TobraDex ST: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: tobramycin and dexamethasone
Dosage form: ophthalmic suspension
Drug class: Ophthalmic steroids with anti-infectives
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TOBRADEX ST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TOBRADEX ST.
TOBRADEX ®ST (tobramycin and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) 0.3%/0.05%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
Indications and Usage for TobraDex ST
TOBRADEX ST is a topical antibiotic and corticosteroid combination for steroid-responsive inflammatory ocular conditions for which a corticosteroid is indicated and where superficial bacterial ocular infection or a risk of bacterial ocular infection exists. ( 1).
TobraDex ST Dosage and Administration
- Instill one drop into the conjunctival sac(s) every 4 to 6 hours. ( 2.1)
- During the initial 24 to 48 hours, dosage may be increased to one drop every 2 hours. ( 2.1)
- Frequency should be decreased gradually as warranted by improvement in clinical signs, but care should be taken not to discontinue therapy prematurely. ( 2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
TOBRADEX ST ophthalmic suspension contains 0.3% (3 mg/mL) tobramycin and 0.05% (0.5 mg/mL) dexamethasone. ( 3)
Contraindications
- TOBRADEX ST, as with other ophthalmic corticosteroids, is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva, including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures. ( 4.1)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the medication ( 4.2)
Warnings and Precautions
- Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Increase: Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. If this product is used for 10 days or longer, IOP should be monitored. ( 5.1).
- Sensitivity to topically applied aminoglycosides may occur. ( 5.2)
- Cataracts: Use of corticosteroids may result in posterior subcapsular cataract formation. ( 5.3)
- Delayed Healing: The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical steroids. The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. ( 5.4)
- Bacterial Infections: Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after 2 days, the patient should be re-evaluated. ( 5.5)
- Viral Infections: Employment of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution. Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex). ( 5.6)
- Fungal Infections: Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local steroid application. Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. ( 5.7)
- Vision Blurred: Vision may be temporarily blurred following dosing with TOBRADEX ST. Care should be exercised in operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle. ( 5.8)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions to topical ocular tobramycin are hypersensitivity and localized ocular toxicity, including eye pain, eyelids pruritus, eyelid edema, and conjunctival hyperemia. The reactions due to the steroid component are increases in IOP with possible development of glaucoma. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Harrow at 1-833-4HARROW(427769) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for TobraDex ST
TOBRADEX ST ophthalmic suspension is indicated for steroid-responsive inflammatory ocular conditions for which a corticosteroid is indicated and where superficial bacterial ocular infection or a risk of bacterial ocular infection exists.
Ocular steroids are indicated in inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea and anterior segment of the globe where the inherent risk of steroid use in certain infective conjunctivitides is accepted to obtain a diminution in edema and inflammation. They are also indicated in chronic anterior uveitis and corneal injury from chemical, radiation or thermal burns, or penetration of foreign bodies.
The use of a combination drug with an anti-infective component is indicated where the risk of superficial ocular infection is high or where there is an expectation that potentially dangerous numbers of bacteria will be present in the eye.
The particular anti-infective drug in this product is active against the following common bacterial eye pathogens: Staphylococci, including S. aureusand S. epidermidis (coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative), including penicillin-resistant isolates. Streptococci, including some Group A and other beta-hemolytic species, some nonhemolytic species, and some Streptococcus pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Proteus mirabilis, Morganella morganii, most Proteus vulgaris isolates, Haemophilus influenzae, H. aegyptius, Moraxella lacunata, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, and some Neisseria species.
2. TobraDex ST Dosage and Administration
2.1 Initiation and Continuation of Treatment
Evaluate intraocular pressure (IOP) prior to the initial prescription and renewal of the medication order [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Perform ophthalmic examination with the aid of magnification, such as slit lamp biomicroscopy, and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining, prior to the initial prescription and renewal of the medication order. Re-evaluate the patient if signs and symptoms fail to improve after 2 days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5)] .
Not more than one bottle should be prescribed initially, and the prescription should not be refilled without further evaluation.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Instill one drop into the conjunctival sac(s) every 4 to 6 hours. During the initial 24 to 48 hours, the dosage may be increased to one drop every 2 hours. Frequency should be decreased gradually as warranted by improvement in clinical signs. Care should be taken not to discontinue therapy prematurely. Shake well before use.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
TOBRADEX ST ophthalmic suspension 0.3%/0.05% contains 3 mg/mL tobramycin and 0.5 mg/mL dexamethasone.
