 5 days.
- A regimen may be further individually adjusted to less or more frequent dosing.
Children (7 to <12 years of age):
- The recommended initial dosage regimen is 60 IU/kg twice weekly.
- Adjust the dose based on the patient's clinical response and/or recovery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Preparation and Reconstitution
Reconstitute and administer JIVI with the components provided with each package. If any component of the package is opened or damaged, do not use this component.
Reconstitution
Work on a clean surface and wash hands thoroughly using soap and warm water before performing the procedures.
|
|
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
2.3 Administration
For intravenous use only.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
- Do not use if you notice any particulate matter or discoloration and immediately contact Bayer Medical Communications at 1-888-84-BAYER (1-888-842-2937).
- Administer reconstituted JIVI as soon as possible. If not, store at room temperature for no longer than 3 hours.
- Infuse JIVI intravenously over a period of 1 to 15 minutes. Adapt the rate of administration to the response of each individual patient (maximum infusion rate 2.5 mL/min).
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
JIVI is available as a white to slightly yellow lyophilized powder in single-dose glass vials containing nominally 500, 1000, 2000, 3000, or 4000 IU of Factor VIII potency per vial.
Each vial of JIVI is labeled with actual Factor VIII potency expressed in IU determined using a chromogenic substrate assay. This potency assignment employs a Factor VIII concentrate standard that is referenced to the current WHO International Standard for Factor VIII concentrate, and is evaluated by appropriate methodology to ensure accuracy of the results.
4. Contraindications
JIVI is contraindicated in patients who have a history of hypersensitivity reactions to the active substance, polyethylene glycol (PEG), mouse or hamster proteins, or other constituents of the product [see Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including severe allergic reactions, have occurred with JIVI. Monitor patients for hypersensitivity symptoms. Early signs of hypersensitivity reactions, which can progress to anaphylaxis, may include chest or throat tightness, dizziness, mild hypotension and nausea. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, immediately discontinue administration and initiate appropriate treatment.
JIVI may contain trace amounts of mouse and hamster proteins [see Description (11)]. Patients treated with this product may develop hypersensitivity to these non-human mammalian proteins.
Hypersensitivity reactions may also be related to antibodies against polyethylene glycol (PEG) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5.2 Neutralizing Antibody Formation
Neutralizing antibody (inhibitor) formation have occurred following administration of JIVI. Carefully monitor patients for the development of Factor VIII inhibitors, using appropriate clinical observations and laboratory tests. If expected plasma Factor VIII activity levels are not attained or if bleeding is not controlled as expected with administered dose, suspect the presence of an inhibitor (neutralizing antibody) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
5.3 Immune Response to Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
An immune response associated with IgM anti-PEG antibodies, manifested as symptoms of acute hypersensitivity and/or loss of drug effect, has occurred with JIVI administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. In the clinical trials, the IgM anti-PEG antibodies disappeared within 4-6 weeks. No immunoglobulin class switching from IgM to IgG has been observed.
A low post-infusion Factor VIII level, in the absence of detectable Factor VIII inhibitors, may be due to loss of treatment effect related to high titers of anti-PEG IgM antibodies. In these cases, discontinue JIVI and switch patients to a different anti-hemophilic product.
A reduced recovery of Factor VIII after start of JIVI treatment may be due to transient low titers of anti-PEG IgM antibodies. In these cases, increase the dose of JIVI until recovery of Factor VIII returns to expected levels.
5.4 Monitoring Laboratory Tests
- If monitoring of Factor VIII activity is performed, use a validated chromogenic assay or a selected validated one-stage clotting assay [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Laboratories intending to measure the Factor VIII activity of JIVI should check their procedures for accuracy. For JIVI, select silica-based one-stage assays may underestimate the Factor VIII activity of JIVI in plasma samples; some reagents, e.g., with kaolin-based activators, have the potential for overestimation. Therefore, the suitability of the assay must be ascertained. If a validated one-stage clotting or chromogenic assay is not available locally, then use of a reference laboratory is recommended.
- Monitor for development of Factor VIII inhibitors. Perform a Bethesda inhibitor assay if expected Factor VIII plasma levels are not attained or if bleeding is not controlled with the expected dose of JIVI. Use Bethesda Units (BU) to report inhibitor titers.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety database described in this section reflects the exposure of JIVI in four clinical studies, Study 1 (Safety and PK Study), Study 2 (PROTECT VIII), Study 3 (PROTECT Kids), and Study 4 (Alfa-PROTECT) [see Clinical Studies (14)]). A total of 256 patients received JIVI.
Patients who received JIVI for perioperative management (n=17) with treatment period of 2 to 3 weeks were excluded from pooled safety analysis but included in analysis for inhibitor development. The median exposure days (EDs) for adults, and pediatric patients ≥ 7 years of age was 92 EDs (range: 1–309) per patient.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 5 patients (<2%), all were hypersensitivity reactions. Of the 5 patients, 1 patient was ≥ 7 years of age (see Anti-PEG Antibodies).
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5%) were headache, fever, cough, and abdominal pain (see Table 3).
| Adverse Reactions | All Patients 2-65 years of age n (%) n=256 | Patients ≥7 years of age n (%) n=208 |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Abdominal pain | 12 (5%) | 10 (5%) |
| Nausea | 9 (4%) | 9 (4%) |
| Vomiting | 11 (4%) | 8 (4%) |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||
| Injection site reactions† | 7 (3%) | 6 (3%) |
| Fever | 23 (9%) | 13 (6%) |
| Immune System Disorders | ||
| Hypersensitivity | 9 (4%) | 4 (2%) |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Dizziness | 3 (1%) | 3 (1%) |
| Dysgeusia | 1 (0.4%) | 0 |
| Headache | 32 (13%) | 30 (14%) |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 5 (2%) | 5 (2%) |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||
| Cough | 22 (9%) | 15 (7%) |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Erythema‡ | 3 (1%) | 2 (1%) |
| Pruritus | 2 (0.8%) | 1 (0.5%) |
| Rash§ | 10 (4%) | 5 (2%) |
| Vascular Disorders | ||
| Flushing | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (0.5%) |
Immunogenicity: Anti-Drug Antibody-Associated Adverse Reactions
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies to JIVI in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in studies with other products.
