Ovarelin (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Ceva Animal Health
Company: Ceva Animal Health
Gonadorelin Injection
Veterinary Use Only
Sterile
For intramuscular use in cattle only.
DIN 02532727
Description
Ovarelin® is a clear colourless solution. Each mL contains 50 μg of gonadorelin (as Gonadorelin diacetate) and 15.0 mg of benzyl alcohol as preservative.
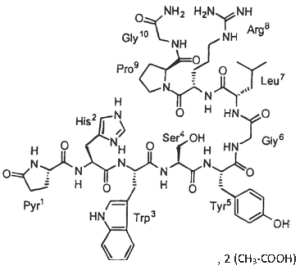
Gonadorelin is a decapeptide composed of the amino acid sequence:
5-oxo Pro-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2.
The empirical formula of gonadorelin (as Gonadorelin diacetate) is C55H75N17O13•x(C2H4O2) y(H2O), (x ≈ 2, y ≈ 4)
Figure 1. The chemical structure of gonadorelin (as Gonadorelin diacetate)
THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION: Gonadotropin-releasing hormones
INDICATIONS: Reproductive Synchronisation
Ovarelin® is indicated for synchronisation of the estrous cycle in combination with prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) or analogue as part of Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) protocols in lactating dairy cattle.
As an aid in management of repeat breeders1
Ovarelin® is indicated for use as an aid in management of repeat breeder dairy cattle.
1A repeat breeder cow or heifer is generally defined as an animal that has been inseminated at least 2 or often 3 times without becoming pregnant, despite having regular normal estrous cycles (every 18-24 days), normal estrus behavior and no clinical abnormalities of the reproductive tract.
Dosage and Administration
Intramuscular use only.100 μg of gonadorelin (as Gonadorelin diacetate) per animal in a single injection; i.e., 2 mL of the product per animal.
Judgement on the protocol to be used should be made by the veterinarian responsible for treatment, on the basis of the treatment objectives of the individual cow or herd.
The following protocols have been evaluated and could be used:
Synchronisation of estrous cycles in combination with a prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) or analogue:
● Day 0: Administration of the first injection of gonadorelin (2 mL of Ovarelin®).
● Day 7: Injection of prostaglandin (PGF2α) or analogue according to the recommended label dose.
● Day 9: Administration of second injection of gonadorelin (2 mL of Ovarelin®).
● The animal should be inseminated within 16-18 hours after the second injection of Ovarelin®.
As an aid in management of repeat-breeding:
To improve the pregnancy rates, the following timing of injection and insemination should be followed:
● Injection of 2 mL of Ovarelin® should be performed between 4 and 10 hours after estrus detection.
● Artificial insemination should be carried out 12 to 24 hours after estrus detection.
Warnings
No withdrawal period or milk withholding time is required for cattle when treated according to the label. The effects of accidental exposure to GnRH analogues in pregnant women or in women with normal reproductive cycles are unknown. Pregnant women should not administer the product and women of child-bearing age should administer the product with caution. People with known hypersensitivity to GnRH analogues should avoid handling this product. When handling the product, caution should be taken to avoid accidental self-injection and contact with skin and eyes. In cases of accidental self-injection, seek medical advice immediately and show the label to the physician. In case of accidental skin or eye contact, rinse immediately with water. Keep out of reach of children.Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Gonadorelin (as gonadorelin diacetate) is a synthetic hormone physiologically and chemically identical to the Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) synthesized in mammalian species.
Gonadorelin stimulates the synthesis and release of the pituitary gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Its action is mediated by a specific plasma membrane receptor. Only 20% GnRH receptor occupancy is required to induce 80% of the maximum biological response. The binding of GnRH to its receptor activates protein kinase C (PKC) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades, which provide an important link for the transmission of signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, permitting the synthesis of the gonadotropin hormones.
In repeat breeding animals, one of the most prominent findings is the delayed and smaller pre-ovulatory LH surge leading to delayed ovulation. Injection of GnRH during oestrus increases the spontaneous LH peak and prevents delay in ovulation in repeat breeding animals.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After intramuscular administration of 100 μg of gonadorelin (as gonadorelin diacetate) to the animal, absorption of GnRH is rapid. The maximum concentration (Cmax) of 123.5 ± 46.3 ng/litre is obtained after 15 min (Tmax). Concentrations of GnRH decreased rapidly in plasma.
The absolute bioavailability of gonadorelin (IM versus IV) was estimated to be around 75%.
