Brexafemme: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: ibrexafungerp
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Drug class: Miscellaneous antifungals
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 10, 2024.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
- Medication Guide
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BREXAFEMME® (ibrexafungerp tablets), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
WARNING: RISK OF EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for the complete boxed warning.
-
BREXAFEMME is contraindicated in pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm based on findings from animal reproductive studies. (4, 5.1)
-
For females of reproductive potential, verify that the patient is not pregnant prior to initiating treatment. Reassessing pregnancy status prior to each dose is recommended when BREXAFEMME is used monthly for 6 months for reduction in the incidence of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC). (2.3, 5.1)
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) and throughout the 6-month treatment period for reduction in the incidence of RVVC with BREXAFEMME and for 4 days after the last dose. (5.1, 8.3)
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Brexafemme
Brexafemme Dosage and Administration
-
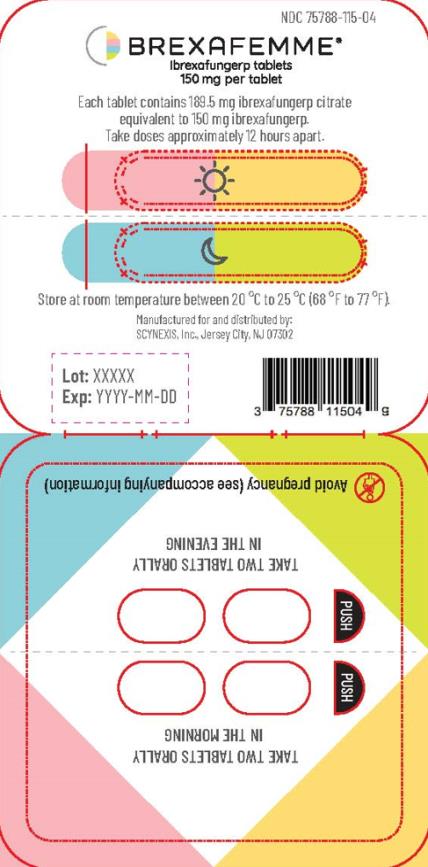
Treatment of VVC: The recommended dosage of BREXAFEMME in adult and post-menarchal pediatric females is 300 mg (two tablets of 150 mg) administered approximately 12 hours apart (e.g., in the morning and in the evening) for one day, for a total treatment dosage of 600 mg (four 150 mg tablets). (
2.1)
-
Reduction in the incidence of RVVC: The recommended dosage of BREXAFEMME in adult and post-menarchal females is 300 mg (two tablets of 150 mg) administered approximately 12 hours apart (e.g., in the morning and in the evening) for one day, for a total daily dosage of 600 mg (four 150 mg tablets) monthly for six months. (
2.1)
- BREXAFEMME may be taken with or without food. ( 2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 150 mg of ibrexafungerp ( 3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
-
Treatment of VVC: The most frequent adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%) reported were diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness, and vomiting. (
6.1)
- Reduction in the incidence of RVVC: The most frequent adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%) reported were headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, urinary tract infection and fatigue. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact SCYNEXIS, Inc. at 1-888-982-7299 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors increases the exposure of ibrexafungerp. Reduce BREXAFEMME dose with concomitant use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor to 150 mg twice daily for one day. (
2.2,
7)
- Concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inducers may significantly reduce the exposure of ibrexafungerp. Avoid concomitant administration of BREXAFEMME with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. ( 7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2022
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
-
BREXAFEMME is contraindicated in pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm based on findings from animal reproductive studies [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
For females of reproductive potential, verify that the patient is not pregnant prior to initiating BREXAFEMME treatment. Reassessing pregnancy status prior to each dose is recommended when BREXAFEMME is used monthly for 6 months for reduction in the incidence of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) and throughout the 6-month treatment period for reduction in the incidence of RVVC with BREXAFEMME and, for 4 days after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
1. Indications and Usage for Brexafemme
2. Brexafemme Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Treatment of VVC: The recommended dosage of BREXAFEMME in adult and post-menarchal pediatric females is 300 mg (two 150 mg tablets) administered approximately 12 hours apart (e.g., in the morning and in the evening) for one day, for a total daily dosage of 600 mg (four 150 mg tablets).
Reduction in the Incidence of RVVC: The recommended dosage of BREXAFEMME to prevent recurrences is 300 mg (two 150 mg tablets) administered approximately 12 hours apart (e.g., in the morning and in the evening) for one day, for a total daily dosage of 600 mg (four 150 mg tablets) monthly for six months.
BREXAFEMME may be taken with or without food.