Immunogenicity was evaluated during clinical trials with JIVI in 158 (including surgery patients ) previously treated adult and pediatric patients (≥ 12 years of age) severe hemophilia A (Factor VIII activity < 1%) patients with previous exposure to Factor VIII concentrates ≥ 150 EDs. There were 108 previously treated pediatric patients < 12 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Factor VIII Inhibitors
In Study 2, a Factor VIII inhibitor (1.7 BU/mL) was reported in 1 out of 144 patients [see Warning and Precautions (5.2)].
In Study 2, immunogenicity against PEG was evaluated by anti-PEG screening and specific IgM anti-PEG ELISA assays. One patient (19 years of age) with asthma, presented at 4 exposure days (EDs) with a clinical hypersensitivity reaction after infusion of JIVI. The patient reported headache, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and flushing, all of which resolved following his standard asthma treatment. No further medical intervention was required. The event was associated with a transient increase of IgM anti-PEG antibody titer, which was negative upon retest during follow-up within 30 days.
In Study 4 (7 to <12 years of age), one pediatric patient developed high titer neutralizing anti-PEG IgM antibodies (titer 1:64) after 2 EDs associated with low post-infusion FVIII levels and loss of efficacy. Antibodies disappeared after discontinuation and patient restarted treatment with JIVI 2 months later.
Three pediatric patients developed low titer and transient anti-PEG IgM antibodies (highest titer 1:4) within the first 4 EDs resulting in reduction of JIVI recovery (lowest recovery 0.8 kg/dl) in two patients and inconclusive data on recovery in one patient.
Related/similar drugs
Lysteda
Lysteda (tranexamic acid) is used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. Includes Lysteda side effects ...
Hemlibra
Hemlibra is a monoclonal antibody that functions in place of a natural blood-clotting factor that ...
Botox
Botox is used for cosmetic purposes and to treat overactive bladder symptoms, urinary incontinence ...
DDAVP
DDAVP is used for diabetes insipidus, hemophilia a, primary nocturnal enuresis, von Willebrand Disease
Qfitlia
Qfitlia is used for hemophilia a, hemophilia a with inhibitors, hemophilia b, hemophilia b with ...
Altuviiio
Altuviiio is a once-weekly recombinant fact VIII replacement therapy used by hemophilia A patients ...
Cyklokapron
Cyklokapron is used for bleeding disorder, factor ix deficiency, hemophilia a
Hympavzi
Hympavzi (marstacimab-hncq) may be used to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes ...
Fitusiran
Fitusiran systemic is used for hemophilia a, hemophilia a with inhibitors, hemophilia b, hemophilia ...
Desmopressin
Desmopressin systemic is used for diabetes insipidus, hemophilia a, nocturia, primary nocturnal ...
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data with JIVI use in pregnant women to inform on drug-associated risk. Animal developmental and reproductive toxicity studies have not been conducted with JIVI. It is not known whether JIVI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of JIVI in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for JIVI and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from JIVI or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of JIVI have been established in previously treated pediatric patients 7 years of age and older. The use of JIVI in this age group was supported by evidence from three clinical studies, Study 2 (PROTECT VIII), Study 3 (PROTECT Kids) and Study 4 (Alfa-PROTECT), which included 108 pediatric patients 2 to <12 years of age and 12 pediatric patients 12 to <17 years of age [see Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)].
In Study 3 with 48 previously treated pediatric patients (PTPs) < 7 years of age, adverse reactions due to immune response to PEG were observed in 10 (21%) patients. In all 10 patients, loss of treatment effect due to neutralizing anti-PEG IgM antibodies was observed during the first 4 exposure days (EDs) and loss of treatment effect combined with hypersensitivity reactions was observed in 3 of those 10 patients (6%) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Compared to adults and pediatric patients ≥12 years of age, a higher clearance, a shorter half-life and lower incremental recovery of Factor VIII have been observed in pediatric patients <12 years of age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In pediatric patients 2 to <7 years of age, efficacy of prophylaxis treatment with JIVI was demonstrated in 28 patients without an immune response to PEG and who had at least a 3 months treatment period. The median (interquartile range) ABR was 2.3 (1.2 – 5.2) and the mean (SD) ABR was 3.5 (3.4).
JIVI is not indicated for use in children below 7 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of JIVI have not been studied in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
11. Jivi Description
JIVI [antihemophilic factor (recombinant), PEGylated-aucl] is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, preservative-free, white to slightly yellow lyophilized powder for reconstitution with sterile Water for Injection (sWFI) as diluent for intravenous (IV) administration. The product is supplied in single-dose vials containing dosage strengths of 500, 1000, 2000 and 3000 IU in 2.5 mL fill size and 4000 IU in 5 mL fill size. For each dosage strength, the actual assayed potency is directly printed on each vial label. The container closure system consists of a 10 mL, Type I glass vial sealed with a bromobutyl grey stopper and an aluminum crimp seal with plastic flip-off cap plus vial adapter. The vial adapter was designed to connect with the sWFI, prefilled diluent syringe. The 500, 1000, 2000, and 3000 IU vials of JIVI are formulated with the following excipients: 59 mg glycine, 27 mg sucrose, 8.4 mg histidine, 4.7 mg sodium chloride, 0.7 mg calcium chloride, and 0.216 mg polysorbate 80. The 4000 IU vial of Jivi is formulated with the following quantities of these excipients: 114 mg glycine, 52 mg sucrose, 16.1 mg histidine, 9.1 mg sodium chloride, 1.9 mg calcium chloride, and 0.416 mg polysorbate 80. The pH of the reconstituted product is 6.6 to 7.0.
The specific activity of JIVI is approximately 10,000 IU/mg protein.
The active protein (or starting molecule), prior to conjugation is a recombinant B-domain deleted human coagulation Factor VIII (BDD-rFVIII) produced by recombinant DNA technology in Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK) cells.
