Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) surgery, or decompression, is used to take pressure off the median nerve in your wrist. Your wrist may be painful or numb for up to a few months. You will need to limit certain hand activities for weeks to months after surgery. You may need to wear a splint to protect your wrist and help limit movement. This depends on the kind of surgery you had. Your healthcare provider will tell you if you need a splint.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- Your stitches come apart.
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- You cannot feel or move your hand or fingers.
- You feel a lump in your wrist.
Call your doctor or hand specialist if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- You feel weak or achy.
- You have pain, even after you take medicine.
- You have swelling or numbness in your fingers that continues longer than you were told to expect.
- Your finger becomes stuck in the same position.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
L-Carnitine
L-Carnitine is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Rexulti
Rexulti (brexpiprazole) is a prescription antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of major ...
Carnitor
Carnitor is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Carnitor SF
Carnitor SF is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Phenytoin
Phenytoin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. Learn about side effects ...
Capsaicin topical
Capsaicin information from Drugs.com, includes Capsaicin side effects, interactions and indications.
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is used to treat epileptic seizures and nerve pain such as trigeminal neuralgia ...
Levocarnitine
Levocarnitine systemic is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Pregabalin
Pregabalin may be used to treat certain types of pain and used in combination with other ...
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help prevent or fight a bacterial infection.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Apply ice to your wrist. Ice helps decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel. Place it on your wrist for 15 to 20 minutes every hour, or as directed.
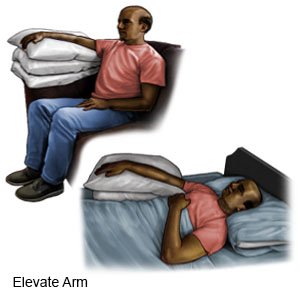
- Keep your hand elevated (raised) while you sleep after surgery. Prop your arm on pillows to keep your hand elevated comfortably. Your healthcare provider may tell you to do this for the first week after surgery. You may need to elevate your arm several times a day. This helps decrease pain and swelling.
- Wear your splint, if directed. Your healthcare provider will tell you when to wear it, and for how many days. Keep moving your fingers while you wear the splint.
- Limit activity as directed. Do not pull, lift, or move heavy objects until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Ask when you can return to work, drive, or play contact sports. Take time to rest your hand. If you work on a computer, rest your hand often.
- Go to physical or occupational therapy, if directed. A physical therapist can teach you exercises to help improve movement and strength. Physical therapy can also help decrease pain and loss of function. An occupational therapist can help you find ways to do work and other activities to reduce strain on your wrist.
Follow up with your doctor or hand specialist as directed:
You may need to return about 10 days after surgery to have your stitches taken out. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
