Potassium Citrate-Sodium Citrate-Citric Acid Solution: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: potassium citrate and citric acid monohydrate
Dosage form: oral solution
Drug class: Minerals and electrolytes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 23, 2023.
On This Page
Potassium Citrate-Sodium Citrate-Citric Acid Solution Description
Potassium Citrate, Sodium Citrate and Citric Acid Oral Solution is a stable and pleasant-tasting oral systemic alkalizer containing potassium citrate, sodium citrate, and citric acid in a sugar-free, non alcoholic base.
Potassium Citrate, Sodium Citrate, and Citric Acid Oral Solution contains in each teaspoonful (5 mL):
| Potassium Citrate Monohydrate | 550 mg |
| Sodium Citrate Dihydrate | 500 mg |
| Citric Acid Monohydrate | 334 mg |
Each mL contains 1 mEq potassium ion and 1 mEq sodium ion and is equivalent to 2 mEq bicarbonate (HCO3).
INACTIVE INGREDIENTS
FD&C yellow #6, purified water, raspberry flavor, sodium benzoate, sodium saccharin, sorbital solution.
Potassium Citrate Monohydrate has the chemical name: 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, tripotassium salt, monohydrate. Its chemical structure is as follows
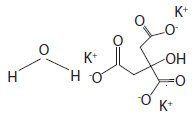
C6H5K3O7 + H2O M.W. 324.41
Sodium Citrate Dihydrate has the chemical name: 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, trisodium salt, dihydrate. Its chemical structure is as follows.
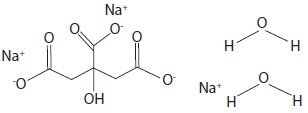
C6H5Na3O7 + 2H2O M.W. 294.10
Citric Acid Monohydrate has the chemical name: 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-,monohydrate. Its chemical structure is as follows.
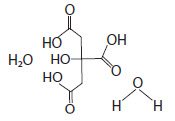
C6H8O7 + H2O M.W. 210.14
Potassium Citrate-Sodium Citrate-Citric Acid Solution - Clinical Pharmacology
Potassium citrate and sodium citrate are absorbed and metabolized to potassium bicarbonate and sodium bicarbonate, thus acting as systemic alkalizers. The effects are essentially those of chlorides before absorption and those of bicarbonates subsequently. Oxidation is virtually complete so that less than 5% of the citrates are excreted in the urine unchanged.
Indications and Usage for Potassium Citrate-Sodium Citrate-Citric Acid Solution
Potassium Citrate, Sodium Citrate and Citric Acid Oral Solution is an effective alkalinizing agent useful in those conditions where long-term maintenance of an alkaline urine is desirable, such as in patients with uric acid and cystine calculi of the urinary tract. In addition, it is a valuable adjuvant when administered with uricosuric agents in gout therapy, since urates tend to crystallize out of an acid urine. It is also effective in correcting the acidosis of certain renal tubular disorders. This product is highly concentrated and when administered after meals and before bedtime, allows one to maintain an alkaline urine pH around the clock, usually without the necessity of a 2 A.M. dose. This product alkalinizes the urine without producing a systemic alkalosis in recommended dosages. It is highly palatable, pleasant tasting, and tolerable, even when administered for long periods. Potassium citrate and sodium citrate do not neutralize the gastric juice or disturb digestion.
Contraindications
Severe renal impairment with oliguria or azotemia, untreated Addison's disease, or severe myocardial damage. In certain situations, when patients are on a sodium-restricted diet, the use of potassium citrate may be preferable; or, when patients are on a potassium-restricted diet, the use of sodium citrate may be preferable.
Warnings
There have been several reports, published and unpublished, concerning nonspecific small-bowel lesions consisting of stenosis, with or without ulceration, associated with the administration of enteric-coated thiazides with potassium salts. These lesions may occur with enteric-coated potassium tablets alone or when they are used with nonenteric-coated thiazides, or certain other oral diuretics. These small-bowel lesions have caused obstruction, hemorrhage, and perforation. Surgery was frequently required and deaths have occurred. Based on a large survey of physicians and hospitals, both United States and foreign, the incidence of these lesions is low, and a casual relationship in man has not been definitely established. Available information tends to implicate enteric-coated potassium salts, although lesions of this type also occur spontaneously. Therefore, coated potassium-containing formulations should be administered only when indicated, and should be discontinued immediately if abdominal pain, distention, nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal bleeding occur.