JIVI is produced by site-specific conjugation of the BDD-rFVIII variant K1804C at the cysteine amino acid position 1804 (within the A3 domain) with a single maleimide-derivatized, 60 kilodalton (kDa) branched PEG (two 30 kDa PEG) moiety. The A3 domain was selected for conjugation to provide both a consistent coagulation activity and high PEGylation efficiency.
The molecular weight of JIVI is approximately 234 kDa based on the calculated average molecular weight of the BDD-rFVIII variant of 165 kDa, plus glycosylation (~4 kDa), and the average molecular weight of the PEG-maleimide of approximately 60 kDa. Functional characterization of JIVI shows comparable mechanism of action to that of rFVIII product with an extended plasma half-life [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
The manufacturing process of JIVI involves propagation of the recombinant production cell line with the harvest isolation process consisting of continuous filtration of tissue culture fluid and anion exchange chromatography on a membrane adsorber capsule. The process intermediate is purified from process- and product-related impurities using a series of chromatography and filtration steps, including 20 nm viral filtration, prior to conjugation to the 60 kDa maleimide PEG moiety. The mono-PEGylated JIVI active molecule is separated from product-related species by chromatography and then formulated by ultrafiltration. The cell culture, PEGylation, purification process and formulation used in the manufacture of JIVI do not use any additives of human or animal origins.
12. Jivi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
JIVI, a site-specifically PEGylated recombinant antihemophilic factor [see Description (11)], temporarily replaces the missing coagulation Factor VIII. The site-specific PEGylation in the A3 domain reduces binding to the physiological Factor VIII clearance receptors resulting in an extended half-life and increased AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The aPTT is prolonged in people with hemophilia A.
Determination of aPTT is a conventional in vitro assay for biological activity of Factor VIII. Treatment with JIVI normalizes the aPTT similar to that achieved with plasma-derived Factor VIII. The administration of JIVI increases plasma levels of Factor VIII and can temporarily correct the coagulation defect in hemophilia A patients.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The PK of JIVI was evaluated in two cohorts after single doses of 25 IU/kg and 60 IU/kg and after 25 IU/kg given twice weekly and 60 IU/kg given once weekly for 8 weeks in Study 1 (Safety and PK study).
The PK profile obtained at Week 8, after repeated dosing, was comparable with the PK profile obtained after the first dose.
In Study 2 (PROTECT VIII), the PK of JIVI was investigated in 22 previously treated severe Hemophilia A patients (≥ 12 years of age) following administration of a single dose, 60 IU/kg, of JIVI prior to initiation of prophylactic treatment and in 16 patients after 6 months of prophylaxis treatment with JIVI. In Study 3 (PROTECT Kids) the PK of JIVI was investigated in 12 previously treated severe Hemophilia A patients (7 to <12 years of age) following administration of a single dose, 60 IU/kg, of JIVI. Table 4 summarizes the PK parameters of adults and adolescents (≥12 years of age) and children (7 to <12 years of age) after a single dose of JIVI. Higher clearance, a shorter half-life and lower incremental recovery of JIVI have been observed in children 7 to <12 years of age.
| PK Parameters (unit) | Adults and Adolescents (≥ 12 years of age) | Children (7 to <12 years of age) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromogenic assay | One-stage assay | Chromogenic assay | |||
| 25 IU/kg | 60 IU/kg* | 25 IU/kg | 60 IU/kg* | 60 IU/kg | |
| n=7 | n=29 | n=7 | n=29 | n=12 | |
| AUC: area under the curve; Cmax: maximum drug concentration in plasma after single dose; t½: terminal half-life; MRTIV: mean residence time after an IV administration; VSS: apparent volume distribution at steady-state; CL: clearance | |||||
| AUC (IU*h/dL) | 1640 ± 550 | 4060 ± 1420 | 1640 ± 660 | 4150 ± 1060 | 2890± 547 |
| Cmax (IU/dL) | 64.2 ± 9.2 | 167 ± 30 | 69.4 ± 11.3 | 213 ± 71 | 130 ± 25.0† |
| t½ (h) | 18.6 ± 4.6 | 17.9 ± 4.0 | 21.4 ± 13.1 | 17.4 ± 3.8 | 16.0± 3.61‡ |
| MRTIV (h) | 26.7 ± 6.6 | 25.8 ± 5.9 | 29.0 ± 14.0 | 24.5 ± 5.4 | 24.1± 5.97 |
| Vss (mL/kg) | 42.8 ± 5.0 | 39.4 ± 6.3 | 44.7 ± 5.4 | 36.0 ± 6.5 | 50.5± 9.89 |
| CL (mL/h/kg) | 1.68 ± 0.39 | 1.63 ± 0.52 | 1.74 ± 0.54 | 1.52 ± 0.38 | 2.14± 0.433 |
| Recovery [(IU/dL)/(IU/kg)] | 2.13 ± 0.47 | 2.53 ± 0.43§ | 2.21 ± 0.55 | 3.25 ± 0.84b | 1.93 ± 0.54¶ |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic or genotoxic potential of JIVI, or studies to determine the effects of JIVI on fertility, have not been performed. No effect on male and female reproductive organs was seen in repeated-administration toxicity studies. Genotoxicity studies conducted with the PEG component of JIVI showed no indication of genotoxicity.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
No adverse effects were observed in immune-deficient rats intravenously injected with JIVI (40–1200 IU/kg/injection), twice weekly for 26 weeks. No evidence of accumulation of the PEG component of JIVI was detected by immunohistochemical staining in the brain (including the choroid plexus), spleen, or kidneys in animals sacrificed at 13 and 26 weeks.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of JIVI for on-demand treatment, perioperative management of bleeding, and routine prophylaxis was evaluated in three clinical studies, Study 2 (PROTECT VIII; NCT01580293) in patients ≥12 years, Study 3 (PROTECT Kids; NCT01775618) in patients 2 to < 12 years of age, and Study 4 (Alfa-PROTECT; NCT05147662) in patients 7 to <12 years of age as described below.
