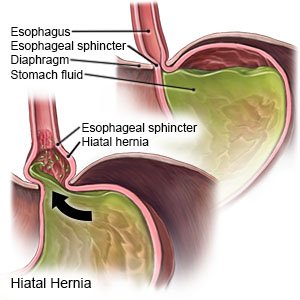
Hiatal Hernia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
A hiatal hernia is a condition that causes part of your stomach to bulge through the hiatus (small opening) in your diaphragm. The part of the stomach may move up and down, or it may get trapped above the diaphragm.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Nutrition:
A dietitian may talk to you about foods you should avoid to manage heartburn. If you continue to have trouble swallowing, a swallowing therapist may teach you a safer way to swallow. The swallowing therapist will also tell you which foods and liquids are safe to eat and drink.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
Medicines:
- Antacids decrease stomach acid that can irritate your esophagus and stomach.
- A histamine type-2 receptor blocker (H2-blocker) help reduce the amount of acid made in the stomach.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) block acid from being made in the stomach.
- Promotility agents help to tighten the esophageal sphincter.
Tests:
- An upper GI series test includes x-rays of your esophagus, stomach, and your small intestines. It is also called a barium swallow test. You will be given barium (a chalky liquid) to drink before the pictures are taken. This liquid helps your stomach and intestines show up better on the x-rays. An upper GI series can show if you have an ulcer, a blocked intestine, or other problems.
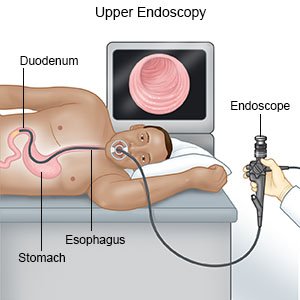
- An endoscopy uses a scope to see the inside of your esophagus and stomach. A scope is a long, bendable tube with a light on the end. A camera may be hooked to the scope to take pictures.
- Esophageal manometry measures the pressure within the esophagus and stomach.
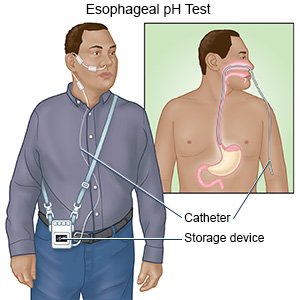
- Esophageal pH monitoring measures the amount of stomach acid that enters your esophagus. A small probe is placed inside the esophagus to check the pH level. The pH level measures how acidic or alkaline (basic) something is. The probe may stay attached to the catheter. If so, the catheter is taped to your nose to hold it in place. Sometimes the probe is wireless, so the catheter is removed after the probe is placed.
Treatment:
Surgery may be done when medicines cannot control your symptoms, or other problems are present. Your healthcare provider may also suggest surgery depending on the type of hernia you have. A surgeon can put your stomach back into its normal location. The surgeon may make the hiatus (hole) smaller and anchor your stomach in your abdomen. Fundoplication is a surgery that wraps the upper part of the stomach around the esophageal sphincter to strengthen it.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- omeprazole
- famotidine
- lansoprazole
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide/simethicone
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium trisilicate
RISKS:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) caused by a hiatal hernia may lead to ulcers and bleeding in the esophagus. The hiatal hernia may also slide into your chest, get trapped, and not slide back into your abdomen. The tissue from the part of your stomach that is trapped may die if its blood supply is cut off. You may also have sudden severe chest pain and problems swallowing. This may lead to other serious health problems.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hiatal Hernia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