2.2 Dosage Modifications in Patients due to Concomitant Use of a Strong Inhibitor of Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes (CYP) 3A
With concomitant use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, administer BREXAFEMME 150 mg approximately 12 hours apart (e.g., in the morning and in the evening) for one day. No dosage adjustment is warranted in patients with concomitant use of a weak or moderate CYP3A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Pregnancy Evaluation Prior to Initiating Treatment
For females of reproductive potential, verify that the patient is not pregnant prior to initiating treatment with BREXAFEMME. Reassessment of pregnancy status prior to each dose is recommended when BREXAFEMME is used monthly for 6 months for reduction in the incidence of RVVC [see Contraindications (4), Warning and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
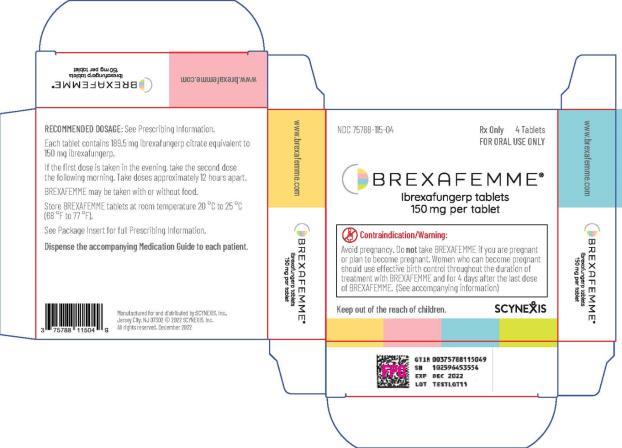
BREXAFEMME tablets are purple, oval, biconvex shaped tablets debossed with 150 on one side and SCYX on the other side containing 150 mg of ibrexafungerp.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies, BREXAFEMME use is contraindicated in pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm. In animal reproduction studies, ibrexafungerp administered orally to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis was associated with fetal malformations including absent forelimb(s), absent hindpaw, absent ear pinna, and thoracogastroschisis at dose exposures greater or equal to approximately 5 times the human exposure at the recommended human dose (RHD).
For females of reproductive potential, verify that the patient is not pregnant prior to initiating treatment with BREXAFEMME. Reassessment of pregnancy status prior to each dose is recommended when BREXAFEMME is used monthly for 6 months for reduction in the incidence of RVVC. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment of VVC and throughout the 6-month treatment period for reduction in the incidence of RVVC with BREXAFEMME and, for 4 days after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Treatment of VVC
A total of 545 patients were exposed to BREXAFEMME in two clinical trials of post-menarchal females with VVC (Trial 1 and Trial 2). The patients were treated with BREXAFEMME 300 mg (two 150 mg tablets) twice a day, 12 hours apart, for one day. The patients were 18 to 76 years of age (mean 34 years); 69% were White and 28% were Black or African American; 18% were of Hispanic or Latina ethnicity.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are presented in Table 1.
There were no serious adverse reactions and 2 out of 545 (0.4%) patients discontinued treatment with BREXAFEMME due to vomiting (1 patient) and dizziness (1 patient).
| Adverse Reaction | BREXAFEMME
N = 545 n (%) | Placebo
N = 275 n (%) |
| Diarrhea
Nausea Abdominal pain 1 Dizziness 2 Vomiting | 91 (16.7%)
65 (11.9%) 62 (11.4%) 18 (3.3%) 11 (2.0%) | 9 (3.3%)
11 (4.0%) 14 (5.1%) 7 (2.5%) 2 (0.7%) |
1 Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, and abdominal discomfort
2 Includes dizziness and postural dizziness
Other Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions occurred in < 2% of patients receiving BREXAFEMME in Trial 1 and Trial 2: dysmenorrhea, flatulence, back pain, elevated transaminases, vaginal bleeding, rash/hypersensitivity reaction.
Reduction in the Incidence of RVVC
A total of 130 patients were exposed to BREXAFEMME in a clinical trial of post-menarchal females with RVVC (Trial 3). The patients were treated with BREXAFEMME 300 mg (two 150 mg tablets) twice a day, 12 hours apart, for one day, monthly for six consecutive months. The patients were 18 to 65 years of age (mean 34 years), of which, 59% of patients were between 18 to 35 years, and 41% between 36 to 65 years. Ninety two percent (92%) were White, 7% were Black or African American, and 1% were Asian. Nine percent (9%) of patients were of Hispanic or Latina ethnicity.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are presented in Table 2.