Immunocompetent patients with severe hemophilia A (Factor VIII activity <1%) and no history of Factor VIII inhibitors were eligible for the trials.
Study 2
A multinational, prospective, single-arm study in adult and pediatric previously treated patients (PTP) 12 to 65 years of age with ≥ 150 exposure days (EDs). The study consisted of three parts: Part A (Weeks 0 – 36); an optional extension phase for patients who completed Part A to accumulate at least 100 EDs; and Part B, a surgical phase.
Part A of the study evaluated the PK (single dose of 60 IU/kg), safety and efficacy of JIVI for on-demand treatment and routine prophylaxis. A total of 134 PTPs received at least one infusion of JIVI, including 20 on-demand treating patients with a median age of 48 years (range: 22 to 61), 114 prophylaxis-treating patients with a median age of 33 years (range: 12 to 62). The prophylaxis group (n=112, excluding 2 patients who dropped out after single infusion) completed a 10-week run-in phase during which patients received 25 IU/kg twice weekly JIVI before patients were randomized to the different dosing regimens based on their bleeding frequency for weeks 10–36. The on-demand group (n=20) treated with JIVI on-demand for the full 36 weeks. One hundred thirty two patients were evaluable for efficacy, of which 126 (94%) patients (prophylaxis group: n=108; on-demand group: n=18) completed the 36 weeks of treatment in Part A. The primary efficacy endpoint was annualized bleed rate (ABR).
A total of 121 patients received treatment during the extension phase (107 patients received prophylaxis and 14 patients continued on-demand treatment).
Safety and efficacy of JIVI in hemostasis during major surgical procedures were evaluated in 17 patients in Part B.
Study 3
A multi-center, prospective, single-arm trial to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of JIVI for prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding in previously treated pediatric patients <12 years of age with severe hemophilia A. The study consisted of three parts: the main study with 2 subgroups by age (<6 years and 6 to <12 years), an expansion study in children <6 years and an optional extension study. The main study evaluated the PK (single dose of 60 IU/kg) in each age subgroup, safety and efficacy of JIVI for on-demand treatment and routine prophylaxis for a minimum of 50 EDs and 6 months. A total of 73 PTPs were included, and were treated prophylactically with regimens of twice weekly (25-60 IU/kg) or every 5 days (45-60 IU/kg) or every 7 days at any given time as per investigator's discretion. The median age was 5 years (range: 2 to 11). The primary efficacy endpoint was the annualized bleed rate (ABR).
Study 4
A multi-center, prospective, single-arm, study to evaluate the safety of JIVI infusions for prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding in previously treated pediatric patients 7 to <12 years of age with severe hemophilia A. The study evaluated the potential risk of hypersensitivity and loss of drug effect associated with an immune response to polyethylene glycol (PEG) during the first 4 exposure days to JIVI. A total of 35 patients with a median age of 8 years (range: 7 to 11) were enrolled and treated prophylactically for a minimum of 50 EDs and 26 weeks. The patients received a treatment regimen of JIVI twice weekly (40-60 IU/kg) at investigator's discretion. Thirty-two patients completed the treatment phase and were offered continuation in an 18 months extension study. A key secondary endpoint was the annualized bleed rate (ABR).
On-demand Treatment and Control of Bleeding Episodes
In Study 2, approximately 91% of bleeds were successfully treated with 1 or 2 infusions in both the on-demand and prophylaxis groups. In Studies 3 and 4, approximately 97% of bleeds were successfully treated with 1 or 2 infusions. Efficacy in control of bleeding episodes is summarized in Table 5.
| Characteristics of Bleeding Episodes | Adults and Adolescents (≥12 Years of Age) | Children (7 to <12 Years of Age)* |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Demand n=20 | Routine Prophylaxis n=112 | Routine prophylaxis n=42 |
|
| Definitions: Excellent: Abrupt pain relief and/or improvement in signs of bleeding with no additional infusion administered Good: Definite pain relief and/or improvement in signs of bleeding, but possibly requiring more than one infusion for complete resolution Moderate: Probable or slight improvement, with at least one additional infusion for complete resolution Poor: No improvement or condition worsened |
|||
| Total number of bleeds treated | 388† | 317a | 36 |
| 1 infusion | 309 (80%) | 263 (83%) | 30 (83%) |
| 2 infusions | 45 (11%) | 22 (7%) | 5 (14%) |
| ≥ 3 infusions | 34 (9%) | 32 (10%) | 1 (3%) |
| Number of bleeds with assessment | 384 | 310 | 36 |
| Number of responses to treatment of bleeds assessed as 'Excellent' or 'Good' (%) | 253 (66%) | 256 (83%) | 30 (83%) |
| Number of responses to treatment of bleeds assessed as 'Moderate' | 115 (30%) | 47 (15%) | 5 (14%) |
| Number of responses to treatment of bleeds assessed as 'Poor' | 16 (4%) | 7 (2%) | 1 (3%) |
Perioperative Management
In Study 2, a total of 17 patients successfully completed 20 major surgeries. In Part B of the study, 14 patients underwent 17 surgeries and in the extension study, 3 patients underwent 3 surgeries, using JIVI for hemostasis. There were 6 non-orthopedic surgeries and 14 orthopedic surgeries (3 arthroplasties, 6 joint replacements, 3 synovectomies, and 2 other joint procedures). Treatment with JIVI provided 'good' or 'excellent' hemostatic control during all 20 major surgeries. The initial JIVI pre-surgery doses administered ranged between 2500 and 5000 IU. The median total dose per surgery was 219 IU/kg with a median of 35 IU/kg/infusion and a median of 7 infusions per surgery (up to 3 weeks). The median number of infusions on day of surgery was 2 (range: 1 – 3).
An additional 17 minor surgeries were performed in 10 patients during Part A of Study 2 . The adequacy of hemostasis during minor surgeries was assessed as either 'good' or 'excellent' in 16 cases and not reported in one case.
A total of 7 patients in the age group 7 to <12 years, 5 patients in Study 3 and 2 patients in Study 4 had 10 minor surgeries. The adequacy of hemostasis during minor surgeries was assessed as either 'good' or 'excellent' in 4 cases, moderate in 1 case and not reported in 5 cases.
