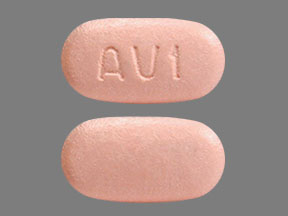
Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 15, 2024.
Pronunciation
(om BIT as vir, par i TA pre vir, & ri TOE na vir)
Index Terms
- Paritaprevir, Ombitasvir, and Ritonavir
- Ritonavir, Ombitasvir, and Paritaprevir
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet, Oral:
Technivie: Ombitasvir 12.5 mg, paritaprevir 75 mg, and ritonavir 50 mg
Brand Names: U.S.
- Technivie
Pharmacologic Category
- Antihepaciviral, NS3/4A Protease Inhibitor (Anti-HCV)
- Antihepaciviral, NS5A Inhibitor
- Cytochrome P-450 Inhibitor
- NS3/4A Inhibitor
- NS5A Inhibitor
Pharmacology
Combines 2 direct-acting hepatitis C virus antiviral agents with distinct mechanisms of action. Ombitasvir inhibits HCV NS5A, and interferes with viral RNA replication and virion assembly. Paritaprevir inhibits HCV NS3/4A protease and interferes with HCV coded polyprotein cleavage necessary for viral replication.
Ritonavir is not active against HCV. Ritonavir is a potent CYP3A inhibitor that increases peak and trough plasma drug concentrations of paritaprevir and overall drug exposure (ie, AUC).
Absorption
Well absorbed when administered with food
Distribution
Ombitasvir: Vd: 173 L
Paritaprevir: Vd: 103 L
Ritonavir: Vd: 21.5 L
Metabolism
Ombitasvir: Metabolized by amide hydrolysis and oxidative metabolism
Paritaprevir: Metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent CYP3A5
Ritonavir: Metabolized by CYP3A and to a lesser extent CYP2D6
Excretion
Ombitasvir: Feces (90.2%, mainly as unchanged drug); urine (1.91%, mainly as unchanged drug)
Paritaprevir: Feces (88%, mainly as metabolites); urine (8.8%, mainly as metabolites)
Ritonavir: Feces (86.4%); urine (11.3%)
Time to Peak
Ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir: 4 to 5 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Ombitasvir: 21 to 25 hours; Paritaprevir: 5.5 hours; Ritonavir: 4 hours
Protein Binding
Ombitasvir: 99.9%; Paritaprevir: ~98%; Ritonavir: >99%
Use: Labeled Indications
Chronic hepatitis C: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 4 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis, in combination with ribavirin.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ritonavir (eg, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome) or any component of the formulation; moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C); concurrent use of drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events; concurrent use of moderate or strong inducers of CYP3A. Concurrent use of drugs that are contraindicated include, but are not necessarily limited to: Alfuzosin, apalutamide, atorvastatin, colchicine (in patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment), carbamazepine, cisapride, dronedarone, ergot derivatives (ergonovine, ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, methylergonovine), ethinyl estradiol-containing products, efavirenz, everolimus, lomitapide, lovastatin, lurasidone, midazolam (oral), phenobarbital, phenytoin, pimozide, ranolazine, rifampin, sildenafil (when used for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension [eg, Revatio]), simvastatin, sirolimus, St John's wort, tacrolimus, triazolam. Note: Contraindications to ribavirin also apply; see ribavirin prescribing information.
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in US labeling): Concurrent use with avasimibe (not available in Canada), nafcillin (not available in Canada), fusidic acid (oral) (not available in Canada), astemizole, disopyramide, terfenadine, etravirine, nevirapine, bosentan, salmeterol, or modafinil; women who are pregnant; males whose female partners are pregnant, may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant
Dosing: Adult
Chronic hepatitis C, genotype 4 (treatment-naive or peginterferon/ribavirin-experienced without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis [Child-Pugh class A]) (alternative regimen): Oral: Two tablets once daily (every morning) for 12 weeks, in combination with ribavirin (AASLD/IDSA 2018).
Dosage adjustment for concomitant therapy: Significant drug interactions exist, requiring dose/frequency adjustment or avoidance. Consult drug interactions database for more information.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Administration
Oral: Administer in the morning with a meal.
Storage
Store at or below 30°C (86°F). Dispense in original carton.
Drug Interactions
Abametapir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Abemaciclib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Abemaciclib. Management: In patients taking abemaciclib at a dose of 200 mg or 150 mg twice daily, reduce the dose to 100 mg twice daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. In patients taking abemaciclib 100 mg twice daily, decrease the dose to 50 mg twice daily. Consider therapy modification
Acalabrutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Acalabrutinib. Avoid combination
Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine. Specifically, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase concentrations of the cytotoxic DM1 component. Management: Avoid concomitant use of ado-trastuzumab emtansine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. Consider alternatives that do not inhibit CYP3A4 or consider administering after CYP3A4 inhibitor discontinuation. Monitor for toxicities if combined. Consider therapy modification
Afatinib: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Afatinib. Management: If combined, administer the P-gp inhibitor simultaneously with, or after, the dose of afatinib. Monitor closely for signs and symptoms of afatinib toxicity and if the combination is not tolerated, reduce the afatinib dose by 10 mg. Consider therapy modification
Alfentanil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alfentanil. Management: If use of alfentanil and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is necessary, consider dosage reduction of alfentanil until stable drug effects are achieved. Frequently monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation when these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
Alfuzosin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alfuzosin. Avoid combination
Aliskiren: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Aliskiren. Monitor therapy
Alitretinoin (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alitretinoin (Systemic). Management: Consider reducing the alitretinoin dose to 10 mg when used together with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Monitor for increased alitretinoin effects/toxicities if combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Almotriptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Almotriptan. Management: Limit initial almotriptan dose to 6.25 mg and maximum dose to 12.5 mg in any 24-period when used with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Avoid concurrent use in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Consider therapy modification
Alosetron: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alosetron. Monitor therapy
Alpelisib: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Alpelisib. Management: Avoid coadministration of BCRP/ABCG2 inhibitors and alpelisib due to the potential for increased alpelisib concentrations and toxicities. If coadministration cannot be avoided, closely monitor for increased alpelisib adverse reactions. Consider therapy modification
ALPRAZolam: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of ALPRAZolam. Monitor therapy
Amiodarone: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Amiodarone. Monitor therapy
AmLODIPine: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of AmLODIPine. Management: Reduce amlodipine dose by at least 50% and monitor for increased amlodipine effects (eg, hypotension) if an antihepaciviral combination product is initiated. Consider therapy modification
Antidiabetic Agents: Direct Acting Antiviral Agents (HCV) may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of Antidiabetic Agents. Monitor therapy
Apixaban: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Apixaban. Management: US labeling recommends a 50% apixaban dose reduction in patients who would otherwise receive 5 or 10 mg twice daily, and avoiding in patients who would otherwise receive 2.5 mg twice daily. Canadian labeling lists any combined use as contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Aprepitant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Aprepitant. Avoid combination
ARIPiprazole: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of ARIPiprazole. Management: Aripiprazole dose reductions are required for indications other than major depressive disorder. Dose reductions vary based on formulation, CYP2D6 genotype, and use of CYP2D6 inhibitors. See full interaction monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
ARIPiprazole Lauroxil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of ARIPiprazole Lauroxil. Management: Decrease aripiprazole lauroxil dose to next lower strength if used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors for over 14 days. No dose adjustment needed if using the lowest dose (441 mg). Max dose is 441 mg in CYP2D6 PMs or if also taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Astemizole: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Astemizole. Avoid combination
Asunaprevir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Asunaprevir. Avoid combination
Asunaprevir: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Asunaprevir. Avoid combination
Atazanavir: May increase the serum concentration of Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir. Specifically, the paritaprevir component may increase significantly. Avoid combination
AtorvaSTATin: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of AtorvaSTATin. Avoid combination
Avanafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Avanafil. Avoid combination
Avapritinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Avapritinib. Avoid combination
Axitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Axitinib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of axitinib with any strong CYP3A inhibitor whenever possible. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be used with axitinib, a 50% axitinib dose reduction is recommended. Consider therapy modification
Barnidipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Barnidipine. Avoid combination
Bedaquiline: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bedaquiline. Management: Limit duration of concurrent use of bedaquiline with CYP3A4 inhibitors to no more than 14 days, unless the benefit of continued use outweighs the possible risks. Monitor for toxic effects of bedaquiline. Consider therapy modification
Benperidol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Benperidol. Monitor therapy
Benzhydrocodone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Benzhydrocodone. Specifically, the concentration of hydrocodone may be increased. Monitor therapy
Bepridil: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Bepridil. Monitor therapy
Betamethasone (Ophthalmic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Betamethasone (Ophthalmic). Monitor therapy
Betamethasone (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Betamethasone (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Betrixaban: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Betrixaban. Management: Decrease adult betrixaban dose to an initial single dose of 80 mg followed by 40 mg once daily if combined with a P-gp inhibitor. Avoid concomitant use of betrixaban and P-gp inhibitors in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCL less than 30 mL/min). Consider therapy modification
Bictegravir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bictegravir. Monitor therapy
Bilastine: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Bilastine. Avoid combination
Blonanserin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Blonanserin. Avoid combination
Bortezomib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bortezomib. Monitor therapy
Bosutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bosutinib. Avoid combination
Brentuximab Vedotin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brentuximab Vedotin. Specifically, concentrations of the active monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) component may be increased. Monitor therapy
Brexpiprazole: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brexpiprazole. Management: Reduce brexpiprazole dose 50% with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors; reduce to 25% of usual if used with both a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and a CYP2D6 inhibitor in patients not being treated for MDD, or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor used in a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer. Consider therapy modification
Brigatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brigatinib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of brigatinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combination cannot be avoided, reduce the brigatinib dose by approximately 50%, rounding to the nearest tablet strength (ie, from 180 mg to 90 mg, or from 90 mg to 60 mg). Consider therapy modification
Bromperidol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bromperidol. Monitor therapy
Budesonide (Nasal): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Nasal). Monitor therapy
Budesonide (Oral Inhalation): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Oral Inhalation). Monitor therapy
Budesonide (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Systemic). Management: Avoid the concomitant use of CYP3A4 inhibitors and oral budesonide. If patients receive both budesonide and a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, they should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of corticosteroid excess. Consider therapy modification
Budesonide (Topical): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Topical). Avoid combination
Buprenorphine: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Buprenorphine. Monitor therapy
BuPROPion: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may decrease the serum concentration of BuPROPion. Monitor therapy
BusPIRone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of BusPIRone. Management: Limit the buspirone dose to 2.5 mg daily and monitor patients for increased buspirone effects/toxicities if combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Cabazitaxel: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cabazitaxel. Management: Concurrent use of cabazitaxel with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 should be avoided when possible. If such a combination must be used, consider a 25% reduction in the cabazitaxel dose. Consider therapy modification
Cabozantinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cabozantinib. Management: Avoid use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor with cabozantinib if possible. If combined, decrease cabozantinib capsules (Cometriq) by 40 mg from previous dose or decrease cabozantinib tablets (Cabometyx) by 20 mg from previous dose. Consider therapy modification
Calcifediol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Calcifediol. Monitor therapy
Candesartan: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Candesartan. Management: Consider decreasing the candesartan dose and monitoring for evidence of hypotension and worsening renal function if these agents are used in combination. Consider therapy modification
Cannabidiol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Cannabis: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cannabis. More specifically, tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol serum concentrations may be increased. Monitor therapy
Capmatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Capmatinib. Monitor therapy
Cariprazine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cariprazine. Management: Decrease cariprazine dose 50% (4.5 mg to 1.5 mg or 3 mg; 1.5 mg to 1.5 mg every other day) if starting a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. If on a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, start cariprazine at 1.5 mg day 1, 0 mg day 2, then 1.5 mg daily. May increase to 3 mg daily Consider therapy modification
Carisoprodol: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Carisoprodol. Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Carisoprodol. Monitor therapy
Celiprolol: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Celiprolol. Monitor therapy
Ceritinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ceritinib. Management: If such combinations cannot be avoided, the ceritinib dose should be reduced by approximately one-third (to the nearest 150 mg). Resume the prior ceritinib dose after cessation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Ciclesonide (Oral Inhalation): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ciclesonide (Oral Inhalation). Monitor therapy
Cilostazol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cilostazol. Management: Consider reducing the cilostazol dose to 50 mg twice daily in adult patients who are also receiving strong inhibitors of CYP3A4. Consider therapy modification
Cinacalcet: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cinacalcet. Monitor therapy
Cisapride: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Cisapride. Avoid combination
Cladribine: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Cladribine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of BCRP inhibitors during the 4 to 5 day oral cladribine treatment cycles whenever possible. If combined, consider dose reduction of the BCRP inhibitor and separation in the timing of administration. Consider therapy modification
Clarithromycin: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Clarithromycin. Management: Avoid clarithromycin doses greater than 1000 mg/day when used with an antihepaciviral combination product. Further dose reductions may be needed in patients with impaired renal function. Consider an alternative antimicrobial for any non-MAC infection. Consider therapy modification
Clofazimine: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CloZAPine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of CloZAPine. Monitor therapy
CloZAPine: CYP1A2 Inducers (Weak) may decrease the serum concentration of CloZAPine. Monitor therapy
Cobimetinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cobimetinib. Avoid combination
Codeine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Codeine. Monitor therapy
Colchicine: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Colchicine. Avoid combination
Conivaptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Conivaptan. Avoid combination
Conivaptan: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Copanlisib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Copanlisib. Management: If concomitant use of copanlisib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce the copanlisib dose to 45 mg. Monitor patients for increased copanlisib effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Cortisone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cortisone. Monitor therapy
Crizotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Crizotinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of crizotinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors whenever possible. If combined use cannot be avoided, decrease the crizotinib dose to 250 mg daily. Consider therapy modification
Cyclobenzaprine: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Cyclobenzaprine. Monitor therapy
CycloSPORINE (Systemic): Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). Management: Reduce cyclosporine dose by 80% when initiating therapy with ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and monitor cyclosporine blood levels closely. Consider therapy modification
CYP3A4 Inducers (Moderate): May decrease the serum concentration of Antihepaciviral Combination Products. Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May decrease the serum concentration of Antihepaciviral Combination Products. Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Consider avoiding this combination. Some combinations are specifically contraindicated by manufacturers; others may have recommended dose adjustments. If combined, monitor for increased substrate effects. Consider therapy modification
CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Consider avoiding this combination. Some combinations are specifically contraindicated by manufacturers; others may have recommended dose adjustments. If combined, monitor for increased substrate effects. Consider therapy modification
Dabigatran Etexilate: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Dabigatran Etexilate. Monitor therapy
Dabrafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dabrafenib. Avoid combination
Daclatasvir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Daclatasvir. Management: Decrease the daclatasvir dose to 30 mg once daily if combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. No dose adjustment is needed when daclatasvir is used with darunavir/cobicistat. Consider therapy modification
Dapoxetine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dapoxetine. Avoid combination
Darifenacin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Darifenacin. Management: Limit the darifenacin dose to no more than 7.5 mg daily if combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Monitor patients for increased darifenacin toxicities (eg, dry mouth, constipation, headache, CNS effects) when these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
Darolutamide: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Darolutamide. Monitor therapy
Darunavir: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Darunavir. Management: These agents can be combined in treatment naive patients or those with no darunavir resistance if the darunavir dose is 800 mg daily, darunavir is administered at the same time as the combination product, and darunavir is given without ritonavir. Consider therapy modification
Dasatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dasatinib. Management: This combination should be avoided if possible. If combined, decrease dasatinib dose from 140 mg to 40 mg, 100 mg to 20 mg, or 70 mg to 20 mg. For patients taking 60 mg or 40 mg daily, stop dasatinib until the CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued. Consider therapy modification
Deferasirox: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Deflazacort: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Deflazacort. Management: Administer one third of the recommended deflazacort dose when used together with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Delamanid: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Delamanid. Management: Increase ECG monitoring frequency if delamanid is combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors due to the risk for QTc interval prolongation. Continue frequent ECG assessments throughout full delamanid treatment period. Consider therapy modification
DexAMETHasone (Ophthalmic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of DexAMETHasone (Ophthalmic). Monitor therapy
DiazePAM: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of DiazePAM. Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of DiazePAM. Monitor therapy
Dienogest: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dienogest. Monitor therapy
Digitoxin: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Digitoxin. Monitor therapy
Digoxin: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Digoxin. Management: Measure digoxin serum concentrations before initiating treatment with these P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors. Reduce digoxin concentrations by either reducing the digoxin dose by 15% to 30% or by modifying the dosing frequency. Consider therapy modification
DOCEtaxel: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of DOCEtaxel. Management: Avoid the concomitant use of docetaxel and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined use is unavoidable, consider a 50% docetaxel dose reduction and monitor for increased docetaxel toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Dofetilide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dofetilide. Monitor therapy
Domperidone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Domperidone. Avoid combination
Doxercalciferol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Doxercalciferol. Monitor therapy
DOXOrubicin (Conventional): P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of DOXOrubicin (Conventional). Avoid combination
Dronabinol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dronabinol. Monitor therapy
Dronedarone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dronedarone. Management: Concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with dronedarone is contraindicated according to dronedarone prescribing information. Avoid combination
Drospirenone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Drospirenone. Management: Drospirenone use is contraindicated specifically when the strong CYP3A4 inhibitors atazanavir and cobicistat are administered concurrently. Caution should be used when drospirenone is coadministered with other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Dutasteride: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dutasteride. Monitor therapy
Duvelisib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Duvelisib. Management: Reduce the dose of duvelisib to 15 mg twice a day when used together with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor closely for evidence of altered response to treatment. Consider therapy modification
Edoxaban: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Edoxaban. Monitor therapy
Elagolix: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Elagolix. Avoid combination
Elagolix, Estradiol, and Norethindrone: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Elagolix, Estradiol, and Norethindrone. Specifically, concentrations of elagolix may be increased. Avoid combination
Elagolix, Estradiol, and Norethindrone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Elagolix, Estradiol, and Norethindrone. Avoid combination
Eletriptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eletriptan. Avoid combination
Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor, and Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor, and Ivacaftor. Management: When combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, administer two elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets (100 mg/50 mg/75 mg) in the morning, twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening doses of ivacaftor (150 mg) alone should be administered. Consider therapy modification
Eliglustat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eliglustat. Management: Reduce eliglustat dose to 84 mg daily in CYP2D6 EMs when used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated in CYP2D6 IMs, PMs, or in CYP2D6 EMs who are also taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Eluxadoline: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Eluxadoline. Management: Decrease the eluxadoline dose to 75 mg twice daily if combined with OATP1B1/1B3 inhibitors and monitor patients for increased eluxadoline effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Encorafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Encorafenib. Management: Avoid use of encorafenib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined, decrease encorafenib from 450 mg to 150 mg; or from 300 mg, 225 mg, or 150 mg to 75 mg. Once the CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued for 3 to 5 half-lives, resume prior dose. Consider therapy modification
Enfortumab Vedotin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Enfortumab Vedotin. Specifically, concentrations of the active monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) component may be increased. Monitor therapy
Entrectinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Entrectinib. Management: Avoid strong CYP3A4 inhibitors during treatment with entrectinib when possible. If combined in adults and those 12 yrs of age or older with a BSA of at least 1.5 square meters, reduce dose to 100 mg/day. Avoid if BSA is less than 1.5 square meters. Consider therapy modification
Eplerenone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eplerenone. Avoid combination
Erdafitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Erdafitinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of erdafitinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined, monitor closely for erdafitinib adverse reactions and consider dose modifications accordingly. Consider therapy modification
Ergot Derivatives: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Erlotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Erlotinib. Management: Avoid use of this combination when possible. When the combination must be used, monitor the patient closely for the development of severe adverse reactions, and if such severe reactions occur, reduce the erlotinib dose (in 50 mg decrements). Consider therapy modification
Estrogen Derivatives: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Estrogen Derivatives. Monitor therapy
Eszopiclone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eszopiclone. Management: Limit the eszopiclone dose to 2 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and monitor for increased eszopiclone effects and toxicities (eg, somnolence, drowsiness, CNS depression). Consider therapy modification
Ethinyl Estradiol: May enhance the hepatotoxic effect of Antihepaciviral Combination Products. Management: Use of ethinyl estradiol must be discontinued prior to use of this combination; ethinyl estradiol can be restarted 2 weeks after cessation of the antihepaciviral combination product. Avoid combination
Etizolam: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Etizolam. Management: Consider use of lower etizolam doses when using this combination; specific recommendations concerning dose adjustment are not available. Monitor clinical response to the combination closely. Consider therapy modification
Etoposide: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Etoposide. Monitor therapy
Etoposide Phosphate: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Etoposide Phosphate. Monitor therapy
