Kloxxado: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: naloxone hydrochloride
Dosage form: nasal spray
Drug class: Antidotes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 3, 2024.
On This Page
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KLOXXADOTM (naloxone hydrochloride) nasal spray
Initial U.S. Approval: 1971
Indications and Usage for Kloxxado
KLOXXADO is an opioid antagonist indicated for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose, as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression, for adult and pediatric patients. (1)
KLOXXADO is intended for immediate administration as emergency therapy in settings where opioids may be present.
KLOXXADO is not a substitute for emergency medical care. (1)
Kloxxado Dosage and Administration
- •
- KLOXXADO is for intranasal use only. (2.1)
- •
- Seek emergency medical care immediately after use. (2.1)
- •
- Administer a single spray of KLOXXADO to adult or pediatric patients intranasally into one nostril. (2.2)
- •
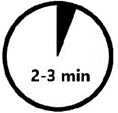
- Administer additional doses of KLOXXADO, using a new nasal spray with each dose, if the patient does not respond or responds and then relapses into respiratory depression. Additional doses of KLOXXADO may be given every 2 to 3 minutes until emergency medical assistance arrives. (2.2)
- Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
nasal spray: naloxone hydrochloride 8 mg in 0.1 mL. (3) (3)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to naloxone hydrochloride or to any of the other ingredients. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- •
- Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and CNS Depression: Due to the duration of action of naloxone relative to the opioid, keep patient under continued surveillance and administer repeat doses of naloxone using a new nasal spray with each dose, as necessary, while awaiting emergency medical assistance. (5.1)
- •
- Risk of Limited Efficacy with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonist/Antagonists: Reversal of respiratory depression caused by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists, such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete. Larger or repeat doses may be necessary. (5.2)
- •
- Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal: Use in patients who are opioid dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal. In neonates, opioid withdrawal may be life-threatening if not recognized and properly treated. Monitor for the development of opioid withdrawal. (5.3)
- •
- Risk of Cardiovascular (CV) Effects: Abrupt postoperative reversal of opioid depression may result in adverse CV effects. These events have primarily occurred in patients who had preexisting CV disorders or received other drugs that may have similar adverse CV effects. Monitor these patients closely in an appropriate healthcare setting after use of naloxone hydrochloride. (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions were reported with KLOXXADO in two adult subjects each: abdominal pain, asthenia, dizziness, headache, nasal discomfort, and presyncope. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hikma Specialty USA Inc. at 1-800-962-8364 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2024
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Kloxxado
KLOXXADO is indicated for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose, as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression, for adult and pediatric patients.
KLOXXADO is intended for immediate administration as emergency therapy in settings where opioids may be present.
KLOXXADO is not a substitute for emergency medical care.
2. Kloxxado Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
- •
- KLOXXADO is for intranasal use only.
- •
- The device is ready to use. Do not prime or test prior to administration.
- •
- Do not attempt to reuse KLOXXADO. Each KLOXXADO contains a single dose of naloxone and cannot be reused.
- •
- Because suspected opioid overdose is usually managed by someone other than the patient, instruct the prescription recipient to inform those around them about the presence of KLOXXADO and the Instructions for Use.
- Instruct the patient or caregiver to read the Instructions for Use at the time they receive a prescription for KLOXXADO. Emphasize the following instructions to the patient or caregiver.
- •
- Administer KLOXXADO as quickly as possible because prolonged respiratory depression may result in damage to the central nervous system or death.
- •
- Always seek immediate emergency medical assistance after the first dose of KLOXXADO has been administered in the event of a suspected, potentially life-threatening opioid emergency because the duration of action of most opioids exceeds that of naloxone hydrochloride. Keep the patient under continued surveillance and administer repeated doses of KLOXXADO, as necessary, until emergency personnel arrive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Administer KLOXXADO according to the printed instructions on the carton and the Instructions for Use.
- •
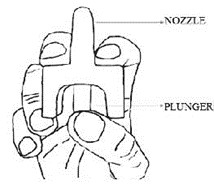
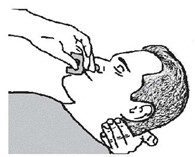
- Place the patient in the supine position. Prior to administration, be sure the device nozzle is inserted in either nostril of the patient and provide support to the back of the neck to allow the head to tilt back. Do not prime or test the device prior to administration.
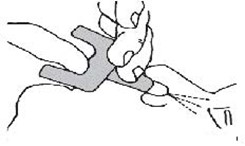
- •
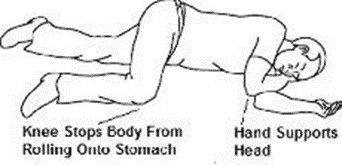
- To administer the dose, press firmly on the device plunger and remove the device nozzle from the nostril after use. Place the patient in recovery position by turning him/her onto their side as shown in the Instructions for Use and call for emergency medical assistance immediately after the first dose of KLOXXADO.