Do not exceed recommended dosage. Discontinue use if adverse reactions occur. Should be used with caution by patients with low urinary output or reduced glomerular filtration rates unless under the supervision of a physician. Aluminum-based antacids should be avoided in these patients. Patients should be directed to dilute adequately with water and, preferably, to take each dose after meals, to minimize the possibility of gastrointestinal injury associated with oral ingestion of potassium salt perparations and to avoid saline laxative effect. Sodium salts should be used cautiously in patients with cardiac failure, hypertension, peripheral and pulmonary edema, and toxemia of pregnancy.
Concurrent administration of potassium-containing medication, potassium-sparing diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, or cardiac glycosides may lead to toxicity. Periodic examination and determinations of serum electrolytes, particularly serum bicarbonate level, should be carried out in those patients with renal disease in order to avoid these complications.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Potassium Citrate, Sodium Citrate and Citric Acid Oral Solution is generally well tolerated without any unpleasant side effects when given in recommended doses to patients with normal renal function and urinary output. However, as with any alkalinizing agent, caution must be used in certain patients with abnormal renal mechanisms to avoid development of hyperkalemia or alkalosis, especially in the presence of hypocalcemia. Potassium intoxication causes listlessness, weakness, mental confusion, and tingling of extremities.
Overdosage
Overdosage with sodium salts may cause diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, hypernoia, and convulsions. Overdosage with potassium salts may cause hyperkalemia and alkalosis, especially in the presence of renal disease.
Potassium Citrate-Sodium Citrate-Citric Acid Solution Dosage and Administration
Potassium Citrate, Sodium Citrate and Citric Acid Oral Solution should be administered by diluting with water, followed by additional water, if desired. Palatability is enhanced if chilled before taking.
Usual Adult Dosage
3 to 6 teaspoonfuls (15 to 30 mL), diluted with water, for times a day, after meals and at bedtime, or as directed by a physician.
Usual Pediatric Dosage
1 to 3 teaspoonfuls (5 to 15 mL), diluted with water, four times a day, after meals and at bedtime, or as directed by a physician.
Usual Dosage Range
2 to 3 teaspoonfuls (10 to 15 mL), diluted with water, taken four times a day, will usually maintain a urinary pH of 6.5-7.4. 3 to 4 teaspoonfuls (15 to 20 mL), diluted with water taken four times a day, will usually maintain a urinary pH of 7.0-7.6 throughout most of the 24 hours without unpleasant side effects. To check urine pH, HYDRION Paper (pH 6.0-8.0) or NITRAZINE Paper (pH 4.5-7.5) are available and easy to use.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING
How is Potassium Citrate-Sodium Citrate-Citric Acid Solution supplied
Potassium Citrate, Sodium Citrate and Citric Acid Oral Solution (orange colored, raspberry flavored) is supplied in the following form:
NDC 69367-322-16 (16 fl oz bottles).
STORAGE
Keep tightly closed. Store at controlled room temperature, 20°-25° C (68° - 77°F). Protect from excessive heat and freezing.
Tamper evident by foil seal under cap. Do not use if foil seal is broken or missing.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF with a child-resistant closure.
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSAGE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 473 mL Bottle Label
NDC: 69367-322-16
Rx Only
Potassium Citrate,
Sodium Citrate
and Citric Acid
Oral Solution
550 mg/500 mg/ 334mg per 5 mL
A SUGAR-FREE
SYSTEMIC ALKALIZER
EACH TEASPOONFUL (5 mL) CONTAINS:
POTASSIUM CITRATE MONOHYDRATE
550 mg
SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE
500 mg
CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE
334 mg
Each mL contains 1 mEq Potassium Ion and
1 mEq Sodium Ion, and is equivalent to 2
mEq Bicarbonate (HCO3).
May not meet USP monograph.
16 FL OZ (473 mL)
Westminster
Pharmaceuticals

| POTASSIUM CITRATE, SODIUM CITRATE, AND CITRIC ACID
potassium citrate, sodium citrate, and citric acid monohydrate solution |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Westminster Pharmaceuticals, LLC (079516651) |
More about citric acid/potassium citrate/sodium citrate
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Drug class: minerals and electrolytes
- En español
Patient resources
- Citric acid, potassium citrate, and sodium citrate drug information
- Citric Acid, Sodium Citrate, and Potassium Citrate