Everolimus: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Everolimus. Avoid combination
Everolimus: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Everolimus. Avoid combination
Evogliptin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Evogliptin. Monitor therapy
Fedratinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fedratinib. Management: Consider alternatives when possible. If used together, decrease fedratinib dose to 200 mg/day. After the inhibitor is stopped, increase fedratinib to 300 mg/day for the first 2 weeks and then to 400 mg/day as tolerated. Consider therapy modification
FentaNYL: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of FentaNYL. Management: Consider fentanyl dose reductions when combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor for respiratory depression and sedation. Upon discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inhibitor, consider a fentanyl dose increase; monitor for signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Consider therapy modification
Fesoterodine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Fesoterodine. Management: Limit fesoterodine doses to 4 mg daily in patients who are also receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Flecainide: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Flecainide. Management: Canadian labeling recommends avoiding this combination. Monitor therapy
Flibanserin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Flibanserin. Management: Use of flibanserin with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated. If starting flibanserin, start 2 weeks after the last dose of the CYP3A4 inhibitor. If starting a CYP3A4 inhibitor, start 2 days after the last dose of flibanserin. Avoid combination
Fluticasone (Nasal): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fluticasone (Nasal). Avoid combination
Fluticasone (Oral Inhalation): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fluticasone (Oral Inhalation). Consider therapy modification
Fosaprepitant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fosaprepitant. Avoid combination
Fosnetupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fostamatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Fostamatinib. Monitor therapy
Fusidic Acid (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Galantamine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Galantamine. Monitor therapy
Gefitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Gefitinib. Monitor therapy
Gilteritinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Gilteritinib. Management: Consider alternatives to the use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor with gilteritinib. If the combination cannot be avoided, monitor more closely for evidence of gilteritinib toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Glasdegib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Glasdegib. Management: Consider alternatives to this combination when possible. If the combination must be used, monitor closely for evidence of QT interval prolongation and other adverse reactions to glasdegib. Consider therapy modification
Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir. Monitor therapy
Grazoprevir: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Grazoprevir. Avoid combination
GuanFACINE: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of GuanFACINE. Management: Reduce the extended-release guanfacine dose 50% when combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor for increased guanfacine toxicities when these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
Halofantrine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Halofantrine. Management: The combination of halofantrine with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor should be avoided whenever possible due to the risk for QTc interval prolongation. Avoid combination
HYDROcodone: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of HYDROcodone. Management: Reduce the hydrocodone dose by 50% during concurrent use of ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir; monitor closely for both analgesic effectiveness and for signs of toxicity or withdrawal. Consider therapy modification
Hydrocortisone (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Hydrocortisone (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Ibrutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ibrutinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of ibrutinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor must be used short-term (eg, anti-infectives for 7 days or less), interrupt ibrutinib therapy until the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued. Avoid combination
Idelalisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Ifosfamide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ifosfamide. Monitor therapy
Iloperidone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Iloperidone. Specifically, concentrations of the metabolites P88 and P95 may be increased. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Iloperidone. Management: Reduce iloperidone dose by half when administered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Imatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Imatinib. Monitor therapy
Imidafenacin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Imidafenacin. Monitor therapy
Irinotecan Products: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Irinotecan Products. Specifically, serum concentrations of SN-38 may be increased. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Irinotecan Products. Avoid combination
Isavuconazonium Sulfate: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Isavuconazonium Sulfate. Specifically, CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase isavuconazole serum concentrations. Management: Combined use is considered contraindicated per US labeling. Lopinavir/ritonavir (and possibly other uses of ritonavir doses less than 400 mg every 12 hours) is treated as a possible exception to this contraindication despite strongly inhibiting CYP3A4. Avoid combination
Istradefylline: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Istradefylline. Management: Limit the maximum istradefylline dose to 20 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and monitor for increased istradefylline effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Ivabradine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ivabradine. Avoid combination
Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ivacaftor. Management: Ivacaftor dose reductions are required; consult full drug interaction monograph content for age- and weight-specific recommendations. Consider therapy modification
Ivosidenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ivosidenib. Management: Avoid use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor with ivosidenib whenever possible. When combined use is required, reduce the ivosidenib dose to 250 mg once daily. Consider therapy modification
Ixabepilone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ixabepilone. Management: Avoid use of ixabepilone and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined, reduce the ixabepilone dose to 20 mg/m2. The previous ixabepilone dose can be resumed 1 week after discontinuation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Ketoconazole (Systemic): Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Ketoconazole (Systemic). Ketoconazole (Systemic) may increase the serum concentration of Antihepaciviral Combination Products. Specifically, ketoconazole may increase serum concentrations of paritaprevir. Management: Limit the dose of ketoconazole to 200 mg per day in patients taking antihepaciviral combination products. Additionally, monitor for increased ketoconazole effects/toxicities and for increased paritaprevir effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Lapatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lapatinib. Management: Avoid use of lapatinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined, reduce lapatinib dose to 500 mg daily. The previous lapatinib dose can be resumed 1 week after discontinuation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Larotrectinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Larotrectinib. Management: Avoid use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with larotrectinib. If this combination cannot be avoided, reduce the larotrectinib dose by 50%. Increase to previous dose after stopping the inhibitor after a period of 3 to 5 times the inhibitor's half-life. Consider therapy modification
Lefamulin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lefamulin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of lefamulin tablets and strong inhibitors of CYP3A4. Avoid combination
Lemborexant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lemborexant. Avoid combination
Lercanidipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lercanidipine. Avoid combination
Levamlodipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Levamlodipine. Monitor therapy
Levobupivacaine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Levobupivacaine. Monitor therapy
Levomilnacipran: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Levomilnacipran. Management: Do not exceed a maximum adult levomilnacipran dose of 80 mg/day in patients also receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
LinaGLIPtin: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of LinaGLIPtin. Monitor therapy
Lomitapide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lomitapide. Avoid combination
Lopinavir: May increase the serum concentration of Antihepaciviral Combination Products. Specifically, the serum concentrations of the paritaprevir component may increase significantly. Avoid combination
Losartan: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Losartan. Management: Consider decreasing the losartan dose and monitoring for evidence of hypotension and worsening renal function if these agents are used in combination. Consider therapy modification
Lovastatin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lovastatin. Avoid combination
Lumateperone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lumateperone. Avoid combination