Routine Prophylaxis
Adults and Adolescents (≥12 years of age)
In Study 2, the primary assessment of efficacy was based on 110 patients who received JIVI for routine prophylaxis during Weeks 10–36 of Part A. Of these, 107 patients participated in the optional extension phase.
All patients in the prophylaxis treatment arms began treatment with twice weekly infusions of 25 IU/kg for 10 weeks (run-in phase). After the run-in phase (Weeks 0 – 10), patients (97 of 110; 88%) who experienced ≤ 1 breakthrough bleeds during the first 10 weeks of treatment qualified for randomization to a less frequent dosing regimen, 86 were randomized 1:1 (n = 43 to either arm) to either every 5 days of 45–60 IU/kg, with a median of 45.3 IU/kg (range: 39 to 58) or every 7 days for an additional 26 weeks (Weeks 10–36; 6.5 months). Eleven additional patients, who completed the run-in phase and were eligible for randomization after the every 5- and 7-day arms were filled, remained in the twice weekly regimen of 30–40 IU/kg, with a median of 30.6 (range: 29 to 41). Dose adjustments were recommended for randomized patients who experienced 2 joint and/or muscle bleeds within a 10-week interval during week 10–36 and included the increase of the dose up to 60 IU/kg or changing to more frequent dosing.
Twelve percent of patients (n=13) who experienced ≥ 2 spontaneous bleeds during the 10 week run-in phase were ineligible for randomization and continued on the 2 times per week dosing frequency at a higher dose of 30–40 IU/kg, with a median of 39.2 IU/kg (range: 33 to 42) for the additional 26 weeks. Nine of the 13 patients were on prior prophylaxis (n=9) and were observed to have a higher mean number of bleeds in the 12 months prior to study entry of 17.4 compared to a mean of 5–7 bleeds for all other patients eligible for randomization to less frequent dosing regimens. The median cumulative number of days in the study (Part A plus extension) was 716 (range: 0 to 952) with a median number of 137 EDs (range: 1 to 309).
In Weeks 10–36 of Part A, the majority [99/110 (90%)] of patients did not change their treatment regimens. All patients randomized to the every 5-day regimen (43/43 patients) or assigned to the 2 times per week regimen (24/24 patients) remained in their assigned treatment arm until Week 36. Treatment success in the every 7 day arm was not established. For ABR by regimen, see Table 6.
During the extension phase of Study 2, the median prophylaxis dose was maintained for the median duration of 1.3 years (range: 0.1–1.9).
An analysis compared ABRs between the on-demand group and the different prophylaxis regimens indicated that the ABR was significantly reduced by 88.2% in the every 5-days (p<0.0001) in comparison with on-demand treatment. There was no significant difference in ABRs between the twice weekly and extended interval treatment arms. Nineteen (19) of 43 patients in the every 5-day arm (44%) experienced no bleeding episode during week 10–36.
| Main Study (Week 10 – 36) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Regimen (n) | Type of Bleed | Patients with Zero Bleeds, % (n) | ||||
| Total | Spontaneous | Joint | ||||
| 2 times per week 30–40 IU/kg | Eligible for randomization (11) | Median (Q1; Q3) | 1.9 (0.0; 5.2) | 0.0 (0.0; 1.9) | 1.9 (0.0; 5.2) | 46% (5) |
| Mean (SD) | 2.2 (2.7) | 1.2 (2.2) | 2.2 (2.7) | |||
| Ineligible for randomization (13) | Median (Q1; Q3) | 4.1 (2.0; 10.6) | 3.9 (0.0; 4.1) | 4.0 (2; 8.0) | 15% (2) | |
| Mean (SD) | 7.2 (7.5) | 3.9 (4.3) | 5.2 (4.8) | |||
| Every 5 days 45 – 60 IU/kg (43) | Median (Q1; Q3) | 1.9 (0.0; 4.2) | 0.0 (0.0; 4) | 1.9 (0.0; 4) | 44% (19) | |
| Mean (SD) | 3.3 (4.3) | 1.8 (2.6) | 2.5 (3.5) | |||
| On-Demand†
(20) | Median (Q1; Q3) | 24.1 (17.8; 37.3) | 14.3 (7.3; 22.7) | 16.3 (11.6; 30.3) | 0 (0) | |
| Mean (SD) | 28.8 (17.8) | 17.2 (13.2) | 22.2 (16.7) | |||
Children (7 to <12 years of age)
In Study 3 and Study 4, the efficacy of prophylactic treatment was assessed in 57 patients. Forty-two of 57 patients were treated with a twice weekly regimen of 25-60 IU/kg, with a median dose per infusion of 51.7 IU/kg (range: 22 to 69). The median cumulative number of days in the study for patients in the twice weekly treatment group was 182 (range: 172-238 days) with a median number of 53.5 EDs (range: 35-62 EDs). The ABR is presented in Table 7.
| Treatment Regimen (n)† | Type of Bleed | Patients with Zero Bleeds, % (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Spontaneous | Joint | |||
| 2 times per week 25-60 IU/kg (n=42) | Median (Q1; Q3) | 0.0 (0.0; 2.0) | 0.0 (0.0; 0.0) | 0.0 (0.0; 0.0) | 67% (28) |
| Mean (SD) | 1.7 (3.0) | 0.9 (2.0) | 0.9 (2.1) | ||
16. How is Jivi supplied
How Supplied
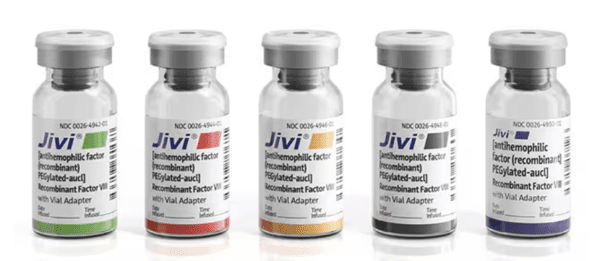
JIVI is available as a lyophilized powder in single-dose glass vials, one vial per carton. It is supplied with a sterile vial adapter with 15-micrometer filter and a prefilled diluent glass barrel syringe, which together serve as a needleless reconstitution system. The prefilled diluent syringe contains sterile Water for Injection, USP. An administration set is also provided in the package. Available sizes:
| Nominal Strength (IU) | Diluent (mL) | Kit NDC Number | Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 2.5 | 0026-3942-25 | Green |
| 1000 | 2.5 | 0026-3944-25 | Red |
| 2000 | 2.5 | 0026-3946-25 | Yellow |
| 3000 | 2.5 | 0026-3948-25 | Gray |
| 4000 | 5 | 0026-3950-50 | Purple |
Actual Factor VIII activity in IU is stated on the label of each JIVI vial.
