Clotting Disorders during Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 7, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about clotting disorders during pregnancy:
Pregnancy increases your risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE). A VTE is a blood clot (thrombus) that has formed in a vein. A VTE can form anywhere in your body and block blood flow. A VTE in the deep veins in the calfs, thighs, pelvis, or arms is called a deep venous thrombosis (DVT). A piece of the clot may break loose. This is called an embolus. The embolus can travel to your lungs and cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism (PE). The 6 weeks after delivery is also a period of increased risk. A condition with abnormal clotting of your blood (thrombophilia) can develop on its own. It can also be inherited. Thrombophilia also increases your risk of VTE. Thrombophilia puts you at risk for problems during pregnancy such as preeclampsia and miscarriage.
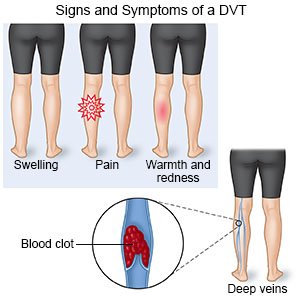
Signs and symptoms of a VTE or DVT:
Your symptoms will depend on the location of the clot. You may have any of the following:
- Swelling
- Redness
- Warmth, pain, or tenderness
 |
Signs and symptoms of a PE:
- Sudden shortness of breath or fast breathing
- Sudden chest pain that is worse when you take a deep breath
- Fast heartbeat
- Fever and coughing up blood
- Bluish nails
- Cold, pale, clammy skin
- Fainting
Call or have someone call your local emergency number (911) in the US if:
- You have sudden shortness of breath.
- You have chest pain that gets worse with a deep breath.
- You are lightheaded or you pass out.
- You have bleeding that does not stop after 10 minutes of holding pressure on the area.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have signs of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal spotting or heavy bleeding
- Pain or cramping in your abdomen or lower back
- Discharge of bloody fluid, tissue, or blood clots from your vagina
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness
Call your doctor or obstetrician if:
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for clotting disorders
may include anticoagulant medicines such as heparin used throughout your pregnancy. You may also need the medicine for a short time after you give birth.
Prevent blood clots:
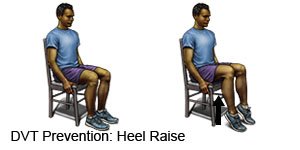
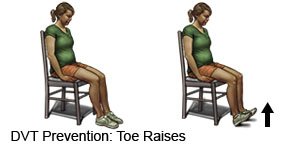
- Change your body position or move around often. Move and stretch in your seat several times each hour if you travel by car or work at a desk. In an airplane, get up and walk every hour. Move your legs by tightening and releasing your leg muscles while sitting. You can move your legs while sitting by raising and lowering your heels. Keep your toes on the floor while you do this. You can also raise and lower your toes while keeping your heels on the floor.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider how much weight you should gain during pregnancy. Ask him or her to help you create a food plan to help you stay within his or her guidelines.
- Drink plenty of liquids. Liquids help keep blood vessels working properly. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Do not drink caffeine or alcohol. Blood vessels become narrow with caffeine and alcohol. Narrowed vessels increase your risk for blood clots. Your baby can have problems if you drink alcohol while you are pregnant.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to prevent a blood clot. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
Follow up with your doctor or obstetrician as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