Lumefantrine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lumefantrine. Monitor therapy
Lurasidone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lurasidone. Avoid combination
Lurbinectedin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lurbinectedin. Avoid combination
Macitentan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Macitentan. Avoid combination
Manidipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Manidipine. Management: Consider avoiding concomitant use of manidipine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If combined, monitor closely for increased manidipine effects and toxicities. Manidipine dose reductions may be required. Consider therapy modification
Maraviroc: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Maraviroc. Management: Reduce maraviroc to 150mg twice/day in adult and pediatrics weighing 40kg or more. See full interaction monograph for dose adjustments in pediatrics weighing 10 to less than 40kg. Do not use if CrCl less than 30mL/min or in those weighing less than 10 kg. Consider therapy modification
MedroxyPROGESTERone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of MedroxyPROGESTERone. Monitor therapy
Meperidine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Meperidine. Monitor therapy
MetFORMIN: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of MetFORMIN. Specifically, the risk for lactic acidosis may be increased. Monitor therapy
Mexiletine: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Mexiletine. Monitor therapy
Midazolam: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Midazolam. Management: Oral midazolam contraindicated with antihepaciviral combination products. When used with intravenous midazolam, monitor for increased midazolam effects (eg, sedation, respiratory depression) and consider using a reduced midazolam dose. Avoid combination
Midostaurin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Midostaurin. Management: Seek alternatives to the concomitant use of midostaurin and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors if possible. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor patients for increased risk of adverse reactions. Consider therapy modification
MiFEPRIStone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of MiFEPRIStone. Management: For treatment of hyperglycemia in Cushing's syndrome, start mifepristone at 300 mg/day, may titrate to a maximum of 900 mg/day. If starting a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and taking >300 mg/day mifepristone, decrease the mifepristone dose by 300 mg/day. Consider therapy modification
MiFEPRIStone: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Minimize doses of CYP3A4 substrates, and monitor for increased concentrations/toxicity, during and 2 weeks following treatment with mifepristone. Avoid cyclosporine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, fentanyl, pimozide, quinidine, sirolimus, and tacrolimus. Consider therapy modification
Mirodenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Mirodenafil. Management: Consider using a lower dose of mirodenafil when used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Monitor for increased mirodenafil effects/toxicities with the use of this combination. Consider therapy modification
Mirtazapine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Mirtazapine. Monitor therapy
Mometasone (Oral Inhalation): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Mometasone (Oral Inhalation). Monitor therapy
Morphine (Systemic): P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Morphine (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Nadolol: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Nadolol. Monitor therapy
Naldemedine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Naldemedine. Monitor therapy
Nalfurafine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Nalfurafine. Monitor therapy
Naloxegol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Naloxegol. Avoid combination
Neratinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Neratinib. Avoid combination
Netupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Nilotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Nilotinib. Management: Avoid if possible. If combination needed, decrease nilotinib to 300 mg once/day for patients with resistant or intolerant Ph+ CML or to 200 mg once/day for patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML in chronic phase. Consider therapy modification
NiMODipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Avoid combination
Nintedanib: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Nintedanib. Monitor therapy
Nisoldipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Nisoldipine. Avoid combination
OLANZapine: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may decrease the serum concentration of OLANZapine. Monitor therapy
Olaparib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Olaparib. Management: Avoid use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with olaparib, if possible. If such concurrent use cannot be avoided, the dose of olaparib tablets should be reduced to 100 mg twice daily and the dose of olaparib capsules should be reduced to 150 mg twice daily. Consider therapy modification
Oliceridine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Oliceridine. Monitor therapy
Osilodrostat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Osilodrostat. Management: Reduce osilodrostat dose by 50% during coadministration with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Ospemifene: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ospemifene. Monitor therapy
Oxybutynin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Oxybutynin. Monitor therapy
Ozanimod: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ozanimod. Avoid combination
Palbociclib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Palbociclib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with palbociclib when possible. If the use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be avoided, decrease the palbociclib dose to 75 mg/day. Consider therapy modification
Panobinostat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Panobinostat. Management: Reduce the panobinostat dose to 10 mg when it must be used with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor patient response to therapy closely for evidence of more severe adverse effects related to panobinostat therapy. Consider therapy modification
Parecoxib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Parecoxib. Specifically, serum concentrations of the active moiety valdecoxib may be increased. Monitor therapy
Paricalcitol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Paricalcitol. Monitor therapy
PAZOPanib: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of PAZOPanib. Avoid combination
PAZOPanib: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of PAZOPanib. Avoid combination
Pemigatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pemigatinib. Management: If combined use cannot be avoided, reduce the pemigatinib dose from 13.5 mg daily to 9 mg daily, or from 9 mg daily to 4.5 mg daily. Resume prior pemigatinib dose after stopping the strong inhibitor once 3 half-lives of the inhibitor has passed. Consider therapy modification
Pimavanserin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pimavanserin. Management: Decrease the pimavanserin dose to 10 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Pimecrolimus: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease the metabolism of Pimecrolimus. Monitor therapy
Pimozide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pimozide. Avoid combination
Piperaquine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Piperaquine. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Piperaquine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of piperaquine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If the combination cannot be avoided, frequent ECG monitoring is recommended due to the risk for QTc prolongation. Consider therapy modification
Polatuzumab Vedotin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Polatuzumab Vedotin. Exposure to unconjugated MMAE, the cytotoxic small molecule component of polatuzumab vedotin, may be increased. Monitor therapy
PONATinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of PONATinib. Management: Reduce the adult starting dose of ponatinib to 30 mg daily during treatment with any strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Pralsetinib: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Pralsetinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use if possible. If combined, reduce the pralsetinib dose. If taking 400 mg or 300 mg once daily, reduce to 200 mg once daily. If taking 200 mg once daily, reduce to 100 mg once daily. Consider therapy modification
Pranlukast: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pranlukast. Monitor therapy
Pravastatin: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Pravastatin. Management: Limit the pravastatin dose to a maximum of 40 mg per day when used with antihepaciviral combination products and monitor patients for evidence of pravastatin toxicities (eg, myopathy). Consider therapy modification
Praziquantel: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Praziquantel. Monitor therapy
PrednisoLONE (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of PrednisoLONE (Systemic). Monitor therapy
PredniSONE: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of PredniSONE. Monitor therapy
Proguanil: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may decrease the serum concentration of Proguanil. Monitor therapy
Propafenone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Propafenone. Monitor therapy
Propafenone: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Propafenone. Management: Canadian labeling recommends avoiding this combination. Monitor therapy
QUEtiapine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of QUEtiapine. Management: In quetiapine treated patients, reduce quetiapine to one-sixth of regular dose after starting strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. In those on strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, start quetiapine at lowest dose and up-titrate as needed. Consider therapy modification