- •
- Administer additional doses of KLOXXADO, using a new nasal spray, every 2 to 3 minutes as needed if the patient does not respond or responds and then relapses into respiratory depression. Administer KLOXXADO in alternate nostrils with each dose [see Dosing and Administration (2.2)].
2.2 Dosing in Adult and Pediatric Patients
Initial Dosing
The recommended initial dose of KLOXXADO in adult and pediatric patients is one spray delivered by intranasal administration into one nostril, which delivers 8 mg of naloxone hydrochloride to adult or pediatric patients.
Repeat Dosing
Seek emergency medical assistance as soon as possible, after administering the first dose of KLOXXADO.
If the desired response is not obtained after 2 or 3 minutes, administer an additional dose using a new KLOXXADO in alternate nostril. If there is still no response and additional doses are available, administer additional doses of KLOXXADO every 2 to 3 minutes, alternating nostrils and using a new KLOXXADO, until emergency medical assistance arrives. The requirement for repeat doses of KLOXXADO depends upon the amount, type, and route of administration of the opioid being antagonized.
If the patient responds to KLOXXADO and subsequently relapses back into respiratory depression before emergency assistance arrives, administer an additional dose using a new KLOXXADO, in the opposite nostril, and continue surveillance of the patient.
Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance.
Reversal of respiratory depression by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists, such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete and require repeated administration of KLOXXADO using a new nasal spray [see Warnings and Precautions(5.2)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
KLOXXADO is supplied as a single-dose, intranasal spray containing 8 mg of naloxone hydrochloride (equivalent to 7.2 mg naloxone) in 0.1 mL. It is a clear, colorless to yellow solution filled into a clear glass vial, stoppered and fitted with a unit-dose nasal spray device.
4. Contraindications
KLOXXADO is contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive to naloxone hydrochloride or to any of the other ingredients in KLOXXADO.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression
The duration of action of most opioids may exceed that of KLOXXADO resulting in a return of respiratory and/or central nervous system depression after an initial improvement in symptoms. Therefore, it is necessary to seek emergency assistance immediately after administration of the first dose of KLOXXADO and to keep the patient under continued surveillance. Administer additional doses of KLOXXADO if the patient is not adequately responding or responds and then relapses back into respiratory depression, as necessary [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measure may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance.
5.2 Risk of Limited Efficacy with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonist/Antagonists
Reversal of respiratory depression by partial agonists or mixed/antagonists such as buprenorphine and pentazocine may be incomplete. Larger or repeat doses of naloxone hydrochloride may be required to antagonize buprenorphine because the latter has a long duration of action due to its slow rate of binding and subsequent slow dissociation from the opioid receptor [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Buprenorphine antagonism is characterized by a gradual onset of the reversal effects and a decreased duration of action of the normally prolonged respiratory depression.
5.3 Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal
The use of KLOXXADO in patients who are opioid-dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal characterized by the following signs and symptoms: body aches, diarrhea, tachycardia, fever, runny nose, sneezing, piloerection, sweating, yawning, nausea or vomiting, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, shivering or trembling, abdominal cramps, weakness, and increased blood pressure. In neonates, opioid withdrawal may be life-threatening if not recognized and properly treated and may include the following signs and symptoms: convulsion, excessive crying, and hyperactive reflexes. Monitor the patient for the development of the signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
Abrupt postoperative reversal of opioid depression after using naloxone hydrochloride may result in nausea, vomiting, sweating, tremulousness, tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, seizures, ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, pulmonary edema, and cardiac arrest. Death, coma, and encephalopathy have been reported as sequelae of these events. These events have primarily occurred in patients who had pre-existing cardiovascular disorders or received other drugs that may have similar adverse cardiovascular effects. Monitor patients with pre-existing cardiac disease or patients who have received medications with potential adverse cardiovascular effects for hypotension, ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, and pulmonary edema in an appropriate healthcare setting. It has been suggested that the pathogenesis of pulmonary edema associated with the use of naloxone hydrochloride is similar to neurogenic pulmonary edema, i.e., a centrally mediated massive catecholamine response leading to a dramatic shift of blood volume into the pulmonary vascular bed resulting in increased hydrostatic pressures.
