Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD)?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is an infection caused by a virus. HFMD is easily spread from person to person through direct contact. Anyone can get HFMD, but it is most common in children younger than 5 years.
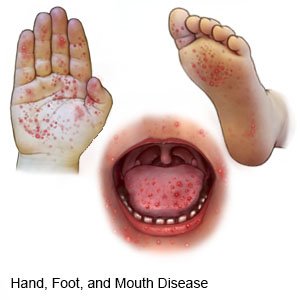 |
What are the signs and symptoms of HFMD?
The following may appear 3 to 7 days after infection and normally go away within 7 to 10 days:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Lack of appetite
- A rash, sores, or painful red blisters in or around the mouth, throat, hands, feet, or diaper area
How is HFMD diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can usually diagnose HFMD by examining you. Tell him or her if you have been near anyone who has HFMD. A provider may also swab your throat or nose, or collect a sample of your bowel movement. These samples will be sent to a lab to test for a virus that causes HFMD.
How is HFMD treated?
HFMD usually goes away on its own without treatment. The following can help you feel more comfortable until your symptoms go away:
- Drink extra liquids, as directed. Liquid will hep prevent dehydration. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day, and which liquids are best for you.
- Have foods and liquids that are easy to swallow. Examples include cold foods such as popsicles, smoothies, or ice cream. Do not have sodas, hot drinks, or acidic foods such as tomato sauce or orange juice.
- Medicines may help decrease a fever or pain. Your healthcare provider will tell you which medicines to use, and how long to use them. Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Aspirin can cause a life-threatening condition called Reye syndrome.
How do I prevent the spread of HFMD?
You can spread the virus for weeks after your symptoms have gone away. The following can help prevent the spread of HFMD:
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water. Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a child's diapers, or sneeze. Wash your hands before you prepare or eat food.

- Stay home from work or school while you have a fever or open blisters. Do not kiss, hug, or share food or drinks.
- Wash all items and surfaces with diluted bleach. This includes toys, tables, counter tops, and door knobs.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have trouble breathing, are breathing very fast, or you cough up pink, foamy spit.
- You have a high fever and your heart is beating much faster than it usually does.
- You have a severe headache, stiff neck, and back pain.
- You become confused and sleepy.
- You have trouble moving, or cannot move part of your body.
- You urinate less than normal or not at all.
When should I call my doctor?
- Your mouth or throat are so sore you cannot eat or drink.
- Your fever, sore throat, mouth sores, or rash do not go away after 10 days.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