QuiNIDine: Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of QuiNIDine. Management: Canadian labeling recommends avoiding this combination. Monitor therapy
Quinidine (Non-Therapeutic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Quinidine (Non-Therapeutic). Monitor therapy
QuiNINE: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of QuiNINE. Avoid combination
Radotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Radotinib. Avoid combination
Ramelteon: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ramelteon. Monitor therapy
Ranolazine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ranolazine. Avoid combination
Red Yeast Rice: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Red Yeast Rice. Specifically, concentrations of lovastatin and related compounds found in Red Yeast Rice may be increased. Avoid combination
Regorafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Regorafenib. Avoid combination
Repaglinide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Repaglinide. Management: The addition of a CYP2C8 inhibitor to this drug combination may substantially increase the magnitude of increase in repaglinide exposure. Monitor therapy
Retapamulin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Retapamulin. Management: Avoid this combination in patients less than 2 years old. No action is required in other populations. Monitor therapy
Revefenacin: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Revefenacin. Avoid combination
Ribociclib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ribociclib. Management: Avoid use of ribociclib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible; if combined use cannot be avoided, reduce ribociclib dose to 400 mg once daily. Consider therapy modification
RifAXIMin: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of RifAXIMin. Monitor therapy
Rilpivirine: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Rilpivirine. Avoid combination
Rimegepant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Rimegepant. Avoid combination
Riociguat: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Riociguat. Management: Consider a riociguat starting dose of 0.5 mg 3 times a day when initiating riociguat in patients receiving strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitors. Monitor for hypotension when these agents are combined and reduce the riociguat dose as needed. Consider therapy modification
Riociguat: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and BCRP may increase the serum concentration of Riociguat. Management: Consider a riociguat starting dose of 0.5 mg 3 times a day when initiating riociguat in patients receiving strong CYP3A4 and BCRP inhibitors. Monitor for hypotension when these agents are combined and reduce the riociguat dose as needed. Consider therapy modification
Ripretinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ripretinib. Monitor therapy
RisperiDONE: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of RisperiDONE. Monitor therapy
Rivaroxaban: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Rivaroxaban. Avoid combination
RomiDEPsin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of RomiDEPsin. Monitor therapy
RomiDEPsin: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of RomiDEPsin. Monitor therapy
Rupatadine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Rupatadine. Avoid combination
Ruxolitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ruxolitinib. Management: This combination should be avoided under some circumstances; dose adjustments may be required in some circumstances and depend on the indication for ruxolitinib. See monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Sacituzumab Govitecan: UGT1A1 Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Sacituzumab Govitecan. Specifically, concentrations of SN-38 may be increased. Avoid combination
Salmeterol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Salmeterol. Avoid combination
Sarilumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
SAXagliptin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SAXagliptin. Management: Limit the saxagliptin dose to 2.5 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. When using the saxagliptin combination products saxagliptin/dapagliflozin or saxagliptin/dapagliflozin/metformin, avoid use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Selpercatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Selpercatinib. Management: Avoid combination if possible. If use is necessary, reduce selpercatinib dose as follows: from 120 mg twice/day to 40 mg twice/day, or from 160 mg twice/day to 80 mg twice/day. Consider therapy modification
Selumetinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Selumetinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use when possible. If combined, selumetinib dose reductions are recommended and vary based on body surface area and selumetinib dose. For details, see the full drug interaction monograph or selumetinib prescribing information. Consider therapy modification
Sibutramine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Sibutramine. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sibutramine. Monitor therapy
Sildenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sildenafil. Management: Use of sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension should be avoided with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. When used for erectile dysfunction, starting adult dose should be reduced to 25 mg. Maximum adult dose with ritonavir or cobicistat is 25 mg per 48 hours. Consider therapy modification
Silodosin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Silodosin. Avoid combination
Siltuximab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Simeprevir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Simeprevir. Avoid combination
Simvastatin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Simvastatin. Avoid combination
Sirolimus: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Sirolimus. Avoid combination
Solifenacin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Solifenacin. Management: Limit adult solifenacin doses to 5 mg daily and limit doses in pediatric patients to the recommended weight-based starting dose (and do not increase the dose) when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Sonidegib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sonidegib. Avoid combination
SORAfenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SORAfenib. Monitor therapy
Stiripentol: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Use of stiripentol with CYP3A4 substrates that are considered to have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided due to the increased risk for adverse effects and toxicity. Any CYP3A4 substrate used with stiripentol requires closer monitoring. Consider therapy modification
SUFentanil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SUFentanil. Management: If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is initiated in a patient on sufentanil, consider a sufentanil dose reduction and monitor for increased sufentanil effects and toxicities (eg, respiratory depression). Consider therapy modification
SUNItinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SUNItinib. Management: Avoid when possible. If combined, decrease sunitinib dose to a minimum of 37.5 mg daily when treating GIST or RCC. Decrease sunitinib dose to a minimum of 25 mg daily when treating PNET. Monitor patients for both reduced efficacy and increased toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Suvorexant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Suvorexant. Avoid combination
Tacrolimus (Systemic): Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Tacrolimus (Systemic). Avoid combination
Tacrolimus (Topical): Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Tacrolimus (Topical). Monitor therapy
Tadalafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tadalafil. Management: Avoid this combination in patients taking tadalafil for pulmonary arterial hypertension. In patients taking tadalafil for ED or BPH, max tadalafil dose is 2.5 mg if taking daily or 10 mg no more frequently than every 72 hours if used as needed. Consider therapy modification
Talazoparib: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Talazoparib. Monitor therapy
Talazoparib: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Talazoparib. Monitor therapy
Tamsulosin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tamsulosin. Avoid combination
Tasimelteon: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tasimelteon. Monitor therapy
Tazemetostat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tazemetostat. Avoid combination
Tegaserod: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Tegaserod. Monitor therapy
Temsirolimus: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Temsirolimus. Management: Avoid concomitant use of temsirolimus and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If coadministration is unavoidable, decrease temsirolimus dose to 12.5 mg per week. Resume previous temsirolimus dose 1 week after discontinuation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Terfenadine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Terfenadine. Avoid combination
Tetrahydrocannabinol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tetrahydrocannabinol. Monitor therapy
Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor. Management: If combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, tezacaftor/ivacaftor should be administered in the morning, twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. Tezacaftor/ivacaftor dose depends on age and weight; see full Lexi-Interact monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Thiotepa: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Thiotepa. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Thiotepa. Management: Thiotepa prescribing information recommends avoiding concomitant use of thiotepa and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If concomitant use is unavoidable, monitor for adverse effects and decreased efficacy. Consider therapy modification