The product vial and diluent syringe are not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
Product as Packaged for Sale
- Store JIVI at +2°C to +8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 months from the date of manufacture. Do not freeze. Within this period, JIVI may be stored for a single period of up to 6 months at temperatures up to +25°C or 77°F.
- Record the starting date of room temperature storage on the unopened product carton. Once stored at room temperature, do not return the product to the refrigerator. The shelf-life then expires after storage at room temperature for 6 months, or after the expiration date on the product vial, whichever is earlier.
- Do not use JIVI after the expiration date indicated on the vial.
- Protect JIVI from extreme exposure to light and store the vial with the lyophilized powder in the carton prior to use.
Product After Reconstitution
- Administer reconstituted JIVI as soon as possible. If you do not administer the reconstituted JIVI immediately, then store at room temperature for no longer than 3 hours.
- Do not use JIVI if the reconstituted solution is cloudy or has particulate matter.
- Use the administration set provided.
17. Patient Counseling Information
- Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
- Hypersensitivity reactions are possible with JIVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Warn patients of the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions (including tightness of the chest or throat, dizziness, mild hypotension and nausea during infusion) which can progress to anaphylaxis. Advise patients to discontinue use of the product if these symptoms occur and seek immediate emergency treatment with resuscitative measures such as the administration of epinephrine and oxygen.
- Inhibitor formation may occur at any time in the treatment of a patient with hemophilia A [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Advise patients to contact their physician or treatment center for further treatment and/or assessment, if they experience a lack of clinical response to Factor VIII replacement therapy, as this may be a manifestation of an inhibitor.
- Allergic reactions to polyethylene glycol (PEG), a component of JIVI, are possible. Advise patients to contact their physician or treatment center if they experience a lack of clinical response from their usual dose. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
- Advise patients to discard all equipment, including any unused product, in an appropriate container.
- Advise patients to consult with their healthcare provider prior to travel. Advise patients to bring an adequate supply of JIVI while traveling based on their current regimen of treatment.
| PATIENT INFORMATION JIVI (JIHV-ee) [antihemophilic factor (recombinant), PEGylated-aucl] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 5/2025 | ||
| This leaflet summarizes important information about JIVI with vial adapter. Please read it carefully before using this medicine. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider, and it does not include all of the important information about JIVI. If you have any questions after reading this, ask your healthcare provider. Do not attempt to self-infuse, unless your healthcare provider or hemophilia center has taught you how to self-infuse. |
|||
| What is JIVI?
JIVI is an injectable medicine used to replace clotting factor (Factor VIII or antihemophilic factor) that is missing in people with hemophilia A (congenital Factor VIII deficiency). JIVI is used to treat and control bleeding in previously treated adults and children 7 years of age and older with hemophilia A. Your healthcare provider may also give you JIVI when you have surgery. JIVI can reduce the number of bleeding episodes in adults and children 7 years of age and older with hemophilia A when used regularly (prophylaxis). JIVI is not for use in children < 7 years of age or in previously untreated patients. JIVI is not used to treat von Willebrand disease. |
|||
| Who should not use JIVI?
You should not use JIVI if you:
|
|||
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before I use JIVI?
Tell your healthcare provider about:
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of JIVI?
The common side effects of JIVI are headache, fever, cough, and abdominal pain. Allergic reactions may occur with JIVI. Call your healthcare provider right away and stop treatment if you get tightness of the chest or throat, dizziness, decrease in blood pressure, or nausea. Allergic reactions to polyethylene glycol (PEG), a component of JIVI, are possible. Your body can also make antibodies, called "inhibitors", against JIVI, or certain components of JIVI, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), which may stop JIVI from working properly. Consult with your healthcare provider to make sure you are carefully monitored with blood tests for the development of inhibitors to Factor VIII. If your bleeding is not being controlled with your usual dose of JIVI, consult your doctor immediately. You may have developed Factor VIII inhibitors or antibodies to PEG and your doctor may carry out tests to confirm this. These are not all the possible side effects with JIVI. You can ask your healthcare provider for information that is written for healthcare professionals. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. |
|||
| What are the JIVI dosage strengths?
JIVI with 2.5 mL or 5mL sterile Water for Injection (sWFI) comes in five different dosage strengths labeled as International Units (IU): 500 IU, 1000 IU, 2000 IU, 3000 IU, and 4000 IU. The five different strengths are color-coded as follows: |
|||
| Green | 500 IU with 2.5 mL sWFI | ||
| Red | 1000 IU with 2.5 mL sWFI | ||
| Yellow | 2000 IU with 2.5 mL sWFI | ||
| Gray | 3000 IU with 2.5 mL sWFI | ||
| Purple | 4000 IU with 5 mL sWFI | ||
| How do I store JIVI ?
Do not freeze JIVI . Store JIVI at +2°C to +8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 months from the date of manufacture. Within this period, JIVI may be stored for a period of up to 6 months at temperatures up to +25°C or 77°F. Record the starting date of room temperature storage clearly on the unopened product carton. Once stored at room temperature, do not return the product to the refrigerator. The product then expires after storage at room temperature for 6 months, or after the expiration date on the product vial, whichever is earlier. Store vials in their original carton and protect them from extreme exposure to light. Administer reconstituted JIVI as soon as possible. If not, store at room temperature for no longer than 3 hours. Throw away any unused JIVI after the expiration date. Do not use reconstituted JIVI if it is not clear. |
|||
| What else should I know about JIVI and hemophilia A?
