Repatha: Uses, How It Works, and Common Side Effects
Repatha is a medicine used to help reduce levels of bad cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein, or LDL) circulating in your blood. It is a type of human monoclonal antibody.
Video transcript
This medicine is used together with a low-fat diet and other cholesterol-lowering medications in people with homozygous or heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (inherited types of high cholesterol). These conditions can cause high blood levels of LDL cholesterol, and can also cause plaque to build up inside your arteries.
Repatha is also used to help lower the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other heart complications in people with heart or blood vessel problems caused by plaque build-up or hardening in the arteries (also called atherosclerosis, or arteriosclerosis).
Common side effects may include redness, pain, or bruising where an injection was given, back pain, flu symptoms or cold symptoms such as stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat.
This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your healthcare provider.
More about Repatha (evolocumab)
- Repatha consumer information
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (744)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Patient tips
- During pregnancy
- Support group
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: PCSK9 inhibitors
- Breastfeeding
Related treatment guides
Recommended videos
Hamstring curl with resistance tubing
The hamstring curl with resistance tubing targets the back of the thigh. See how it's done.
Can saline irrigation help nasal allergies?
In a recent survey, almost 90% of family physicians recommended nasal saline irrigation for sinus and nasal symptoms.
Botox: Uses, How It Works, and Common Side Effects
Botox is primarily known for its ability to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles. But did you know that it has several other medical applications too?
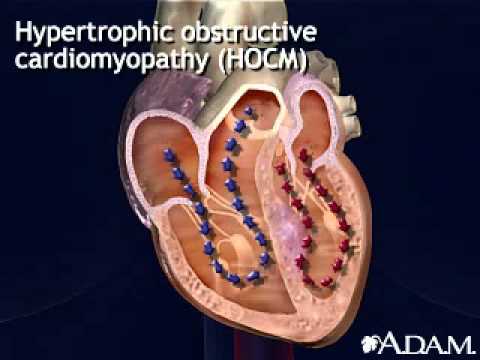
Cardiomyopathy
This animation shows a catheter being inserted into the heart where alcohol is injected causing the swollen ventricle wall to shrink.
Reducing Radiation from Medical X-rays
Medical X-rays are an important tool for diagnosing and treating diseases, but they pose a small risk from radiation. Learn what you can do to reduce the risk in this FDA Consumer Update video.
Browse by category
- ADHD
- Allergy
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Asthma
- Back Pain
- Beauty
- Birth Control
- Cancer
- Children's Health
- Diabetes
- Exercise & Fitness
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Health
- Gout
- Headache
- Hearing
- Heart Disease
- Hypertension
- Injury
- Joint Pain
- Men's Health
- Pain
- Parkinson's Disease
- Pregnancy
- Psoriasis
- Sleep Disorders
- Stroke
- UTI
- Vision
- Women's Health
By medication
- Aimovig
- Ambien
- Amoxicillin
- Austedo
- Biktarvy
- Botox
- Breztri Aerosphere
- Caplyta
- Celebrex
- Cobenfy
- Cosentyx
- Dovato
- Ella
- Emgality
- Entyvio
- Evenity
- Gemtesa
- Humira
- Ibuprofen
- Intuniv
- Jaypirca
- Jornay PM
- Journavx
- Kesimpta
- Keytruda
- Kisunla
- Leqvio
- Lisinopril
- Lyrica
- Mounjaro
- Narcan
- Next Choice One Dose
- Nurtec ODT
- Olumiant
- Omvoh
- Opdivo
- Otezla
- Ozempic
- Padcev
- Plan B One-Step
- Prednisone
- Qulipta
- Quviviq
- Repatha
- Rexulti
- Skyrizi
- Syfovre
- Tagrisso
- Taltz
- Tepezza
- Tramadol
- Trelegy Ellipta
- Trintellix
- Ubrelvy
- Ultomiris
- Verzenio
- Victoza
- Vraylar
- Vumerity
- Vyepti
- Vyvanse
- Xcopri
- Xolair
- Zepbound
- Zoloft