SILEO (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Grey Wolf Animal Health
Company: Grey Wolf Animal Health
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride gel 0.1 mg/mL
Oromucosal Gel for Dogs
DIN 02530392
Veterinary Use Only
NAME AND DESCRIPTION:
Each mL of SILEO contains 0.1 mg dexmedetomidine hydrochloride, USP. The chemical name is (+)-4-[1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl) ethyl]-1H-imidazole monohydrochloride. It is a white, or almost white, crystalline, water soluble substance having a molecular weight of 236.7. The molecular formula is C13H16N2HCl and the structural formula is:
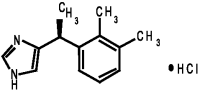
THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION: SILEO is a synthetic alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist.
SILEO Indications
SILEO is indicated for the alleviation of acute anxiety and fear associated with noise in dogs.
Dosage and Administration
SILEO is administered onto the oral mucosa between the dog’s cheek and gum at 125 µg/m2. The gel is absorbed through the oral mucosa and therefore it should NOT be swallowed. If the gel is swallowed, the product may not be effective. If the gel is swallowed, do not repeat the dose for at least two hours.The following table provides the acceptable dosage for each weight range. Each dot (•) represents 0.25 mL of SILEO. Each mL contains the equivalent of 0.1 mg/mL dexmedetomidine hydrochloride.
Table 1. Dosage by body weight
|
Body weight (kg) |
Number of dots |
|
2.0-5.5 |
1 • |
|
5.6-12 |
2 •• |
|
12.1-20 |
3 ••• |
|
20.1-29 |
4 •••• |
|
29.1-39 |
5 ••••• |
|
39.1-50 |
6 •••••• |
|
50.1-62.5 |
7 ••••••• |
|
62.6-75.5 |
8 •••••••• |
|
75.6-89 |
9 ••••••••• |
|
89.1-100 |
10 •••••••••• |
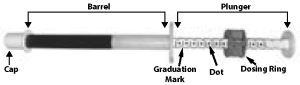
If the dose is more than 6 dots, divide the dose between both sides of the mouth.
OPENING OF THE CHILD-RESISTANT CARTON:
PUSH TO BREAK THE SEALS

PUSH THE BUTTON AND PULL TO OPEN
Make sure that the package is closed correctly so that it remains child-resistant. When closing, the SILEO logo must be on the same side on both the inner and the outer carton so that the yellow button becomes visible.
PREPARATIONS FOR DOSING:

WEAR GLOVES
Wear impermeable disposable gloves when handling SILEO and handling the oral syringe.
HOLD PLUNGER
Hold the oral syringe from the plunger so that you can see the dot markings.
SYRINGE SET UP:
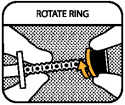
ROTATE RING
When using the syringe for the first time, rotate the dosing ring towards the barrel, until it reaches the opposite end of the plunger.
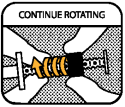
Continue rotating the ring until it reaches the opposite end of the plunger.
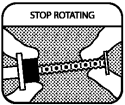
Stop rotating once you have reached the barrel.
DOSE SELECTION:
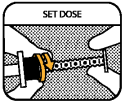
SET THE DOSE
Rotate the dosing ring towards the end of the plunger and position it so that the side nearest the barrel is in line with the graduation mark (black line), and the prescribed number of dots are shown between the barrel and the dosing ring.
Do not pull the plunger
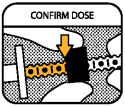
CONFIRM THE DOSE
Make sure that you count the dots from the correct part of the plunger (shown in yellow) and that the ring is in line with the graduation mark (shown with the yellow arrow).
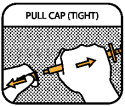
PULL CAP (TIGHT)
Pull the cap strongly while holding the barrel. Note: The cap is very tight (pull, do not twist). Save the cap for replacement.