Ticagrelor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ticagrelor. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ticagrelor. Avoid combination
Tocilizumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Tofacitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tofacitinib. Management: Tofacitinib dose reductions are recommended when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Recommended dose adjustments vary by tofacitinib formulation and therapeutic indication. See full Lexi Interact monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Tolterodine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tolterodine. Management: The maximum recommended dose of tolterodine is 2 mg per day (1 mg twice daily for immediate-release tablets or 2 mg daily for extended-release capsules) when used together with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Tolvaptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tolvaptan. Avoid combination
Topotecan: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Topotecan. Avoid combination
Topotecan: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Topotecan. Avoid combination
Toremifene: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Toremifene. Management: Use of toremifene with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors should be avoided if possible. If coadministration is necessary, monitor for increased toremifene toxicities, including QTc interval prolongation. Consider therapy modification
Trabectedin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Trabectedin. Avoid combination
TraMADol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of TraMADol. Monitor therapy
TraZODone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of TraZODone. Management: Consider the use of a lower trazodone dose and monitor for increased trazodone effects (eg, sedation, QTc prolongation) if combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Triamcinolone (Systemic): Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Triamcinolone (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Triamcinolone (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Triamcinolone (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Triazolam: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Triazolam. Avoid combination
Ubrogepant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ubrogepant. Avoid combination
Udenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Udenafil. Avoid combination
Ulipristal: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ulipristal. Management: This is specific for when ulipristal is being used for signs/symptoms of uterine fibroids (Canadian indication). When ulipristal is used as an emergency contraceptive, patients receiving this combo should be monitored for ulipristal toxicity. Avoid combination
Upadacitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Upadacitinib. Monitor therapy
Valbenazine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Valbenazine. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Valbenazine. Management: Reduce the valbenazine dose to 40 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Valsartan: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may increase the serum concentration of Valsartan. Management: Consider decreasing the valsartan dose and monitoring for evidence of hypotension and worsening renal function if these agents are used in combination. Consider therapy modification
Vardenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vardenafil. Management: Limit Levitra (vardenafil) dose to a single 2.5 mg dose within a 24-hour period if combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Avoid concomitant use of Staxyn (vardenafil) and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Combined use is contraindicated outside of the US. Consider therapy modification
Vemurafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vemurafenib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of vemurafenib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If concomitant use is unavoidable, consider a vemurafenib dose reduction if clinically indicated. Consider therapy modification
Venetoclax: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Venetoclax. Management: Coadministration is contraindicated during venetoclax initiation and ramp-up in CLL/SLL patients. Reduced venetoclax doses are required during ramp-up for patients with AML, and all maintenance therapy. See full Lexi Interact monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Venetoclax: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Venetoclax. Management: Reduce the venetoclax dose by at least 50% in patients requiring concomitant treatment with P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors. Resume the previous venetoclax dose 2 to 3 days after discontinuation of a P-gp inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Verapamil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Verapamil. Management: Consider alternatives to this combination when possible. If combined, monitor for increased verapamil effects and toxicities (eg, hypotension, bradycardia). Consider therapy modification
Vilanterol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vilanterol. Monitor therapy
Vilazodone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vilazodone. Management: Limit the maximum vilazodone dose to 20 mg daily in patients receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. The original vilazodone dose can be resumed following discontinuation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
VinBLAStine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of VinBLAStine. Monitor therapy
VinCRIStine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine. Management: Seek alternatives to this combination when possible. If combined, monitor closely for vincristine toxicities (eg, neurotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, myelosuppression). Consider therapy modification
VinCRIStine (Liposomal): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine (Liposomal). Avoid combination
VinCRIStine (Liposomal): P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine (Liposomal). Avoid combination
Vindesine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vindesine. Monitor therapy
Vinflunine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vinflunine. Avoid combination
Vinorelbine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vinorelbine. Monitor therapy
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Direct Acting Antiviral Agents (HCV) may diminish the anticoagulant effect of Vitamin K Antagonists. Monitor therapy
Vorapaxar: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vorapaxar. Avoid combination
Voriconazole: Antihepaciviral Combination Products may decrease the serum concentration of Voriconazole. Management: Concurrent use of voriconazole with antihepaciviral combination products should be avoided unless the patient-specific benefit/risk ratio justifies the use of voriconazole. Decreased efficacy of voriconazole is possible. Consider therapy modification
Voxelotor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Voxelotor. Management: Avoid concomitant use of voxelotor and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If concomitant use is unavoidable, reduce the voxelotor dose to 1,000 mg once daily. Consider therapy modification
Voxilaprevir: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Voxilaprevir. Avoid combination
Zanubrutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Zanubrutinib. Management: Decrease the zanubrutinib dose to 80 mg once daily during coadministration with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Further dose adjustments may be required for zanubrutinib toxicities, refer to prescribing information for details. Consider therapy modification
Zopiclone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Zopiclone. Management: If coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, initiate zopiclone at 3.75 mg in adults, with a maximum dose of 5 mg. Monitor for zopiclone toxicity (eg, drowsiness, confusion, lethargy, ataxia, respiratory depression). Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
The following adverse drug reactions and incidences are derived from product labeling unless otherwise specified.
>10%: Neuromuscular & skeletal: Asthenia (25%)
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Fatigue (7%), insomnia (5%)
Dermatologic: Allergic skin reaction (5%), pruritus (5%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (9%)
Frequency not defined:
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia, decreased hemoglobin
Hepatic: Increased serum alanine aminotransferase
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Anaphylaxis, erythema multiforme, hepatic failure (in patients with underlying cirrhosis; FDA Safety Alert, October 22, 2015), hypersensitivity reaction (including angioedema), liver decompensation (in patients with underlying cirrhosis; FDA Safety Alert, October 22, 2015), reactivation of HBV (FDA Safety Alert Dec. 8, 2016)
Related/similar drugs
Epclusa
Epclusa treats chronic hepatitis C in adults and children 3+. This once-daily antiviral combines ...
Harvoni
Harvoni is used to treat hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections in adults and children aged 3 years and ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Mavyret
Mavyret (glecaprevir/pibrentasvir) is an oral combination medicine containing fixed doses of two ...
Sovaldi
Sovaldi (sofosbuvir) is used to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Includes Sovaldi ...
Pegasys
Pegasys is used to treat chronic hepatitis B or C. Learn about side effects, interactions and ...
Vosevi
Vosevi (sofosbuvir,velpatasvir and voxilaprevir) is used to treat chronic hepatitis C. Includes ...
Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) is an oral combination medicine containing fixed doses of 2 ...
Interferon alfa-2b
Interferon alfa-2b systemic is used for angioblastoma, condylomata acuminata, conjunctival ...