There may be clinical settings, particularly the postpartum period in neonates with known or suspected exposure to maternal opioid use, where it is preferable to avoid the abrupt precipitation of opioid withdrawal symptoms. In these settings, consider use of an alternative, naloxone-containing product that can be titrated to effect and, where applicable, dosed according to weight [see Use in Specific Population (8.4)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two pharmacokinetic studies a total of 47 healthy adult volunteers were exposed to a single dose of KLOXXADO, one spray in one nostril. The following adverse reactions were reported in two subjects each: abdominal pain, asthenia, dizziness, headache, nasal discomfort, and presyncope. On local tissue assessments for nasal irritation, signs of nasal inflammation and nasal congestion were observed.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events have been identified during the post-approval use of naloxone hydrochloride injection in the postoperative setting. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: hypotension, hypertension, ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, dyspnea, pulmonary edema, and cardiac arrest. Death, coma, and encephalopathy have been reported as sequelae of these events. Excessive doses of naloxone hydrochloride in postoperative patients have resulted in significant reversal of analgesia and have caused agitation.
Abrupt reversal of opioid effects in persons who were physically dependent on opioids has precipitated an acute withdrawal syndrome. Signs and symptoms have included: body aches, fever, sweating, runny nose, sneezing, piloerection, yawning, weakness, shivering or trembling, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, abdominal cramps, increased blood pressure, tachycardia. In some patients, there was aggressive behavior upon abrupt reversal of an opioid overdose. In the neonate, opioid withdrawal has included: convulsions, excessive crying, hyperactive reflexes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
The following most frequently reported events (in decreasing frequency) have been identified primarily during post-approval use of naloxone hydrochloride (all routes of administration): withdrawal syndrome, vomiting, nonresponsiveness to stimuli, drug ineffective, agitation, somnolence, and loss of consciousness.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from retrospective cohort studies on naloxone use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Naloxone may precipitate opioid withdrawal in the pregnant woman and fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Considerations]. In animal reproduction studies, no embryotoxic or teratogenic effects were observed in mice and rats treated with naloxone hydrochloride during the period of organogenesis at doses equivalent to 3-times and 6-times, respectively, a human dose of 16 mg/day (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Maternal and Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Naloxone hydrochloride crosses the placenta, and may precipitate withdrawal in the fetus, as well as in the opioid-dependent mother [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. The fetus should be evaluated for signs of distress after KLOXXADO is used. Careful monitoring is needed until the fetus and mother are stabilized.
Data
Animal Data
Naloxone hydrochloride was administered during organogenesis to mice and rats at doses 3-times and 6-times, respectively, a human dose of 16 mg (from two nasal sprays of KLOXXADO) based on body surface area comparison. These studies demonstrated no embryotoxic or teratogenic effects due to naloxone hydrochloride.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of naloxone in human milk, the effects of naloxone on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Studies in nursing mothers have shown that naloxone does not affect prolactin or oxytocin hormone levels. Naloxone is minimally orally available and is unlikely to affect the breastfed infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of KLOXXADO has been established in pediatric patients of all ages for known or suspected opioid overdose as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression. Use of naloxone hydrochloride in pediatric patients is supported by evidence from adult bioavailability studies with additional evidence from the reported safe and effective use of other naloxone hydrochloride products. No pediatric studies were conducted for KLOXXADO.
Absorption of naloxone hydrochloride following intranasal administration in pediatric patients may be erratic or delayed. Even when the opiate-intoxicated pediatric patient responds appropriately to naloxone hydrochloride, he/she must be carefully monitored for at least 24 hours, as a relapse may occur as naloxone hydrochloride is metabolized.
In opioid-dependent pediatric patients, (including neonates), administration of naloxone hydrochloride may result in an abrupt and complete reversal of opioid effects, precipitating an acute opioid withdrawal syndrome. There may be clinical settings, particularly the postpartum period in neonates with known or suspected exposure to maternal opioid use, where it is preferable to avoid the abrupt precipitation of opioid withdrawal symptoms. Unlike acute opioid withdrawal in adults, acute opioid withdrawal in neonates manifesting as seizures may be life-threatening if not recognized and properly treated. Other signs and symptoms in neonates may include excessive crying and hyperactive reflexes. In these settings where it may be preferable to avoid the abrupt precipitation of acute opioid withdrawal symptoms, consider use of an alternative, naloxone hydrochloride product that can be dosed according to weight and titrated to effect [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Also, in situations where the primary concern is for infants at risk for opioid overdose, consider whether the availability of alternate naloxone-containing products may be better suited than KLOXXADO.