DOSING:
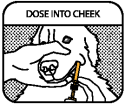
DOSE INTO CHEEK
Place the oral syringe tip between your dog’s cheek and gum, and press the plunger until the ring causes the plunger to stop.
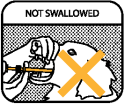
IMPORTANT: The gel should not be swallowed. If the gel is swallowed, it may not be effective.
Avoid feeding and giving treats 15 minutes after giving SILEO.

BACK TO PACKAGE
Recap the oral syringe and return it to the outer package as SILEO is sensitive to light. Make sure that the carton is closed properly. Keep the product out of sight and reach of children at all times. Remove and discard gloves. Use or discard syringe contents within 4 weeks after opening the syringe.
ADMINISTERING FOLLOWING DOSES
When the same syringe is used for redosing, repeat the previous SET THE DOSE and CONFIRM THE DOSE parts of the instructions.
Detailed instructions for use and correct administration of the product can also be found in the Client Information Sheet included with the product.
The first dose of SILEO should be administered 30-60 minutes before the fear and/or anxiety-eliciting noise stimulus, immediately after the dog shows first signs of anxiety or fear related to noise or when the owner detects a typical noise stimulus (e.g., sound of fireworks) eliciting anxiety or fear in the dog.
Typical signs of anxiety and fear associated with noise are panting, trembling, pacing, seeking people, trying to hide, trying to escape, freezing behaviour, refusing to eat food or treats, inappropriate urination or defecation and salivation.
Administering SILEO without use of the SILEO syringe will result in incorrect dosing, which may result in lack of efficacy or overdose.
Dosing should be performed by an adult. Impermeable disposable gloves should be worn when administering SILEO and when handling the SILEO syringe.
If noise lasts longer than 2-3 hours and the dog’s signs of fear and/or anxiety reappear, another dose may need to be given. To avoid overdosing, there should always be at least two hours’ pause between dosages. No more than 5 doses can be given during one noise event.
A partially used syringe can be used again within 4 weeks after initial opening, if there is enough gel for a complete dose for the dog. To minimize the risk of incorrect dosing, a partially used syringe that does not have enough gel for a complete dose should not be used.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Contraindications
Do not use SILEO in dogs with severe cardiovascular, respiratory, liver or kidney disease, or in conditions of shock, severe debilitation or stress due to extreme heat, cold or fatigue. Do not use in dogs with hypersensitivity to dexmedetomidine or to any of the excipients.
Do not use in dogs obviously sedated from previous dosing.
CAUTIONS: For oromucosal use in dogs only. Not intended for ingestion.
SILEO should not be administered in the presence of pre-existing hypotension, hypoxia or bradycardia. Sensitive dogs may experience a drop in body temperature and heart rate and may appear sedated.
These dogs should be kept warm and not offered food or water until the effects of SILEO have worn off (usually within a few hours).
SILEO has not been evaluated in dogs younger than 6 weeks of age or in dogs with dental or gingival diseases that could have an effect on SILEO’s absorption. Efficacy of SILEO has not been evaluated during thunderstorms.
Use caution to prevent SILEO from being swallowed. If the gel is swallowed, it may not be effective. Feeding and giving treats within 15 minutes after administration should be avoided.
The use of other central nervous system depressants may potentiate the effects of SILEO.
The safety and effectiveness of SILEO in breeding, pregnant or lactating dogs has not been evaluated. Administration to pregnant dogs may induce uterine contractions and/or decrease fetal blood pressure.
Warnings
Avoid administering the product if pregnant, as exposure may induce uterine contractions and/or decrease fetal blood pressure.Appropriate precautions should be taken while handling and using filled syringes. Impermeable disposable gloves should be worn when handling the syringe, administering SILEO or when coming in contact with the dog’s mouth after application.
If skin is damaged, dexmedetomidine can be absorbed into the body. In case of skin contact, wash with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing. SILEO can be absorbed following direct exposure to skin, eyes or mouth. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes. If wearing contact lenses, eyes should be rinsed first, then remove contact lenses and continue rinsing and seek medical attention immediately.