ALERT: U.S. Boxed Warning
Hepatitis B virus reactivation:Test all patients for evidence of current or prior hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection before initiating treatment. HBV reactivation has been reported in hepatitis C virus (HCV)/HBV co-infected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV direct acting antivirals and were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy. Some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. Monitor HCV/HBV co-infected patients for hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during HCV treatment and post-treatment follow-up. Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated.
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
• Hepatic effects: Hepatic decompensation and hepatic failure, including liver transplantation and fatal cases, have been reported with ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir, with or without ribavirin; most patients had evidence of cirrhosis prior to treatment initiation. Typically occurs between 1 and 4 weeks of treatment initiation; characterized by acute elevation of direct bilirubin, without ALT elevation, and signs and symptoms of hepatic decompensation. Assess hepatic function (including direct bilirubin) prior to treatment initiation, during the first 4 weeks of starting treatment, and as clinically indicated; monitor patients with compensated cirrhosis for signs/symptoms of hepatic decompensation (eg, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, variceal hemorrhage). Discontinue treatment in patients who develop signs/symptoms of hepatic decompensation.
• Hepatic enzyme elevations: Elevations of ALT (>5 × ULN) have been reported. Elevations are usually asymptomatic, occur within 4 weeks of treatment initiation, and decline within 2 to 8 weeks with continued dosing. Monitor hepatic enzymes during the first 4 weeks of treatment initiation and thereafter as clinically indicated. If ALT is elevated, repeat testing and continue to monitor closely; inform patients to contact their health care provider immediately if fatigue, weakness, lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting, jaundice, or discolored feces occur. Consider discontinuation if ALT remains persistently >10 × ULN. Discontinue if ALT increase is accompanied by signs of hepatic inflammation, elevated direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, or INR. Women taking ethinyl estradiol products are at increased risk. For management of women taking concomitant estrogen products, refer to Reproductive Considerations.
Disease-related concerns:
• Diabetes: Rapid reduction in hepatitis C viral load during direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for hepatitis C may lead to improvement in glucose metabolism in patients with diabetes, potentially resulting in symptomatic hypoglycemia if antidiabetic agents are continued at the same dose. Monitor for changes in glucose tolerance and inform patients of the risk of hypoglycemia during DAA therapy, particularly within the first 3 months. Modifications of antidiabetic therapy may be necessary (Ciancio 2018; Dawood 2017; Hum 2017).
• Hepatic impairment: Use is contraindicated in moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C).
• Hepatitis B virus reactivation: [US Boxed Warning]: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported in hepatitis C virus (HCV)/HBV co-infected patients who were receiving or had completed treatment with HCV direct-acting antivirals and were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy; some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. Test all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection prior to initiation of treatment; monitor HCV/HBV co-infected patients for hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during treatment and post-treatment follow-up. Initiate treatment for HBV infection as clinically indicated. HBV reactivation has been reported in HBsAg positive patients and in patients with serologic evidence of resolved HBV infection (ie, HBsAg negative and anti-HBc positive) and is characterized by an abrupt increase in HBV replication manifested as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA level; reappearance of HBsAg may occur in patients with resolved HBV infection. Risk of HBV reactivation may be increased in patients receiving certain immunosuppressants or chemotherapeutic agents.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
• Concomitant therapy: Contraindications of ribavirin, particularly pregnancy avoidance warnings, also apply. See ribavirin prescribing information.
Other warnings/precautions:
• Risk of HIV-1 protease inhibitor drug resistance: Ritonavir, a component of the product, is also an HIV-1 protease inhibitor. In HCV/HIV co-infected patients, ritonavir can select for HIV-1 protease inhibitor resistance-associated substitutions. Any HCV/HIV-1 co-infected patients should also be taking a suppressive antiretroviral regimen to reduce resistance risk.
Monitoring Parameters
Baseline (within 12 weeks prior to treatment initiation) CBC, INR, hepatic function (albumin, total and direct bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase), calculated GFR; baseline (obtain any time prior to treatment initiation) hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype and subtype, quantitative HCV viral load. During treatment, monitor CBC, serum creatinine, calculated GFR, hepatic function panel (after 4 weeks of therapy and as clinically indicated); quantitative HCV viral load testing (after 4 weeks of therapy and at 12 weeks after completion of therapy). If quantitative HCV viral load is detectable at treatment week 4, repeat testing is recommended after 2 additional weeks of treatment (treatment week 6) (AASLD/IDSA 2018).
Hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core antibody prior to initiation; in patients with serologic evidence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, monitor for clinical and laboratory signs of hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during treatment and during posttreatment follow-up.
Reproductive Considerations
HCV-infected females of childbearing potential should consider postponing pregnancy until therapy is complete to reduce the risk of HCV transmission (AASLD/IDSA 2018).
Elevations of ALT (>5 × ULN) have been reported; women taking ethinyl estradiol products are at increased risk. Concurrent use of ethinyl estradiol-containing products such as contraceptives is contraindicated; these products may be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of HCV therapy. Alternative methods of contraception (eg, nonhormonal methods, progestin-only contraception) are recommended during therapy. Women using other estrogens (eg, estradiol, conjugated estrogens) had a rate of ALT elevation similar to patients not receiving any estrogens; coadminister with caution.
If used in combination with ribavirin, all warnings related to the use of ribavirin and contraception should be followed. Refer to the ribavirin monograph for additional information.
Pregnancy Considerations
Treatment of hepatitis C is not currently recommended to treat maternal infection or to decrease the risk of mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy (Tran 2016). When HCV infection is detected during pregnancy, treatment should be deferred until after delivery. Direct-acting antiviral medications should not be used in pregnant females outside of clinical trials until safety and efficacy information is available (SMFM [Hughes 2017]).
If used in combination with ribavirin, all warnings related to the use of ribavirin and pregnancy should be followed. Refer to the ribavirin monograph for additional information.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
• It is used to treat hepatitis C infection.
• This drug may be used with ribavirin. If you are also taking ribavirin, talk with the doctor about the risks and side effects that may happen.
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
• Nausea
• Loss of strength and energy
• Trouble sleeping
• Dizziness
• Headache
• Muscle pain
• Joint pain
WARNING/CAUTION: Even though it may be rare, some people may have very bad and sometimes deadly side effects when taking a drug. Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms that may be related to a very bad side effect:
• Mood changes
• Liver problems like dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin
• Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis like red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin (with or without fever); red or irritated eyes; or sores in mouth, throat, nose, or eyes
• Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a limited summary of general information about the medicine's uses from the patient education leaflet and is not intended to be comprehensive. This limited summary does NOT include all information available about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not intended to provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. For a more detailed summary of information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine, please speak with your healthcare provider and review the entire patient education leaflet.
Frequently asked questions
- What are the new drugs for the treatment of hepatitis C?
- What are the ingredient drugs in Technivie?
More about ombitasvir / paritaprevir / ritonavir
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: antiviral combinations
Patient resources
Other brands
Professional resources
Other brands
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.