There were no serious adverse reactions and no patients discontinued treatment with BREXAFEMME due to adverse reaction.
| Adverse Reaction1 | BREXAFEMME
N = 130 n (%) | Placebo
N = 130 n (%) |
| Headache
Abdominal pain 2 Diarrhea Nausea Urinary tract infection Fatigue | 23 (17.6)
13 (10.0) 10 (7.7) 7 (5.4) 5 (3.8) 4 (3.1) | 10 (7.6)
9 (6.9) 5 (3.8) 5 (3.8) 1(0.8) 0 |
1 A single patient may have had multiple instances of adverse reactions. Only one episode of adverse reaction is counted per patient
2 Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, and abdominal discomfort
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
Ibrexafungerp is a substrate of CYP3A4. Drugs that inhibit or induce CYP3A may alter the plasma concentrations of ibrexafungerp and affect the safety and efficacy of BREXAFEMME [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
| Concomitant Drugs | Effect on Ibrexafungerp Concentration | Recommendation |
| Strong CYP3A inhibitors:
(e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole) | Significantly increased | Reduce the BREXAFEMME dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] |
| Strong and Moderate CYP3A inducers:
(e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort, long acting barbiturates, bosentan, efavirenz, or etravirine) | Not studied in vivo or in vitro, but likely to result in significant reduction
| Avoid concomitant administration |
Ibrexafungerp is an inhibitor of CYP3A4, P-gp and OATP1B3 transporter [(see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. However, given the short treatment duration for VVC, the effect of BREXAFEMME on the pharmacokinetics of substrates of CYP3A4, P-gp and OATP1B3 transporters is not considered to be clinically significant.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies, BREXAFEMME use is contraindicated in pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm. In pregnant rabbits, oral ibrexafungerp administered during organogenesis was associated with rare malformations including absent forelimb(s), absent hindpaw, absent ear pinna, and thoracogastroschisis at dose exposures greater or equal to approximately 5 times the human exposure at the RHD. Oral ibrexafungerp administered to pregnant rats during organogenesis was not associated with fetal toxicity or increased fetal malformations at a dose exposure approximately 5 times the human exposure at the RHD (see Data). Available data on BREXAFEMME use in pregnant women are insufficient to draw conclusions about any drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
There is a pregnancy safety study for BREXAFEMME. If BREXAFEMME is inadvertently administered during pregnancy or if pregnancy is detected within 4 days after a patient receives BREXAFEMME, pregnant women exposed to BREXAFEMME and healthcare providers should report pregnancies to SCYNEXIS, Inc. at 1-888-982-SCYX (7299).
Data
Animal Data
In a rat embryo-fetal study, ibrexafungerp was administered to pregnant rats by oral gavage from gestation days (GDs) 6 through 17 at doses of 10, 20, 35, and 50 mg/kg/day. No fetal malformations or changes in embryo-fetal survival or fetal body weights occurred with any of the doses of ibrexafungerp up to the high-dose of 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the RHD based on plasma AUC comparison).
In an embryo-fetal study in rabbits, ibrexafungerp was administered by oral gavage at doses of 10, 25, and 50 mg/kg/day from GD 7 through GD 19. In the mid-dose group administered 25 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the RHD based on AUC comparison), fetal malformations, including absent ear pinna, craniorachischisis, thoracogastroschisis, trunk kyphosis, absent forelimbs, absent forepaws, and absent hindpaw occurred in a single fetus. Malformations including absent hindpaw and anencephaly occurred with an increased litter incidence in the high-dose group of 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 13 times the RHD based on AUC comparison), and other malformations occurred in single fetuses and litters including absent ear pinna, thoracogastroschisis, absent forelimb, and absent thyroid gland. No changes in embryo-fetal survival or fetal body weights were observed with any of the ibrexafungerp doses, and fetal malformations were not observed with the 10 mg/kg/day dose of ibrexafungerp (approximately 2 times the RHD based on AUC comparison).
In a pre-postnatal study in rats, ibrexafungerp was administered by oral gavage from GD 6 through the lactation period until lactation day 20 in maternal doses of 10, 20, 35, and 50 mg/kg/day. No maternal toxicity or adverse effects on the survival, growth, behavior, or reproduction of first-generation offspring occurred with any of the ibrexafungerp doses up to the high dose of 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the RHD based on AUC comparison).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of ibrexafungerp in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breast-fed infant, or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for BREXAFEMME and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from BREXAFEMME or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data, BREXAFEMME may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
For females of reproductive potential, verify that the patient is not pregnant prior to initiating treatment with BREXAFEMME. Reassessment of pregnancy status prior to each dose is recommended when BREXAFEMME is used monthly for 6 months for reduction in the incidence of RVVC [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
For treatment of VVC, advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with BREXAFEMME and for 4 days after the last dose.
For reduction in the incidence of RVVC, advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception throughout the 6-month treatment period with BREXAFEMME and, for 4 days after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of BREXAFEMME for treatment of VVC have been established in post-menarchal pediatric females. BREXAFEMME is also indicated for the reduction in the incidence of RVVC [ see Indications and Usage (1.1)]. Use of BREXAFEMME in post-menarchal pediatric patients is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of BREXAFEMME in adult non-pregnant women with additional pharmacokinetic and safety data from post-menarchal pediatric females [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of BREXAFEMME have not been established in pre-menarchal pediatric females.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies with ibrexafungerp did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics of ibrexafungerp were observed in geriatric patients compared to younger adults [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of BREXAFEMME is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B).