Accidental exposure may cause sedation and changes in blood pressure. In case of accidental exposure, seek medical attention immediately. Exposure to the product may induce a local or systemic allergic reaction in sensitized individuals.
Keep out of reach of children.
Note to physician: This product contains an alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist.
Adverse Reactions
OVERDOSE: Signs of sedation may occur when the recommended dose is exceeded. The level and duration of sedation is dose dependent. If sedation occurs, the dog should be kept warm.
Reduced heart rate may be seen after administration of higher than recommended doses of SILEO.
Blood pressure and respiratory rate may decrease slightly below normal levels.
Higher than recommended doses of SILEO may also induce a number of other alpha-2 adrenoceptor mediated effects, including mydriasis, depression of motor and secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract, temporary AV-blocks, diuresis and hyperglycemia. A slight decrease in body temperature may be observed.
The effects of dexmedetomidine can be eliminated by administering an alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist.
POST-MARKET INFORMATION: Although all adverse reactions are not reported, the following information is based on voluntary post-approval drug experience reporting. It is generally recognized that this results in significant under-reporting.
The adverse events listed here reflect reporting and not necessarily causality. Adverse events are listed by body system, in decreasing order of frequency:
Neurological disorders: Sedation, ataxia, somnolence
Systemic disorders: lack of efficacy, lethargy, pale mucous membrane, anorexia
Behavioural disorders: anxiety, behavioural disorder [not otherwise specified (NOS)]
Digestive tract disorders: emesis, diarrhea
Cardiovascular disorders: bradycardia
FIELD STUDY DATA: In a well-controlled European field study, which included a total of 182 dogs ranging from 2 to 17 years of age and representing both mixed and pure breed dogs (89 treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel and 93 treated with control), no serious adverse reactions were attributed to administration of dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel.
Table 2 shows the number of dogs displaying adverse reactions (some dogs experienced more than one adverse reaction).
Table 2. Adverse Reactions - Number (%) of dogs
|
Adverse Reaction |
Control 0 µg/m2 N=93 |
Dexmedetomidine HCl 125 µg/m2 N=89 |
|
Emesis |
1 (1.1%) |
4 (4.5%) |
|
Gastroenteritis |
0 |
1 (1.1%) |
|
Periorbital edema |
0 |
1 (1.1%) |
|
Drowsiness |
0 |
1 (1.1%) |
|
Sedation |
0 |
1 (1.1%) |
Pale mucous membranes were frequently seen in dogs treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel. In most cases, the effect was transient and no adverse reactions due to mucosal irritation were reported.
In a second well-controlled European field study, which included a total of 36 dogs ranging from 2 to 11 years of age and representing both mixed and pure breed dogs (12 treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel at 125 μg/m2, 12 treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel at 250 µg/m2, and 12 treated with a vehicle control), no serious adverse reactions were attributed to administration of dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel. Table 3 shows the number of dogs displaying adverse reactions (some dogs experienced more than one adverse reaction).
Table 3. Adverse Reactions - Number (%) of dogs
|
Adverse Reaction |
Control 0 µg/m2 N=12 |
Dexmedetomidine HCl 125 µg/m2 N=12 |
Dexmedetomidine HCl 250 µg/m2 N=12 |
|
Sedation |
0 |
2 (16.7%) |
4 (33.3%) |
|
Lack of effectiveness |
4 (33.3%) |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
|
Urinary incontinence |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
1 (8.3%) |
|
Emesis |
0 |
2 (16.7%) |
0 |
|
Head tremor |
0 |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
|
Inappropriate urination |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
0 |
|
Ataxia |
0 |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
|
Mydriasis |
0 |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
|
Anxiety disorder |
0 |
0 |
1 (8.3%) |
|
Tachypnea |
1 (8.3%) |
0 |
0 |
|
Lethargy |
1 (8.3%) |
0 |
0 |
|
Tachycardia |
1 (8.3%) |
0 |
0 |
Clinical Pharmacology
Dexmedetomidine is a potent and selective alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist that inhibits the release of noradrenaline from noradrenergic neurons.Oral bioavailability of dexmedetomidine is poor due to extensive first-pass metabolism. No measurable concentrations were found after gastro-intestinal tubing of dexmedetomidine to dogs. When administered via the oral mucosa, enhanced bioavailability is observed as a result of absorption in the oral cavity and the avoidance of first-pass metabolism in the liver.