4. Contraindications
4.1 Nonbacterial Etiology
TOBRADEX ST, as with other ophthalmic corticosteroids, is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva, including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Intraocular Pressure Increase
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure (IOP) should be monitored.
5.4 Delayed Healing
The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical steroids. The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining.
5.5 Bacterial Infections
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after 2 days, the patient should be reevaluated.
5.6 Viral Infections
Employment of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution. Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex).
5.7 Fungal Infections
Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local steroid application. Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use.
5.8 Vision Blurred
Vision may be temporarily blurred following dosing with TOBRADEX ST. Care should be exercised in operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions have occurred with steroid/anti-infective combination drugs, which can be attributed to the steroid component, the anti-infective component, or the combination. Exact incidence figures are not available.
The most frequent adverse reactions to topical ocular tobramycin (TOBREX ®) are hypersensitivity and localized ocular toxicity, including eye pain, eyelids pruritus, eyelid edema, and conjunctival hyperemia. These reactions occur in less than 4% of patients.
The reactions due to the steroid component are: increased IOP with possible development of glaucoma, and infrequent optic nerve disorder; subcapsular cataract; and impaired healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.4)] .
The development of secondary infection has occurred after use of combinations containing steroids and antimicrobials. Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term applications of steroids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] . The possibility of fungal invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where steroid treatment has been used. Secondary bacterial ocular infection following suppression of host responses also occurs.
Non-ocular adverse events occurring at an incidence of 0.5% to 1% included headache and increased blood pressure.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported with the individual components below:
Aminoglycosides: Neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity have occurred in patients receiving systemic aminoglycoside therapy. Aminoglycosides may aggravate muscle weakness in patients with known or suspected neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis or Parkinson's disease, because of their potential effect on neuromuscular function.
Dexamethasone: Cushing's syndrome and adrenal suppression may occur after use of dexamethasone in excess of the listed dosing instructions in predisposed patients, including children and patients treated with CYP3A4 inhibitors.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of TOBRADEX ST. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Additional adverse reactions identified from postapproval use include, anaphylactic reaction, and erythema multiforme.
Related/similar drugs
Chloramphenicol ophthalmic
Chloramphenicol ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial
Moxifloxacin ophthalmic
Moxifloxacin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial, ophthalmic surgery
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Tobramycin ophthalmic
Tobramycin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial
Bacitracin ophthalmic
Bacitracin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial
Ofloxacin ophthalmic
Ofloxacin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial, corneal ulcer, ophthalmic surgery
Gentamicin ophthalmic
Gentamicin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial
Erythromycin ophthalmic
Erythromycin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial
Levofloxacin ophthalmic
Levofloxacin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial, corneal ulcer, ophthalmic surgery
Ciprofloxacin ophthalmic
Ciprofloxacin ophthalmic is used for conjunctivitis, bacterial, corneal ulcer, ophthalmic surgery
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in animal studies. Ocular administration of 0.1% dexamethasone resulted in 15.6% and 32.3% incidence of fetal anomalies in 2 groups of pregnant rabbits. Fetal growth retardation and increased mortality rates have been observed in rats with chronic dexamethasone therapy. Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits with tobramycin at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (equivalent to human doses of 16 and 32 mg/kg/day, respectively) and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. However, prolonged or repeated corticoid use during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of intra-uterine growth retardation. Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be observed carefully for signs of hypoadrenalism. TOBRADEX ST ophthalmic suspension should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)] .
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when TOBRADEX ST is administered to a nursing woman.
11. TobraDex ST Description
TOBRADEX ST (tobramycin and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) 0.3%/0.05% is a sterile, isotonic, white, aqueous antibiotic and steroid suspension with a pH of approximately 5.7 and an osmolality of approximately 290 mOsm/kg.
