Right Hemispheric Stroke
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
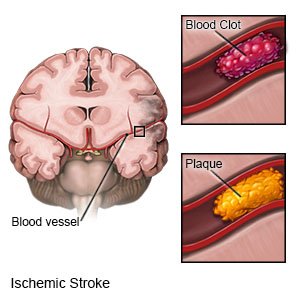
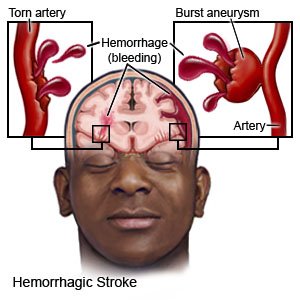
A right hemispheric stroke happens when blood cannot flow to the right hemisphere (side) of your brain. A stroke caused by a blood clot is called an ischemic stroke. A stroke caused by a burst or torn blood vessel is called a hemorrhagic stroke. A stroke is a medical emergency that needs immediate treatment.
 |
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
You may need extra oxygen
if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
Medicines:
- Medicines may help improve your blood's ability to clot and stop the bleeding. You may instead need medicine to break up blood clots, or to prevent them from forming. Examples include blood thinners and low-dose aspirin. Healthcare providers will talk to you or your family members about the risks and benefits of each medicine.
- Blood pressure medicines help prevent or treat high blood pressure.
- Statins help lower cholesterol levels.
- Diabetes medicines may be needed to control your blood sugar level.
Tests:
- CT or MRI pictures may show where the stroke happened and any damage you have. You may be given contrast liquid to help your skull and brain show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- An arteriography is used to take x-rays of your arteries to look for blood flow blockage.
- Blood tests may be needed while you are being treated for your stroke. These tests can tell healthcare providers if you are getting the right amount of medicine.
- A carotid ultrasound uses sound waves to show the blood flow in your carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are blood vessels in your neck that carry blood to your brain. A carotid ultrasound checks for narrow or blocked carotid arteries.
- A swallow study is used to take x-rays as you swallow certain foods and drinks. This test shows if food and liquids travel to your stomach correctly.
Monitoring:
- A neuro exam may show how well your brain works after a stroke. Healthcare providers will check how your pupils react to light. They may check your memory and how easily you wake up. Your hand grasp and balance may also be tested.
- An ICP monitor measures the pressure inside your skull. A small tube is put through your skull and connected to a screen.
Treatment:
- A ventilator is a machine that gives you oxygen and breathes for you when you cannot breathe well on your own. An endotracheal (ET) tube is put into your mouth or nose and attached to the ventilator. You may need a trach if an ET tube cannot be placed. A trach is a tube put through an incision and into your windpipe.
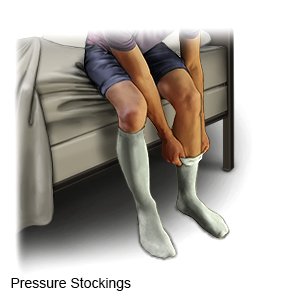
- Pressure stockings or inflatable boots may be needed. The stockings are tight and put pressure on your legs. The boots have an air pump that tightens and loosens different areas of the boots. This improves blood flow and helps prevent clots.
- Therapy can help you recover speech and movement abilities. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. An occupational therapist teaches you skills to help with your daily activities. A speech therapist helps you with speaking and safe swallowing skills. You will continue rehabilitation therapy after you leave the hospital.
- A feeding tube may be needed if you cannot swallow food or liquids.
- Thrombolysis is a procedure used to break apart clots in an artery. A catheter is guided into the artery until it is near the clot. Medicine is put through the catheter that will help break apart the clot. The clot may be pulled out of the artery during the procedure.
- Surgery may be used to remove a blood clot or to relieve pressure within your brain. You may also need surgery to remove plaque buildup from your carotid arteries.
RISKS:
Even with treatment, you may have lasting problems talking, thinking, or moving your body.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