The maximum concentration of dexmedetomidine occurs at about 0.6 hours after both IM and oromucosal administration in dogs. In a pharmacokinetic study in dogs, the oromucosal mean bioavailability of dexmedetomidine was 28%. The apparent volume of distribution of the drug is 0.9 L/kg. In the canine circulation, dexmedetomidine is largely bound to plasma proteins (93%).
Dexmedetomidine is eliminated by biotransformation mainly in the liver with a half-life ranging from 0.5 to 0.7 hours after intravenous (IV) administration and 0.5 to 3 hours after oromucosal administration in dogs. Metabolism accounts for more than 98% of the elimination.
Known metabolites show no or negligible activity. Metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine with a minor fraction found in the feces.
ANIMAL SAFETY:
Canine safety study with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injectable
In a laboratory study of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, doses of 375, 1125 and 1875 µg/m2 (3X, 9X and 15X the proposed oromucosal dose) were administered once daily intravenously (IV), or doses of 500, 1500 and 2500 µg/m2 (4X, 12X and 20X the proposed oromucosal dose) were administered once daily intramuscularly (IM) on three (3) consecutive days. These doses represent low, mid and high doses as described below.
Dexmedetomidine-induced sedation occurred on each dosing day at all dose levels from 2 to 8 hours post-dosing. The duration of sedation increased with the dosage level. A decreased respiratory rate was observed in all groups on each day, but returned to normal within 4 hours in the low IV and IM groups and within 8 hours in the mid and high IV and IM groups. A decreased rectal temperature was observed in all groups on each day. In the low IV and IM groups, the rectal temperature returned to normal or near normal within 4 hours, and in the mid and high IV and IM groups within 8 hours. A decreased heart rate was observed in all groups on each day, with greater decreases in the IV dosing groups. In the low groups, the duration of decrease was 2 hours with the values returning to normal 4 hours after dosing. In the mid groups, the duration of decrease was 4 hours with the values returning to normal 8 hours after dosing. In the high IV dose group, the values also returned to normal at 8 hours after dosing. However, in the high IM group, the values were still slightly depressed at 8 hours after dosing; the values returned to normal by 24 hours after dosing. On electrocardiography, QT time was prolonged in all groups due to decreased heart rate. In the low and mid IM groups, one case each of second degree AV-block was observed. In the high IM group, one dog had first and second degree AV-block.
In the mid IV group, two dogs had second degree AV-block and one dog had first and second degree AV-block. In the mid and high IM groups, one dog each had elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) values. In the high IV group, two dogs had elevated ALT values.
Dexmedetomidine was well-tolerated in the study even at the high doses, and adverse effects on physiology were related to the pharmacology of the drug. There were no toxicological effects on body weight, clinical variables, gross or microscopic pathology.
EFFICACY: SILEO was evaluated in a European randomized multi-centre, double-blind, vehicle-controlled field study. Effectiveness was evaluated in client-owned dogs, ranging in age between 2 and 17 years, and in body weight between 4 and 67 kg. A total of 187 dogs were randomized, 144 of which were evaluated for effectiveness: 71 dogs received 125 µg/m2 of dexmedetomidine oromucosal, and 73 dogs received the vehicle control gel up to 5 times as needed with a minimum interval of 2 hours between doses. All dogs had in previous years suffered from acute fear and/or anxiety due to fireworks.
