Overactive Bladder
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is overactive bladder (OAB)?
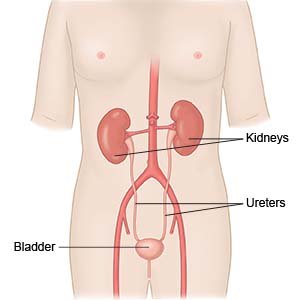
OAB is a sudden urge to urinate that is difficult for you to control. It occurs when the muscles of the bladder contract (tighten) more than normal. This causes a frequent or sudden need to urinate. You usually have to urinate more than 8 times in 24 hours. You may need to get up more than 1 time in the middle of the night to urinate. You may also leak urine before you are able to make it to the bathroom.
 |
What increases my risk for OAB?
Your risk increases as you get older. A past vaginal birth, chronic constipation, or diabetes increases your risk. Obesity, nerve injury, stroke, and spinal cord problems also increase your risk.
How is OAB diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and current medicines. Your provider will examine your pelvic area and abdomen to look for problems that may be causing your symptoms. Tell your provider how much liquid you drink each day. Any of the following may be used to confirm or rule out OAB:
- Urine tests may show an infection or other problem causing your symptoms.
- A cystoscopy is a procedure to look inside your urethra and bladder with a cystoscope. A cystoscope is a small tube with a light and magnifying camera on the end. Your healthcare provider may also do a ureteroscopy during a cystoscopy. A ureteroscopy is a procedure to look inside your ureters and kidneys.
- Cystometry is used to check the function of your urinary system. The pressure in your bladder is measured while it is filled with fluid. Your bladder pressure may also be tested when your bladder is full and while you urinate.
- X-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan pictures may show problems with parts of your urinary system. You may be given contrast liquid to help your urinary system show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI machine uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
Related medications
What can I do to manage OAB?
- Keep a record of when you urinate. Write down the number of times you urinate over 24 hours, the amount, and if you have urine leakage. Bring the record with you to follow-up appointments with your healthcare providers.
- Train your bladder. Go to the bathroom at set times, such as every 2 hours, even if you do not feel the urge to go. You can also try to hold your urine when you feel the urge to go. For example, hold your urine for 5 minutes when you feel the urge to go. As that becomes easier, hold your urine for 10 minutes. Work up to every 3 or 4 hours to help control your bladder.
- Limit liquids as directed. This may help decrease the amount you urinate. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Do not drink liquids several hours before you go to sleep. Limit caffeine and alcohol.
- Be physically active and maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Extra weight puts pressure on your bladder and may make your symptoms worse. Your provider can help you create a weight loss plan, if needed. The plan will include ways to be physically active that will not put extra pressure on your bladder.
- Do pelvic muscle exercises often. Your pelvic muscles help you stop urinating. Squeeze these muscles tightly for 5 seconds, then relax for 5 seconds. Gradually work up to squeezing for 10 seconds. Do 3 sets of 15 repetitions a day, or as directed. This will help strengthen your pelvic muscles and improve bladder control.
How is OAB treated?
The following treatments may be done if other methods are not working:
- Medicines may be given to relax your bladder or to stop your bladder from contracting on its own.
- Sacral nerve stimulation sends electrical signals to your sacral nerve through a small device implanted under your skin. Your sacral nerve controls your bladder, sphincter, and pelvic floor muscles.
- Surgery may be used to widen your urethra. If you have severe OAB, urinary diversion may be needed. This is surgery to remove the bladder and create a new way for urine to leave your body.
- An indwelling catheter may be placed if you cannot use other ways to treat OAB. The catheter goes through your urethra and into your bladder. Urine flows through the catheter and collects in a container you will empty when it is full. An indwelling catheter stays in place at all times.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
When should I call my doctor or urologist?
- Your urine is pink, or you notice blood in your urine.
- You have pain when you urinate.
- You continue to have symptoms even after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Overactive Bladder
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
