Foot Sprain
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is a foot sprain?
A foot sprain happens when a ligament stretches or tears. Ligaments connect bones, support joints, and keep bones in place.
What are the signs and symptoms of a foot sprain?
- Trouble moving your ankle or foot
- Pain when you touch or put weight on your foot
- Bruised, swollen, tender, or misshapen foot
How is a foot sprain diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your injury and examine you. Your provider will check the movement and strength of your foot. Contrast liquid may be given before x-ray or MRI pictures are taken. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- X-ray pictures may show the sprain or an injury in your foot.
- An MRI may show what is causing the sprain. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell a healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is a foot sprain treated?
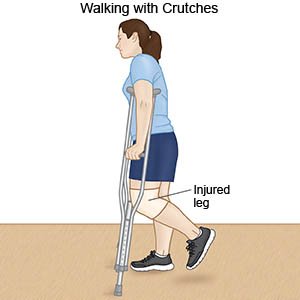
- Support devices , such as a brace, cast, or splint, may be needed to limit your movement and protect your joint. You may need to use crutches to decrease your pain as you move around.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
How can I manage my foot sprain?
- Rest your foot. Limit movement in your sprained foot for the first 2 to 3 days. You may need crutches to take weight off your injured foot as it heals. Use crutches as directed.
- Apply ice on your foot to decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you apply it to your foot. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed.
- Compress your foot. You may need to use tape or an elastic bandage to support your foot if you have a mild sprain. You may need a splint on your foot for support if your sprain is severe. Wear your splint for as many days as directed.
- Elevate your foot above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your foot on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably.

- Go to physical therapy, if directed. A physical therapist can teach you exercises to help restore strength and increase the range of motion in your foot. Ask your provider when you can return to your normal activities or play sports.
How can I prevent another foot sprain?
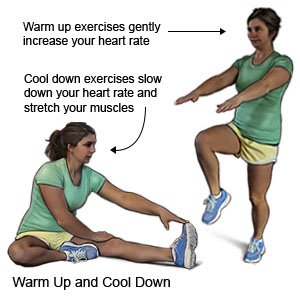
- Warm up and stretch before you exercise or play sports. This helps your joints become strong and flexible.
- Use the right equipment. Always wear shoes that fit well and are made for the activity that you are doing. You may also need ankle supports, elbow and knee pads, or braces.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have numbness or tingling below the injury, such as in your toes.
- The skin on your injured foot is blue or pale.
- You have increased pain, even after you take pain medicine.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have new weakness in your foot.
- You have new or increased swelling in your foot.
- You have new or increased stiffness when you move your injured foot.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
