Blood Thinners
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Feb 9, 2025.
Blood thinners are medicines that prevent blood clots from forming in an artery, vein, or the heart. These medicines may also prevent a blood clot from getting bigger. Blood clots prevent the flow of blood to organs and tissues such as the heart or a leg. The 2 main types of blood thinners are antiplatelet medicine and anticoagulant medicine. Antiplatelet medicine prevents platelets from sticking together and forming a clot. Anticoagulant medicine prevents the blood from clotting too much.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You are bleeding from a wound or skin injury and it will not stop after holding pressure for 10 minutes.
- You have a fall or injury to the head.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a bad stomachache or headache that does not go away.
- You feel weak, faint, or dizzy.
- You vomit blood.
- You have a fall or injury to any part of your body other than your head.
- You are pregnant or think you may be pregnant.
Call your doctor if:
- Your urine is red or dark brown.
- Your bowel movements are red, dark brown, or black.
- You bleed more than usual during your period.
- You find bruises or blood blisters on your skin.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or you have a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Eliquis
Eliquis (apixaban) is used to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with ...
Xarelto
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a factor Xa inhibitor used to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke in ...
Revatio
Revatio (sildenafil) is used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension. Includes Revatio side ...
Coumadin
Coumadin is used to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clots in veins and arteries. Learn ...
Letairis
Letairis is used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adults. It improves your ability ...
Tadalafil
Tadalafil increases blood flow to particular areas of the body and is used to treat erectile ...
Enoxaparin
Enoxaparin systemic is used for acute coronary syndrome, angina, deep vein thrombosis, deep vein ...
Sotalol
Sotalol is a beta-blocker with antiarrhythmic properties that affects the heart and circulation ...
Carvedilol
Carvedilol (Coreg) is used to treat heart failure and hypertension (high blood pressure). Includes ...
Flecainide
Flecainide systemic is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular ...
Foods and medicines to avoid:
Do not start any new medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements before you talk to your healthcare provider. Do not make changes to your diet without talking to your provider. Many medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements may prevent blood thinners from working correctly. Ask your provider for a full list of foods and medicines to avoid. The following may cause severe bleeding, or prevent anticoagulants from working correctly:
- Alcohol may increase your risk for bleeding when taken with anticoagulants. Do not drink alcohol unless your provider says it is okay.
- Changes in your regular vitamin K intake can prevent warfarin from working correctly. Warfarin works best if you eat the same amount of vitamin K every day. Some foods that contain vitamin K include spinach, kale, broccoli, romaine lettuce, collard greens, and kiwi. Ask your provider for more information about foods that contain vitamin K.

- NSAIDs may increase your risk for bleeding. Examples include ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen. Do not take these medicines unless your provider says it is okay.
- Some antibiotics may increase your risk for bleeding. Talk to your provider before you take antibiotics.
- Alternative medicines such as ginkgo biloba, garlic, chamomile, and St. John's wort, should not be taken with anticoagulants. Some may prevent anticoagulants from working, and others may increase your risk for bleeding.
Self-care:
- Do not play contact sports. This may increase your risk for bleeding if you get injured or hit. Walk, swim, or do yoga to get exercise. Ask your healthcare provider about other exercises that are safe.
- Use an electric razor to shave. This may prevent cuts that could bleed.
- Use a soft bristled tooth brush and wax floss. This may prevent bleeding from your gums.
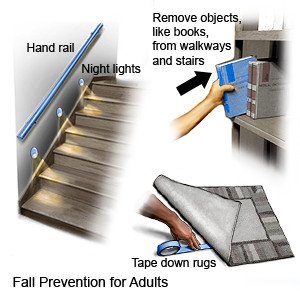
- Prevent falls in and out of your home. Wear non-slip shoes or slippers when you are out of bed. Keep walkways clear. Remove throw rugs and other objects that can cause you to trip and fall. Use assistive devices as directed.
- Be careful with sharp objects. Wear gloves when you work outside with sharp tools or in the garden.
- Use contraception to prevent a pregnancy. Anticoagulants can cause problems with your baby, and dangerous bleeding during pregnancy.
- Carry your medicine with you when you travel. This will prevent you from missing a dose of medicine if your bag gets lost. Talk to your provider before you travel.
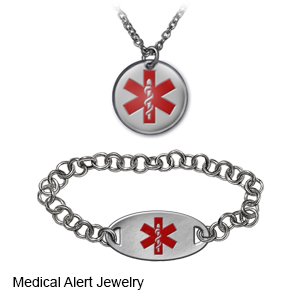
- Wear or carry a medical alert bracelet or necklace at all times. This will alert healthcare providers that you take an anticoagulant if you are unconscious or need emergency medical treatment.
Other important information:
- Tell all of your healthcare providers and dentist that you take a blood thinner. This will help them plan for procedures and surgeries. It will also prevent them from giving you medicine that may interact with your blood thinner.
- You should not take antiplatelet medicine if you have liver or kidney disease, a peptic ulcer, or gastrointestinal disease. You should also not take this medicine if you have a bleeding disorder, uncontrolled asthma, or uncontrolled high blood pressure. These conditions may increase your risk for bleeding.
- Take anticoagulants exactly as prescribed. Do not double up on a dose if you have missed a dose. Some anticoagulants should be taken at the same time every day.
- Keep appointments for blood tests if you are taking warfarin. Blood tests will help your provider make changes to your dose of anticoagulants so that they work correctly. The blood test will measure the amount of time it takes for your blood to clot. This is called the international normalized ratio (INR). If your INR is too high, you may be at an increased risk for bleeding. If your INR is too low, you may be at an increased risk for blood clots. Your provider may change the dose of your anticoagulant medicine depending on the results of your blood test.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