Juvenile Animal Study
In a juvenile animal study, male and female juvenile rats were administered a single intranasal dose of saline, vehicle consisting of 20% alcohol and 5% propylene glycol, or naloxone (123 mg/kg, 185 mg/kg, and 246 mg/kg) on postnatal day 7 (PND 7). There were no test article-related findings on sexual maturation, neuroapoptosis, or on a limited number of neurocognitive endpoints which included social interactions as well as learning and memory. The no-effect dose level for neurodevelopmental toxicity was the high dose tested, which is 6.8-times a neonate dose from two nasal sprays of KLOXXADO based on body surface area comparison and a neonate weight of 2.5 kg.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of KLOXXADO did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
11. Kloxxado Description
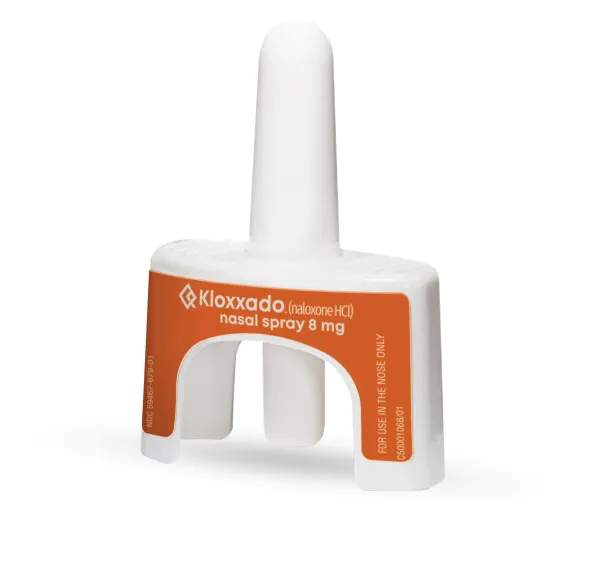
KLOXXADO (naloxone hydrochloride) nasal spray is an opioid antagonist supplied in a pre-filled intranasal device designed to deliver a single dose of 8 mg of naloxone hydrochloride (equivalent to 7.2 mg naloxone) in 0.1mL.
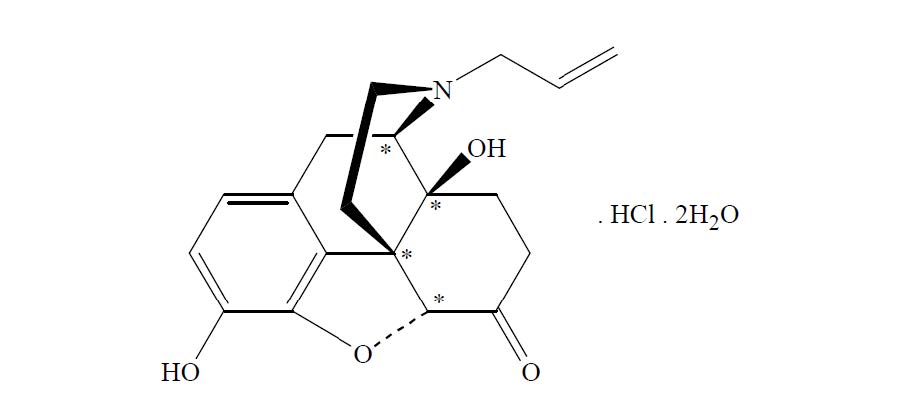
Chemically, naloxone hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride with molecular weight of 363.84 g/mol.
Its molecular formula is C19H21NO4.HCl, and it has the following chemical structure, as shown below.
Naloxone hydrochloride occurs as a white to slightly off-white powder, and is soluble in water, in dilute acids, and in strong alkali; slightly soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in ether and in chloroform.
The inactive ingredients in KLOXXADO include: dehydrated alcohol (20% (w/w)), edetate disodium dihydrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid to adjust pH. The pH range is from 4.0 to 5.5.