The first dose was given on New Year’s Eve before or as soon as the dog showed the first signs of becoming anxious and/or fearful due to fireworks. Re-dosing could be performed as soon as the dog again demonstrated noise aversion behaviours, but at least 2 hours after the previous dose to allow time to assess observable effects of treatment and to avoid potential cumulative effects of dexmedetomidine.
For the first co-primary endpoint, the proportion of dogs with owner-assessed good or excellent treatment effect was higher in dogs treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel (53/71 dogs) than in those administered control (24/73 dogs). The proportion of dogs with some, no, or worse effect was higher in dogs administered control (49/73 dogs) than in those treated with dexmedetomidine (18/71 dogs). Refer to Table 4 below.
Table 4. Owner assessment of treatment effect/score by treatment group
|
Treatment effect |
Dexmedetomidine HCl 125 µg/m2 N=71 |
Control 0 µg/m2 N=73 |
Total N=144 |
|
1 Excellent effect |
12 (16.9%) |
8 (11%) |
20 (13.9%) |
|
2 Good effect |
41 (57.7%) |
16 (21.9%) |
57 (39.6%) |
|
3 Some effect |
7 (9.9%) |
14 (19.1%) |
21 (14.6%) |
|
4 No effect |
8 (11.2%) |
32 (43.8%) |
40 (27.7%) |
|
5 Worse |
3 (4.2%) |
3 (4%) |
6 (4.2%) |
There was a statistically significant difference (p<0.0001) between dexmedetomidine and control in favour of dexmedetomidine. The odds ratio was 5.5876, with 95% confidence interval (2.7635, 11.2976).
For the second co-primary variable, the mean sum of behaviour scores over the treatment period was significantly different between dexmedetomidine and control (p=0.0069). Behaviour scores consisted of a cumulative score using a number of outward signs of noise aversion in dogs such as panting, trembling, vocalizing, and seeking people. The mean score was lower (better) for the dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel treated group than for the control group (LS Means: 4.9661, 7.2456 respectively). Refer to Table 5 below.
Table 5. Mean behavioral sum scores by treatment and time point
|
Dosing Time Point |
Sum of Behavior Scores [Mean Score (Number of Dogs)] |
|
|
Dexmedetomidine HCl 125 µg/m2 |
Control 0 µg/m2 |
|
|
Screening |
18.75 (71) |
19.01 (73) |
|
Prior to dose 1 |
5.04 (71) |
4.96 (73) |
|
1 hour post-dose 1 |
3.75 (68) |
4.72 (71) |
|
Prior to dose 2 |
7.93 (68) |
9.11 (70) |
|
1 hour post-dose 2 |
4.21 (52) |
9.1 (60) |
|
Prior to dose 3 |
8.26 (38) |
17.5 (44) |
|
1 hour post-dose 3 |
6.35 (34) |
11.0 (39) |
|
Prior to dose 4 |
6.92 (12) |
12.95 (21) |
|
1 hour post-dose 4 |
5.42 (12) |
12.7 (21) |
Of the different types of behaviours, dogs treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel displayed less panting, trembling and trying to hide than those treated with the control gel.
Presentation: SILEO is packaged as a 3 mL HDPE dosing syringe enabling doses from 0.25 to 3 mL.
Storage
Store unopened and opened syringes in the carton at 15-30°C. Use contents within 4 weeks after opening the syringe.Replace cap after use.
Return the oral syringe to the outer carton immediately after each use.
Date of Preparation: February, 2024
SILEO® Trademark of Orion Corporation.
Orion Corporation, Turku, Finland
Imported and distributed by:
Grey Wolf Animal Health Inc., Suite No. 85534, RPO Nortown, Toronto, ON M5N 0A2
1-844-400-GWAH (4924)
153959-1
CPN: 2022013.0
SUITE NO. 85534, RPO NORTOWN, TORONTO, ON, M5N 0A2
| Telephone: | 1-844-400-GWAH | |
| Website: | www.greywolfah.com | |
| Email: | support@greywolfah.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-03-02
