Liver Disease Diet
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is a liver disease diet?
A liver disease diet provides the right amount of calories, nutrients, and liquids you need to manage liver disease. Liver diseases, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, may change the way your body uses nutrients from food. Some people with liver disease may not get enough nutrients and lose weight. Your dietitian will work with you to create a meal plan based on the type of liver disease you have.
 |
Which nutrients should I include?
It is important to eat a variety of foods from all the food groups each day to stay at a healthy weight. You may not feel hungry, or you may feel full right away after you eat. Eat 4 to 6 small meals throughout the day to make sure you eat enough calories. Ask your dietitian how many calories and how much of the following nutrients you should have each day:
- Protein is important for helping you keep muscle mass. The following foods are good sources of protein. The amount of protein (in grams) follows each food listed below:
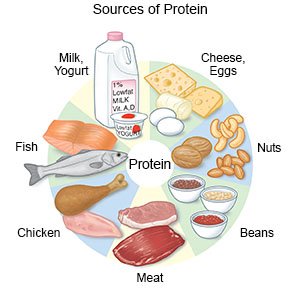
- 3 ounces of meat, pork, turkey, chicken, or fish (21 grams)
- 1 cup of milk or yogurt (8 grams)
- 1 large egg (7 grams)
- 2 tablespoons of peanut butter (7 grams)
- ½ cup of tofu (7 grams)
- ¼ cup of cottage cheese (7 grams)
- 1 ounce of cheese (7 grams)
- ½ cup of cooked pinto, kidney, or navy beans (3 grams)
- Fat can be hard to digest for some people with liver disease. The fat that is not digested is eliminated in bowel movements. If you have this health problem, you may need to eat less fat. Ask your healthcare provider or dietitian for more information about a low-fat diet.
- Carbohydrates (carbs) may need to be limited because they affect blood sugar levels. Liver disease may cause blood sugar levels to be too high or too low in some people. Carbs are found in bread, pasta, rice, cereal, grains (rice, oats), and starchy vegetables (potatoes, corn, peas). Your dietitian can help you create meal plans that have the right amount of carbs for you.
Related medications
What foods should I limit or avoid?
Ask your dietitian if you need to limit or avoid some foods. This will depend on the type of liver disease and other health problems you have.
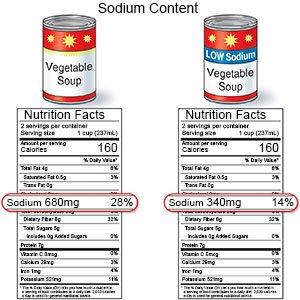
- Sodium may need to be lowered if your body is retaining fluids. When you retain fluids, you will have swelling in your body. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about a low-sodium diet. Some foods that contain high amounts of sodium:
- Table salt
- Bacon, sausage, and deli meats
- Canned vegetables and vegetable juice
- Frozen dinners and packaged snack foods, such as potato chips and pretzels
- Soy, barbecue, and teriyaki sauces
- Soups
- Liquids may need to be limited if you have swelling. Liquids include water, milk, juice, soda, and other beverages. Some foods contain liquid, such as soup. Foods that are liquid at room temperature, such as gelatin or popsicles, must also be counted as a liquid. Ask your dietitian how much liquid you may drink each day.
- Alcohol may make your liver disease worse. It is important for you not to drink alcohol. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions about alcohol or need help to quit drinking.
What other diet guidelines should I follow?
Your healthcare provider may ask you to take a vitamin and mineral supplement. Take only the supplement that your healthcare provider recommends. Liver disease may cause health problems that you can manage through certain diet changes. Talk to your dietitian about any other changes you need to make in your diet.
When should I call my doctor or dietitian?
- You gain or lose a lot of weight within a short amount of time.
- You have questions or concerns about the liver disease diet.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