12. Kloxxado - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Naloxone hydrochloride is an opioid antagonist that antagonizes opioid effects by competing for the same receptor sites. Administration of naloxone hydrochloride reverses the effects of opioids, including respiratory depression, sedation and hypotension. It can also reverse the psychotomimetic and dysphoric effects of agonist-antagonists such as pentazocine.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
When naloxone hydrochloride is administered intravenously, the onset of action is generally apparent within two minutes. The time to onset of action is shorter for intravenous compared to subcutaneous or intramuscular routes of administration. The duration of action is dependent upon the dose and route of administration of naloxone hydrochloride.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
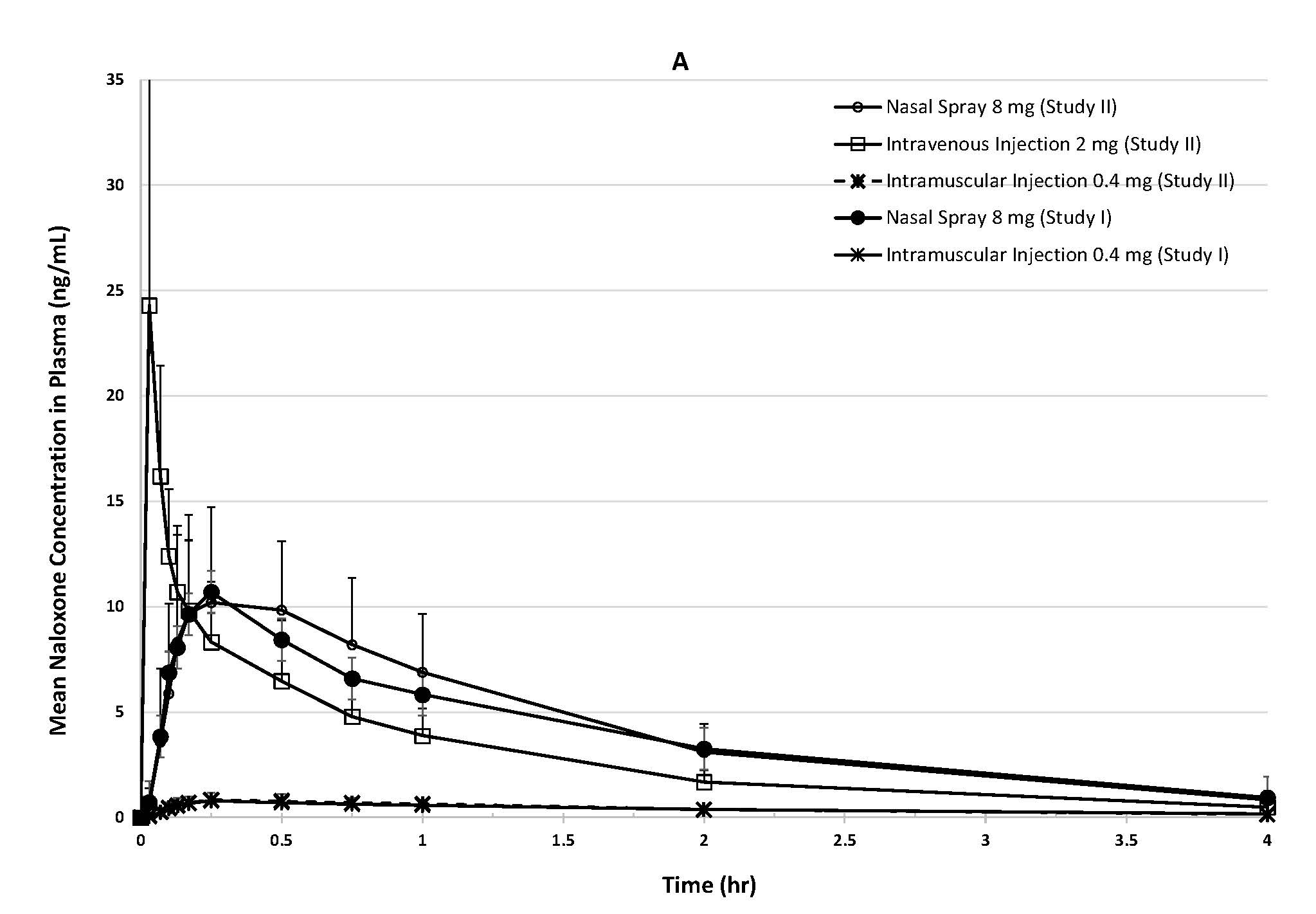
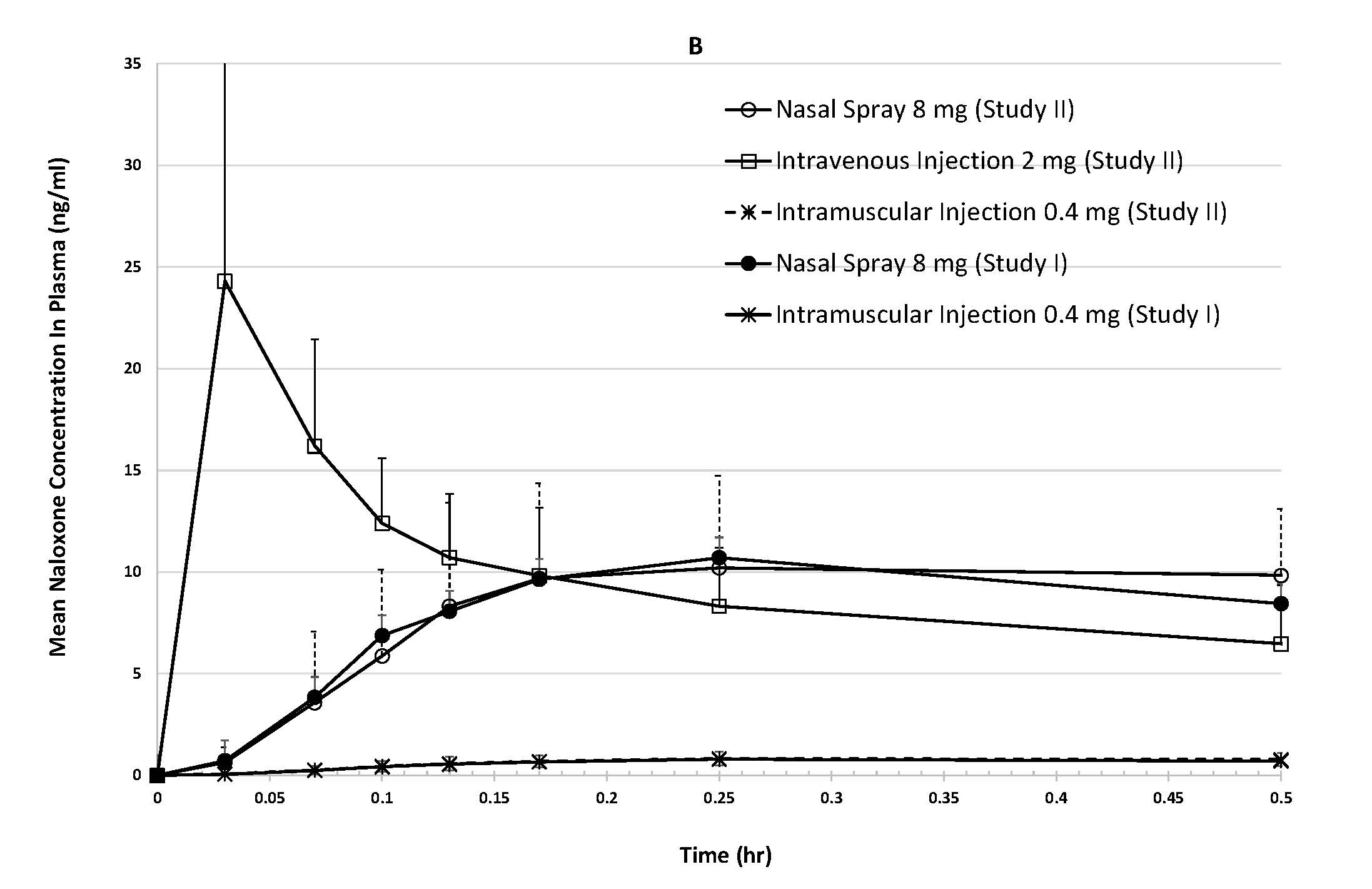
In two pharmacokinetic studies in up to 24 healthy adult volunteers for each study, the bioavailability (BA) of a single 8 mg dose (one spray) of KLOXXADO was compared to a single 0.4 mg intramuscular dose and a single 2 mg intravenous dose of naloxone. Naloxone plasma concentration versus time profiles are shown in Figure 1. The pharmacokinetic parameters of naloxone are summarized in Table 1.
