Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) surgery?
CTS surgery, or decompression, is used to take pressure off the median nerve in your wrist. The median nerve controls muscles and feeling in the hand. Surgery may be done through an opening on your palm. This is called open surgery. Your surgeon may instead put a scope and tools into 1 or 2 small incisions on your wrist or palm. This is called endoscopic surgery.
How do I prepare for CTS surgery?
- Your surgeon will tell you how to prepare for surgery. He or she may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your surgery. Arrange to have someone drive you home after surgery.
- Tell your surgeon all the medicines you currently take. He or she will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for surgery, and when to stop. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of surgery.
- Tell your surgeon about any allergies you have, including to anesthesia or medicines. You may get antibiotics before surgery to prevent an infection. Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to antibiotics.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
L-Carnitine
L-Carnitine is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Repatha
Repatha (evolocumab) is a PCSK9 inhibitor used to lower high cholesterol alongside dietary changes ...
Carnitor
Carnitor is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Carnitor SF
Carnitor SF is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Phenytoin
Phenytoin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. Learn about side effects ...
Capsaicin topical
Capsaicin information from Drugs.com, includes Capsaicin side effects, interactions and indications.
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is used to treat epileptic seizures and nerve pain such as trigeminal neuralgia ...
Levocarnitine
Levocarnitine systemic is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Pregabalin
Pregabalin may be used to treat certain types of pain and used in combination with other ...
What will happen during CTS surgery?
- You may be given local or regional anesthesia to help prevent pain during surgery. Local anesthesia will make only your wrist numb. Regional anesthesia will make your wrist, hand, and arm numb. You may instead be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain. You may need this anesthesia if your surgeon thinks surgery will take a long time or involve a large part of your wrist.
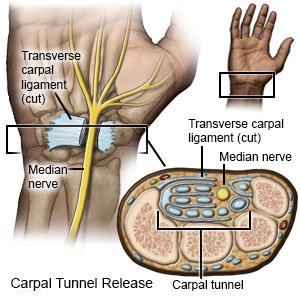
- For open surgery, your surgeon will make an incision on the palm of your hand. The incision may extend to your wrist. A ligament will be cut to release the pressure on the nerve. This ligament is a band of tissue that connects joints in your wrist. Your surgeon may also remove scar tissue or anything else that may be pressing on the nerve.
- For endoscopic surgery, your surgeon will make 1 or 2 incisions on your wrist or palm. He or she will insert the endoscope with the camera through an incision to help guide him or her during surgery. Tools may be put in your wrist to help protect the nerves. Your surgeon will then cut the ligament that is pressing on the nerve.
- The incision will be closed with stitches and covered with bandages.
 |
What should I expect after CTS surgery?
You will be taken to a room where you will rest until you are fully awake and gain feeling in your arm. Do not try to get out of bed until your provider says it is okay.
- A splint may be placed on your wrist to keep it from moving. Your healthcare provider may ask you to move your fingers soon after your surgery.
- Your provider will show you how to keep your hand elevated (raised) above the level of your heart. This helps prevent or relieve pain and swelling. You will need to continue to elevate your hand throughout the day at home. Your provider will tell you how often to do this, and for how many days.
- You may need to return in about 10 days to have stitches removed.
- Pain or numbness in your hand may get better quickly or continue for weeks or months.
- Your provider will tell you activities you can do or need to avoid. This depends on which hand needed surgery. Surgery on your dominant hand will take longer to heal.
What are the risks of CTS surgery?
You may bleed more than expected or get an infection. Your skin may bruise. A thick, painful scar may form where you had surgery. You may develop trigger finger (fingers locked in a bent position). Surgery may cause long-term numbness or weakness in your fingers, hand, or wrist. Your symptoms may not go away, and you may need surgery again.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