Distribution
24 hours after intramuscular administration of 100 μg of radiolabelled gonadorelin (as gonadorelin diacetate), the greatest amounts of radioactivity in tissues were measured in the kidneys, pituitary gland and adrenal glands.
8 or 24 hours after the administration, gonadorelin shows an extensive plasma protein binding of 73%.
Metabolism
Gonadorelin is a naturally occurring peptide which is rapidly broken down into inactive metabolites.
Elimination
After intramuscular administration of gonadorelin to the dairy cow, the principal excretion route is milk followed by urine and faeces. A high percentage of the administered dose is excreted as carbon dioxide in expired air.
ANIMAL SAFETY:
Gonadorelin has been shown to have a low level of toxicity in animals. The LD50 for mice and rats is greater than 60 μg/kg, and for dogs, greater than 600 μg/kg. Untoward effects were not noted among rats or dogs administered 120 μg/kg/day or 72 μg/kg/day intravenously for 15 days.
It had no adverse effects on heart rate, blood pressure, or electrocardiogram (ECG) of un-anesthetized dogs at 60 μg/kg. In anesthetized dogs, it did not produce depression of myocardial or systemic hemodynamics or adversely affect coronary oxygen supply or myocardial oxygen requirements.
The intravenous administration of 60 μg/kg/day of gonadorelin to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis did not cause embryotoxic or teratogenic effects.
Administration of Ovarelin® as either a daily IM injection for three days, each at the recommended label dose, or as a single IM injection up to 5 times the recommended label dose, did not result in significant changes of blood chemistry or hematological parameters assessed, local injection site reactions or systemic adverse events in lactating dairy cows.
ANIMAL EFFICACY:
The effectiveness of Ovarelin® for use with injectable dinoprost to synchronize estrous cycles in lactating dairy cows to allow for fixed time artificial insemination (FTAI) was demonstrated in a field study conducted in France (2 farms) and Germany (1 farm). A total of 192 healthy lactating dairy cows that were at least 60 days in milk were treated and inseminated according to the following protocol.
● Day 0: Administration of 2 mL of Ovarelin® IM.
● Day 7: Administration of 25 mg of dinoprost (as dinoprost trometamol) IM.
● Day 9: Administration of 2 mL of Ovarelin® IM.
● Insemination within 16-18 hours after the second injection of Ovarelin® on Day 9.
Control cows (n = 94) were treated and inseminated as shown in the above protocol, except that Ovarelin® treatments on Day 0 and 9 were replaced with a 2 mL IM placebo injection on each day.
Pregnancy rate to FTAI was significantly higher (P = 0.001) in cows treated with Ovarelin® (40.1%) than cows treated with the placebo product (19.1%).
The effectiveness of Ovarelin® as an aid in management of repeat breeding was assessed in a large field trial that enrolled 559 cows from 196 farms in Germany, Belgium, Spain and France. Animals classified as repeat breeders1 were randomly allocated to be treated with a single 2 mL IM injection of Ovarelin® or placebo. The median time for treatment administration was ~ 3.5 hours after estrus detection (range: 0.5-27.25 hours), and the median time for artificial insemination was ~ 11.5 hours after estrus detection (range: 6.5-36.3 hours).
Cows that were treated 4 to10 hours after estrus detection and inseminated 12 to 24 hours after estrus detection had a higher pregnancy rate than their counterparts in the placebo group (54% and 24%, respectively; OR = 3.71, 95% CI: 1.61-8.56, P < 0.001).
1A cow or heifer that was inseminated at least 2 consecutive times but less than 6 times without becoming pregnant, despite having regular normal estrous cycles, normal estrus behavior and no clinical abnormalities of the reproductive tract.
Storage
Store between 15-25°C. Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light. Use within 28 days after opening the vial.
How Supplied
Ovarelin® is available in 10, 20 & 50 mL glass vials.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
For technical assistance, or to report suspected adverse reactions, call 1-800-510-8864.
Ceva Animal Health Inc., 150 Research Lane, Suite 225, Guelph ON N1G 4T2
OVARELIN® is a registered trademark of Ceva Santé Animale, France
Date of last revision: April 2023
C513-3120105
A5614
CPN: 1221167.0
150 RESEARCH LANE, SUITE 225, GUELPH, ON, N1G 4T2
| Telephone: | 519-650-9570 | |
| Toll-Free: | 800-510-8864 | |
| Fax: | 519-650-9576 | |
| Website: | www.ceva-canada.ca | |
| Email: | service.canada@ceva.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-08-27