Figure 1: Mean ± SD Plasma Concentration-Time Profiles of Naloxone Following A Single Dose of Intranasal versus Intramuscular/Intravenous Administration in Healthy Subjects. (A:0-4 h and B: 0-30 min.)
Table 1: Mean (CV%) Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Naloxone Following a Single Dose of Intranasal and Intramuscular/Intravenous Administration in Healthy Subjects
| Parameter | KLOXXADO
8 mg | Intramuscular Injection
0.4 mg | Intravenous Injection 2 mg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Study |
Study I |
Study II |
Study I |
Study II |
Study II |
|
N |
24 |
23* |
24 |
23* |
24 |
|
Tmax(h)† |
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
NA |
|
Cmax (ng/mL) |
12.3 (55.4) |
12.8 (37.0) |
0.876 (36.7) |
0.910 (36.8) |
26.2 (82.4)‡ |
|
AUClast
|
18.0 (29.6) |
18.4 (33.4) |
1.82 (24.0) |
1.87 (24.7) |
12.7 (27.6) |
|
AUC0-inf(ng•h/mL) |
16.7 (31.9)§ |
19.0 (32.7)¶ |
1.94 (20.9)# |
1.95 (21.9) |
12.8 (27.5) |
|
t1/2 (h) |
2.69 (69.9) |
1.76 (39.7)¶ |
1.41 (20.0)# |
1.40 (38.9) |
1.22 (16.4) |
|
Dose normalized Relative BA (%)
|
41.6 |
47.4 |
100 |
100 |
NA |
|
Dose normalized Absolute BA (%)
|
NA |
36.6 |
NA |
77.2 |
100 |
|
NA= Not applicable |
|||||
Absorption
The median Tmax (15 min) for naloxone following administration of a single dose of 8 mg KLOXXADO nasal spray was the same as following administration of a single intramuscular dose of 0.4 mg naloxone hydrochloride.