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed here. Do not use JIVI for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not share JIVI with other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. This leaflet summarizes the most important information about JIVI that was written for healthcare professionals. Bayer HealthCare LLC Whippany, NJ 07981 USA U.S. License No. 0008 |
|||
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
JIVI
[antihemophilic factor (recombinant), PEGylated-aucl]
Do not attempt to self-infuse unless you have been taught how by your healthcare provider or hemophilia center.
You should always follow the specific instructions given by your healthcare provider. The steps listed below are general guidelines for using JIVI. If you are unsure of the procedures, please call your healthcare provider before using.
If bleeding is not controlled after using JIVI, then call your healthcare provider right away.
Your healthcare provider will prescribe the dose that you should take.
Your healthcare provider may need to take blood tests from time to time.
Talk to your healthcare provider before traveling. You should plan to bring enough JIVI for your treatment during this time.
See the step-by-step instructions below for reconstituting (mixing) JIVI with vial adapter. Follow the specific infusion instruction leaflet included with the infusion set provided.
Carefully handle JIVI. Dispose of all materials, including any leftover reconstituted JIVI product, in an appropriate container.
Use only the components for reconstitution and administration that are provided with each package of JIVI. If a package is opened or damaged, do not use this component. If these components cannot be used, please contact your healthcare provider. Gather all the materials needed for the infusion.
Reconstitution
Always work on a clean flat surface and wash your hands before performing the following procedures.
| 1. Warm the unopened diluent syringe and the concentrate vial to a temperature not to exceed 37°C or 99°F. | |
| 2. Remove protective cap from the vial (A). Aseptically cleanse the rubber stopper with a sterile alcohol swab, being careful not to handle the rubber stopper. | 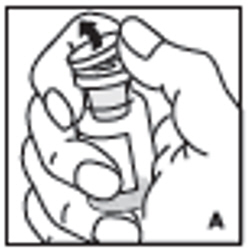 |
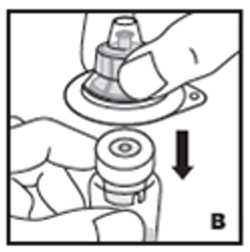
| 3. Place product vial on a firm, non-skid surface. Peel off the paper cover on the vial adapter plastic housing. Do not remove the adapter from the plastic housing. Holding the adapter housing, place over the product vial and firmly press down (B). The adapter will snap over the vial cap. Do not remove the adapter housing at this step. | 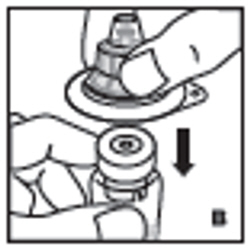 |
| 4. Holding the syringe by the barrel, snap the syringe cap off the tip (C). Do not touch the syringe tip with your hand or any surface. Set the syringe aside for further use. |  |
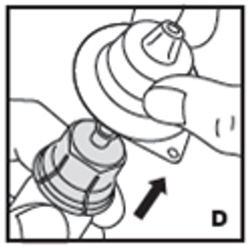
| 5. Now remove and discard the adapter plastic housing (D). |  |
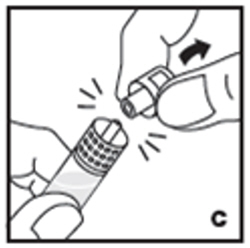
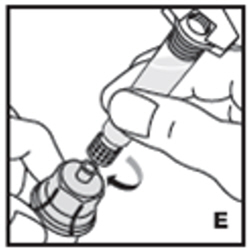
| 6. Attach the prefilled syringe to the vial adapter thread by turning clockwise (E). | 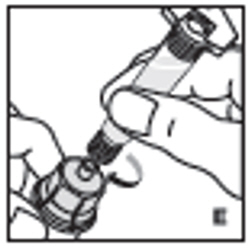 |
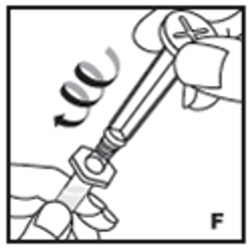
| 7. Remove the clear plastic plunger rod from the carton. Grasp the plunger rod by the top plate. Avoid touching the sides and threads of the plunger rod. Attach the plunger rod by turning it clockwise into the threaded rubber stopper of the prefilled syringe (F). | 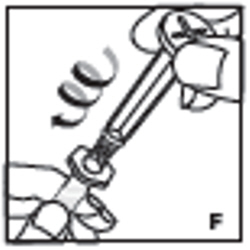 |
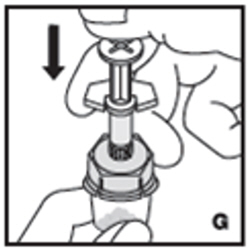
| 8. Inject the diluent slowly by pushing down on the plunger rod (G). | 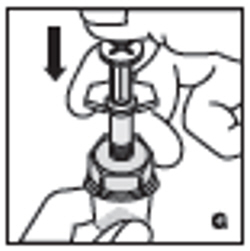 |
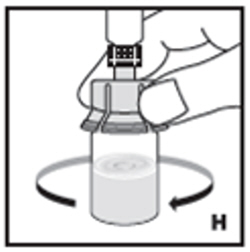
| 9. Swirl vial gently until all powder on all sides of the vial is dissolved (H). Do not shake vial. Be sure that all powder is completely dissolved. Do not use if solution contains visible particles or is cloudy. | 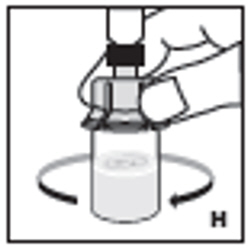 |
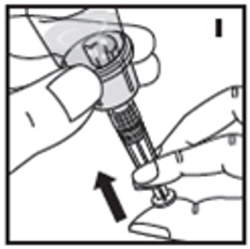
| 10. Push down on the plunger to push all air back into the vial. Then while holding the plunger down, turn the vial with syringe upside-down (invert) so the vial is now above the syringe (I). Pooling: Pooling is a process of combining the contents of multiple vials into a syringe. If the dose requires more than one vial, reconstitute each vial as described above with the diluent syringe provided. To combine the contents of the vials, use a larger plastic syringe (not provided) to pool the solution into the syringe and administer as usual. | 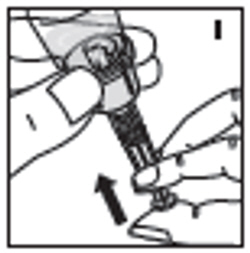 |
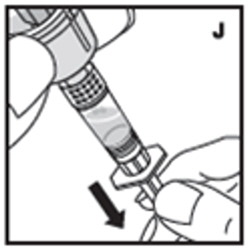