The chemical name of tobramycin is O-3-amino-3-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-[2,6-diamino- 2,3,6-trideoxy-α-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→6)]-2-deoxy- L-streptamine. It has a molecular formula of C 18H 37N 5O 9and a molecular weight of 467.52 g/mol. The chemical structure is:

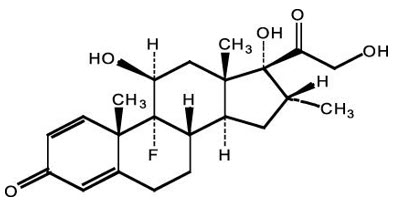
The chemical name of dexamethasone is 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione. It has a molecular formula of C 22H 29FO 5and a molecular weight of 392.47 g/mol. The chemical structure is:
Each mL of TOBRADEX ST contains: Actives:tobramycin 3 mg and dexamethasone 0.5 mg. Preservative:benzalkonium chloride 0.1 mg. Inactives:edetate disodium, hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), propylene glycol, purified water, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, tyloxapol, and xanthan gum.
12. TobraDex ST - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dexamethasone is a potent corticoid. Corticoids suppress the inflammatory response to a variety of agents and they can delay or slow healing. Since corticoids may inhibit the body's defense mechanism against infection, a concomitant antimicrobial drug may be used when this inhibition is considered to be clinically significant.
Tobramycin is an antibacterial drug. It inhibits the growth of bacteria by inhibiting protein synthesis. Tobramycin is included in this combination product to provide action against susceptible bacteria [see Microbiology (12.4)] .
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a multi-center, double-masked, parallel-group, randomized, single-dose pharmacokinetic study in male and female cataract surgery patients, mean dexamethasone concentrations following administration of TOBRADEX ST were similar to dexamethasone concentrations following administration of TOBRADEX (tobramycin and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) 0.3%/0.1%. Aqueous humor concentrations reached a mean peak of 33.7 ng/mL 2 hours following single-dose administration of TOBRADEX ST.
No data are available on the extent of systemic absorption of tobramycin from TOBRADEX ST ophthalmic suspension. Following multiple-dose (4 times a day for 2 days) bilateral ocular administration of TOBRADEX (tobramycin 0.3% and dexamethasone 0.1% ophthalmic suspension) in healthy male and female volunteers, peak plasma concentrations of dexamethasone were less than 1 ng/mL and occurred within 2 hours post dose across all subjects.
12.4 Microbiology
The antibiotic component (tobramycin) in the combination is included to provide action against susceptible bacteria. In vitrostudies have demonstrated that tobramycin is active against susceptible isolates of the following bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus(includes penicillin-resistant isolates), Staphylococcus epidermidis(includes penicillin-resistant isolates), Streptococci, including some Group A other beta-hemolytic species, some nonhemolytic species, and some Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus aegypticus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Moraxella lacunata, Morganella morganii, Neisseria perflava, Neisseria sicca, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
In vitrobacterial studies demonstrate that in some cases bacteria resistant to gentamicin are susceptible to tobramycin.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. TOBRADEX ST ophthalmic suspension should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
No impairment of fertility was noted in studies of subcutaneous tobramycin in rats at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg/day (equivalent to human doses of 8 and 16 mg/kg/day, at least 2 orders of magnitude greater than the topical ocular dose).
16. How is TobraDex ST supplied
TOBRADEX ST is supplied as a 2.5 mL or 5 mL suspension in a 4 mL or 8 mL natural polyethylene DROP-TAINER ®bottle with a natural polyethylene dispenser tip and a pink polypropylene overcap. Tamper evidence is provided with a shrink band around the closure and neck area of the bottle.
| 2.5 mL | NDC 82667-011-00 |
| 5 mL | NDC 82667-011-05 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Storage and Handling
Instruct the patient to store the bottle upright and away from light. Shake well before using [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)] .
Avoid Contamination
Instruct the patient not to touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the contents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)] .
Contact Lens Wear
Advise the patient that contact lenses should not be worn during the use of this product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
Ability to Drive and Use Machines
Advise the patient that vision may be temporarily blurred following dosing with TOBRADEX ST. Care should be exercised in operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] .
| TOBRADEX ST
tobramycin / dexamethasone suspension/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Harrow Eye, LLC (118526951) |
More about Tobradex ST (dexamethasone / tobramycin ophthalmic)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: ophthalmic steroids with anti-infectives
- En español