The dose normalized relative bioavailability of naloxone following administration of a single dose of 8 mg KLOXXADO was 42 to 47% as compared to following administration of a single intramuscular dose of 0.4 mg naloxone hydrochloride. The absolute bioavailability of naloxone following administration of a single dose of 8 mg KLOXXADO nasal spray was 37% as compared to following administration of a single intravenous dose of 2 mg naloxone hydrochloride.
Distribution
Following parenteral administration, naloxone is distributed in the body and readily crosses the placenta. Plasma protein binding occurs but is relatively weak. Plasma albumin is the major binding constitute, but significant binding of naloxone also occurs to plasma constituents other than albumin. It is not known whether naloxone is excreted into human milk.
Elimination
Following a single intranasal administration of KLOXXADO, the mean half-life (t1/2) of naloxone in plasma was 1.8 (39.7% CV) to 2.7 (69.6% CV) hours. The mean t1/2 was 1.4 (38.9% CV) to 1.4 (20.0% CV) hours for a 0.4 mg naloxone hydrochloride intramuscular injection and 1.2 (16.4% CV) hours for a 2 mg naloxone hydrochloride intravenous injection. In a neonatal study of naloxone hydrochloride the mean (±SD) plasma half-life was observed to be 3.1 ± 0.5 hours.
Metabolism
Naloxone hydrochloride is metabolized in the liver, primarily by glucuronide conjugation, with naloxone-3-glucoronide as the major metabolite.
Excretion
After an oral or intravenous dose, about 25 to 40% of naloxone is excreted as metabolites in urine within 6 hours, about 50% in 24 hours, and 60 to 70% in 72 hours.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Studies in animals to assess the carcinogenic potential of naloxone have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Naloxone was weakly positive in the Ames mutagenicity and in the in vitro human lymphocyte chromosome aberration test but was negative in the in vitro Chinese hamster V79 cell HGPRT mutagenicity assay and in the in vivo rat bone marrow chromosome aberration study.
Impairment of Fertility
Reproduction studies conducted in mice and rats at doses 3-times and 6-times, respectively, a human dose of 16 mg/day (from two nasal sprays of KLOXXADO) based on body surface area comparison, demonstrated no adverse effects on fertility of naloxone hydrochloride.
16. How is Kloxxado supplied
KLOXXADO (naloxone hydrochloride) nasal spray is a clear, colorless to yellow solution supplied in a single-dose spray device that consists of a stoppered glass vial encased in a container holder fitted with a spray actuator, cannula, and spray pin. It delivers a single dose of 8 mg of naloxone hydrochloride (equivalent to 7.2 mg naloxone) in 0.1 mL. Each KLOXXADO carton contains two individual blisters sealed with a paper backing with a “peel off” feature. The carton contains abbreviated instructions-for-use printed on the back. In addition, a quick instructions leaflet is attached to the bottom of each individual blister.
1 Carton containing two nasal spray devices: NDC# 59467-679-01
Not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
Store KLOXXADO in the blister and cartons provided.
Store at 20 to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF), with excursions permitted to 40°C (104°F) and to 5°C (41°F). Do not store at or above 40°C (104°F). Do not freeze. Protect from light.
KLOXXADO freezes at temperatures below -15°C (5°F). If this happens, the device will not spray. If KLOXXADO is frozen and is needed in an emergency, do NOT wait for KLOXXADO to thaw. Get emergency medical help right away. However, KLOXXADO may be thawed by allowing it to sit at room temperature for 15 minutes, and it may still be used if it has been thawed after being previously frozen.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient and family members or caregivers to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Recognition of Opioid Overdose
Inform patients and their family members or caregivers about how to recognize the signs and symptoms of an opioid overdose such as the following:
- •
- Extreme somnolence – inability to awaken a patient verbally or upon a firm sternal rub.
- •
- Respiratory depression – this can range from slow or shallow respiration to no respiration in a patient who is unarousable.
- •
- Other signs and symptoms that may accompany somnolence and respiratory depression include the following:
- •
- Miosis
- •
- Bradycardia and/or hypotension
Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers that, because the duration of action of most opioids may exceed that of KLOXXADO, they must seek immediate emergency medical assistance after the first dose of KLOXXADO and keep the patient under continued surveillance [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Limited Efficacy for/with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonist/Antagonists
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers that the reversal of respiratory depression caused by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists, such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete and may require higher doses of naloxone hydrochloride or repeated administration of KLOXXADO, using a new nasal spray each time [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers that the use of KLOXXADO in patients who are opioid dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Adverse Reactions (6)].
