Gestational Diabetes Diet
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 10, 2025.
What is a gestational diabetes diet?
A gestational diabetes diet is a meal plan that helps control your blood sugar levels throughout your pregnancy. Too much carbohydrate in one meal or snack can cause your blood sugar to rise to a very high level. High blood sugar levels throughout your pregnancy can cause your baby to gain too much weight and lead to other health problems. A healthy meal plan will help you keep your blood sugar within the recommended range.
Which meal plan is right for me?
Carbohydrate counting and diabetes exchanges are meal planning methods that can help you control your blood sugar levels. Your dietitian or healthcare provider will tell you the amount of calories, carbohydrate, and other nutrients you need each day. The amounts depend on your activity levels and if you use insulin. Your dietitian or provider will tell you how many servings of each you can have during meals and snacks. He or she can also help you find the meal plan that meets your nutrient needs and that works best for you.
What are some general carbohydrate guidelines I should follow?
Your healthcare provider may recommend the following:
- Choose complex carbohydrates as often as possible. Examples include beans, vegetables, and grains, such as brown rice. All carbohydrates break down into glucose, but complex carbohydrates break down slowly than simple carbohydrates. Your blood sugar level rises more slowly after complex carbohydrates. Limit simple carbohydrates. Examples include table sugar, honey, and milk sugar (lactose).
- Spread carbohydrates throughout the day. Try eating 3 small to medium meals and 2 to 4 snacks. You may need to eat a snack in the evening to prevent low blood sugar during the night. Eat the same amount of carbohydrate during meals and snacks each day.
- Eat fewer servings of carbohydrate at breakfast than at other meals. The blood sugar level tends to be higher in the morning. Eat fewer servings of carbohydrate to keep your blood sugar level from increasing even more.
- Do not skip meals or cut out carbohydrates to control your blood sugar level. Your blood sugar can fall to a level that is too low to be safe.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Tresiba
Tresiba (insulin degludec) is used to treat diabetes mellitus. Includes Tresiba side effects ...
Levemir
Levemir (insulin detemir) is a long acting insulin used to treat diabetes in adults and children ...
Insulin detemir
Insulin detemir is used to control high blood sugar in adults and children with diabetes mellitus ...
Insulin degludec
Insulin degludec (Tresiba) is a long-acting basal human insulin analog that is used to improve ...
Which foods contain carbohydrates?
One serving of the foods below contains about 15 grams of carbohydrate.
- Breads, cereals, and crackers:
- 1 slice of bread, 1 6-inch tortilla, or ¼ large bagel
- ½ cup of oatmeal
- ½ hamburger, hot dog bun, or English muffin
- 2 taco shells (5-inch size)
- 4 to 6 small crackers or ¾ ounce of pretzels or potato chips
- Pasta, rice, starchy vegetables, and beans:
- ⅓ cup of cooked pasta or rice
- ½ cup of casserole
- ½ cup of pinto beans, black beans, or split peas
- ½ cup of corn, green peas, potatoes, or winter squash
- ¼ of a large baked potato
- Fruit:
- 1 small fresh fruit, such as an apple, orange, or peach
- ½ cup of unsweetened fruit juice, canned fruit, or frozen fruit
- 2 tablespoons of dried fruit
- Milk and yogurt:
- 1 cup of fat-free or low-fat milk or soy milk
- ⅔ cup (6 ounces) of fat-free yogurt sweetened with sugar-free sweetener
- Desserts or sweets:
- 2 small cookies
- ½ cup of ice cream or frozen yogurt
- 1 tablespoon syrup, jam, jelly, table sugar, or honey
What other guidelines should I follow?
- Check your blood sugar level as directed. Ask your healthcare provider when and how often to check your level during the day. Write down your blood sugar level each time you check it. You may need to bring this information to follow-up visits.
- Talk to your providers about the amount of weight you should gain. The amount depends on your weight when you became pregnant. Your providers can help you make a plan to gain a healthy amount of weight during pregnancy.
- Get physical activity as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, can help keep your blood sugar within the recommended levels. Physical activity can also keep your weight in a healthy range during pregnancy. Talk to your healthcare provider about the type and amount of physical activity that is best for you.
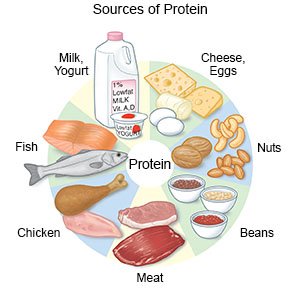
- Choose healthy sources of protein. Examples include lean meat, fish, poultry (such as chicken and turkey), eggs, cooked beans, and nuts.
- Choose foods that are good sources of fiber. Examples include fruits, vegetables, legumes, such as kidney beans and lentils, and whole-grain breads and cereals. Choose cereals with 5 or more grams of fiber per serving.

- Limit sweets and desserts. These foods are high in sugar, fat, and calories and low in healthy nutrients.
- Choose foods that contain healthy fats:
- Unsaturated fats include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Unsaturated fat is found in foods such as soybean, canola, olive, corn, and safflower oils. It is also found in soft tub margarine that is made with liquid vegetable oil.
- Omega-3 fat is found in certain fish, such as salmon, tuna, and trout, and in walnuts and flaxseed. Eat fish high in omega-3 fats at least 2 times a week.

- Drink liquids as directed. Drink water throughout the day to prevent dehydration. Do not have liquids that are high in sugar or calories. Ask your provider about drinks that contain artificial (no sugar) sweeteners. Your provider may tell you to limit the amount you have. Artificial sweeteners help you get fewer calories and carbohydrates but need to be used in moderation. Your provider can give you more information.
When should I call my doctor or dietitian?
- Your blood sugar levels continue to be high, even though you are following your meal plan.
- You have a low blood sugar level during certain times of the day.
- You have questions or concerns about your meal plan, or you are having trouble following the plan.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