| 11. Filter the reconstituted product to remove potential particulate matter in the solution. Filtering is achieved by using the vial adapter. Withdraw all the solution through the vial adapter into the syringe by pulling the plunger rod back slowly and smoothly (J). Tilt the vial to the side and back to make sure all the solution has been drawn toward the large opening in the rubber stopper and into the syringe. Remove as much air as possible before removing the syringe from the vial by slowly and carefully pushing the air back into the vial. | 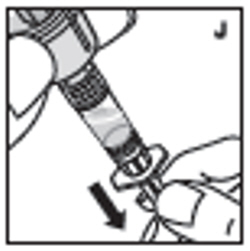 |
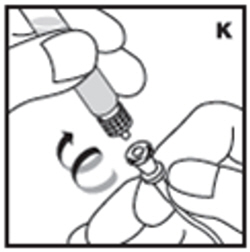
| 12. Detach the syringe with plunger rod from the vial adapter by turning counter-clockwise. Attach the syringe to the infusion set provided and inject the reconstituted product intravenously (K). NOTE: follow instructions for infusion set provided. | 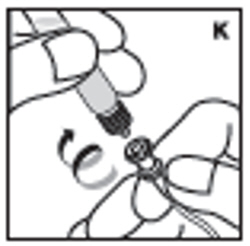 |
Rate of Administration
The entire dose of JIVI can usually be infused within 1 to 15 minutes. The maximum rate is 2.5 mL per minute. Your healthcare provider will determine the rate of administration that is best for you.
Resources at Bayer available to the patient:
For Adverse Reaction Reporting, contact Bayer Medical Communications 1-888-84-BAYER (1-888-842-2937)
To receive more product information, contact JIVI Customer Service 1-888-606-3780
Bayer Reimbursement HELPline 1-800-288-8374
For more information, visit http://www.jivi-us.com
Bayer HealthCare LLC
Whippany, NJ 07981 USA
U.S. License No. 0008
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 5/2025
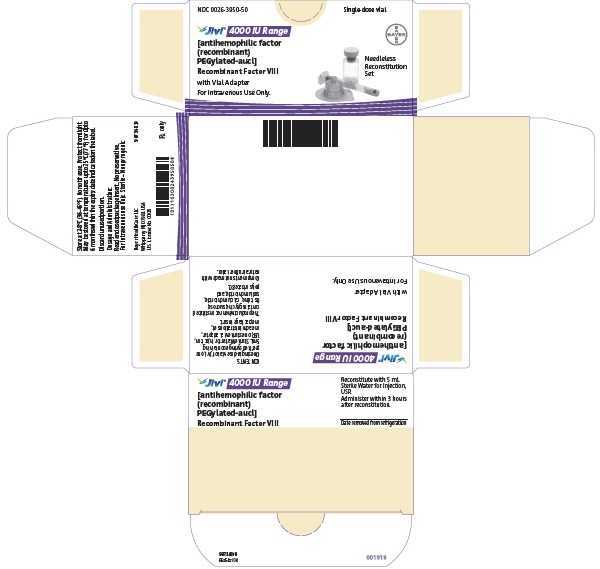
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0026-3942-25
Jivi
500 IU Range
Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)
PEGylated-aucl
Recombinant Factor VIII
with Vial Adapter
For Intravenous Use Only
Needleless Reconstitution Set
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0026-3944-25
Jivi
1000 IU Range
Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)
PEGylated-aucl
Recombinant Factor VIII
with Vial Adapter
For Intravenous Use Only
Needleless Reconstitution Set
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0026-3946-25
Jivi
2000 IU Range
Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)
PEGylated-aucl
Recombinant Factor VIII
with Vial Adapter
For Intravenous Use Only
Needleless Reconstitution Set
| JIVI
antihemophilic factor (recombinant) pegylated-aucl kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| JIVI
antihemophilic factor (recombinant) pegylated-aucl kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| JIVI
antihemophilic factor (recombinant) pegylated-aucl kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| JIVI
antihemophilic factor (recombinant) pegylated-aucl kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| JIVI
antihemophilic factor (recombinant) pegylated-aucl kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bayer HealthCare LLC (127769128) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bayer HealthCare LLC | 127769128 | MANUFACTURE(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , API MANUFACTURE(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , LABEL(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , PACK(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bayer Healthcare Manufacturing Srl | 630762938 | ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , LABEL(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Schuetzenstrasse) | 316126754 | MANUFACTURE(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Mooswiesen) | 312670654 | ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , MANUFACTURE(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , PACK(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , LABEL(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bayer AG | 315097875 | PACK(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , LABEL(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , MANUFACTURE(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Langenargen Eisenbahnstrasse) | 344217323 | ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) , MANUFACTURE(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Helmut-Vetter-Strasse) | 341629292 | ANALYSIS(0026-3942, 0026-4942, 0026-0426, 0026-3944, 0026-4944, 0026-0426, 0026-3946, 0026-4946, 0026-0426, 0026-3948, 0026-4948, 0026-0426, 0026-3950, 0026-4950, 0026-0426) | |
Frequently asked questions
More about Jivi (antihemophilic factor)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Professional resources
Other brands
Altuviiio, Advate, Kovaltry, Afstyla, ... +12 more