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers to:
- •
- Ensure KLOXXADO is present and readily available in locations where a person may be intentionally or accidentally exposed to an opioid overdose (i.e., opioid emergencies).
- •
- Administer KLOXXADO as quickly as possible if a patient is unresponsive and an opioid overdose is suspected, even when in doubt, because prolonged respiratory depression may result in damage to the central nervous system or death. KLOXXADO is not a substitute for emergency medical care [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- •
- Lay the patient on their back and administer KLOXXADO into one nostril while providing support to the back of the neck to allow the head to tilt back [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- •
- Use each nasal spray only one time, DO NOT test or prime prior to use[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- •
- Place patient in a recovery position by turning him/her to their side as shown in the Instructions for Use and call for emergency medical assistance immediately after administration of the first dose of KLOXXADO. Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- •
- Monitor patients and administer additional dose of KLOXXADO using a new KLOXXADO every 2 to 3 minutes, if the patient is not responding or responds and then relapses back into respiratory depression. Administer KLOXXADO in alternate nostrils with each dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- •
- Replace KLOXXADO before its expiration date.
Distr. by: Hikma
Specialty USA Inc.
Columbus, OH 43228
C50001066/01
Revised April 2021
KLOXXADOTM is a trademark of Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Patient Package Insert
|
PATIENT INFORMATION KLOXXADOTM (Kloks-AH-doh) (naloxone hydrochloride) nasal spray |
|
|
You and your family members or caregivers should read this Patient Information leaflet before an opioid emergency happens. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about KLOXXADO nasal spray? KLOXXADO nasal spray is used to temporarily reverse the effects of opioid medicines. The medicine in KLOXXADO nasal spray has no effect in people who are not taking opioid medicines. Always carry KLOXXADO nasal spray with you in case of an opioid emergency.
|
|
|
What is KLOXXADO nasal spray?
|
|
|
Do not use KLOXXADO nasal spray:
|
|
|
Before using KLOXXADO nasal spray, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
|
|
How should I use KLOXXADO nasal spray? Read the “Instructions for Use” at the end of this Patient Information leaflet for detailed information about the right way to use KLOXXADO nasal spray.
|
|
|
What are the possible side effects of KLOXXADO nasal spray? KLOXXADO nasal spray may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
|
|
|
In infants under 4 weeks old who have been receiving opioids regularly, sudden opioid withdrawal may be lifethreatening if not treated the right way. Signs and symptoms include: seizures, crying more than usual, and increased reflexes. The most common side effects of KLOXXADO in adults include: stomach-area (abdomen) pain, weakness, dizziness, headache, nose (nasal) discomfort and a feeling like you are going to faint. These are not all of the possible side effects of KLOXXADO nasal spray. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
|
How should I store KLOXXADO nasal spray?
Keep KLOXXADO nasal spray and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of KLOXXADO nasal spray. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use KLOXXADO nasal spray for a condition for which it was not prescribed. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about KLOXXADO nasal spray that is written for health professionals. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in KLOXXADO nasal spray? Active ingredient: naloxone hydrochloride Inactive ingredients: dehydrated alcohol (20% (w/w)),edetate disodium dihydrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid to adjust pH. KLOXXADO nasal spray is not made with natural rubber latex. |
|
|
Distributed by: Hikma Specialty USA Inc. Columbus, OH 43228 C50001066/02 KLOXXADOTM nasal spray is a trademark of Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. For more information, visit www.Hikma.com or call Hikma Specialty USA Inc. at 1-800-962-8364. |
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: April 2021
Instructions for Use
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: April 2021
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
KLOXXADOTM (naloxone HCl) nasal spray, 8 mg - Folding Carton
NDC # 59467-679-01
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
KLOXXADOTM (naloxone HCl) nasal spray, 8 mg – Foil Peel Backing
NDC # 59467-679-01
| KLOXXADO
naloxone hcl spray |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Hikma Specialty USA Inc. (078883518) |
| Registrant - Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. (080189610) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| West-Ward Columbus Inc. | 058839929 | MANUFACTURE(59467-679) | |
Frequently asked questions
- How long does Narcan (naloxone) block opiates?
- How does Narcan (naloxone) work in an overdose?
- How do I get free Narcan emergency kits?
- What are the different types of buprenorphine/naloxone?
- How do you administer Narcan (naloxone)?
- Is naloxone an addictive drug?
- What's the difference between naltrexone and naloxone?
More about Kloxxado (naloxone)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1)
- Drug images
- Latest FDA alerts (2)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: antidotes
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Professional resources
Other brands
Narcan, RiVive, Evzio, Rezenopy, Zimhi