Administration of BREXAFEMME in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) has not been studied. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
There is no experience with overdosage of BREXAFEMME.
There is no specific antidote for ibrexafungerp. Treatment should be supportive with appropriate monitoring.
11. Brexafemme Description
BREXAFEMME, available as an oral tablet, contains ibrexafungerp citrate, a triterpenoid antifungal agent.
Ibrexafungerp is designated chemically as (1S,4aR,6aS,7R,8R,10aR,10bR,12aR,14R,15R)-15-[(2R)-2-amino-2,3,3-trimethylbutoxy]-1,6a,8,10a-tetramethyl-8-[(2R)-3-methylbutan-2-yl]-14-[5-(pyridine-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-1,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-dodecahydro-2H,4H-1,4a-propanophenanthro[1,2-c]pyran-7-carboxylic acid compound with 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid (1:1) with an empirical formula of C 44H 67N 5O 4 • C 6H 8O 7 and a molecular weight of 922.18 grams per mole. The chemical structure is:
![The chemical structure of Ibrexafungerp is designated chemically as (1S,4aR,6aS,7R,8R,10aR,10bR,12aR,14R,15R)-15-[(2R)-2-amino-2,3,3-trimethylbutoxy]-1,6a,8,10a-tetramethyl-8-[(2R)-3-methylbutan-2-yl]](https://www.drugs.com/pro/images/c33be3a1-c4fd-512c-e053-2995a90a63eb/brexafemme-01.jpg)
• C 6H 8O 7
BREXAFEMME tablet for oral administration is a purple, oval, biconvex shaped, film-coated tablet containing 189.5 mg of ibrexafungerp citrate equivalent to 150 mg of ibrexafungerp. In addition to the active ingredient, the tablet formulation contains butylated hydroxyanisole, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film-coating contains FD&C Blue #2, FD&C Red #40, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose 2910, talc and titanium dioxide.
12. Brexafemme - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Ibrexafungerp exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a concentration of 5 times or greater than that achieved after a single day 300 mg twice daily dose, ibrexafungerp does not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In healthy subjects, ibrexafungerp area under the curve (AUC) and maximal concentration (C max) increased approximately dose-proportionally following single dose administration from 10 to 1600 mg (0.02 to 2.67 times the approved recommended daily dose) and multiple-dose administration from 300-800 mg (0.50 to 1.33 times the approved recommended daily dose).
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis in patients with VVC, the model predicts that 300 mg twice a day for 2 doses achieves a mean (%CV) AUC 0-24 exposure of 6832 (15%) ng•hr/mL and C max of 435 (15%) ng/mL under fasted conditions and a mean AUC 0-24 exposure of 9867 (15%) ng•h/mL and C max of 629 (15%) ng/mL under fed conditions.
Absorption
After oral administration of BREXAFEMME in healthy volunteers, ibrexafungerp generally reaches maximum plasma concentrations 4 to 6 hours after single and multiple dosing.
Effect of Food
Following administration of BREXAFEMME to healthy volunteers, the ibrexafungerp C max increased 32% and the AUC increased 38% with a high fat meal (800-1000 calories; 50% fat), compared to fasted conditions. This exposure change is not considered clinically significant [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Distribution
The mean steady state volume of distribution (Vss) of ibrexafungerp is approximately 600 L. Ibrexafungerp is highly protein bound (greater than 99%), predominantly to albumin. Animal studies demonstrate a 9-fold higher exposure in vaginal tissue than in blood.
Elimination
Ibrexafungerp is eliminated mainly via metabolism and biliary excretion. The elimination half-life is approximately 20 hours.
Metabolism
In vitro studies show that ibrexafungerp undergoes hydroxylation by CYP3A4, followed by glucuronidation and sulfation of a hydroxylated inactive metabolite.
Excretion
Following oral administration of radio-labeled ibrexafungerp to healthy volunteers, a mean of 90% of the radioactive dose (51% as unchanged ibrexafungerp) was recovered in feces and 1% was recovered in urine.
Specific Populations
Post-Menarchal Pediatric Females and Geriatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of ibrexafungerp were not altered in post-menarchal pediatric females (ages 13 to 17 years) or in geriatric patients (ages 65 to 76 years).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of ibrexafungerp were not altered in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) to moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment when the total AUC estimates were compared to healthy subjects.
The impact of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on the pharmacokinetics of ibrexafungerp is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Ibrexafungerp is a substrate of CYP3A4 and P-gp. In vitro, ibrexafungerp is an inhibitor of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, P-gp transporter, and OATP1B3 transporter. Ibrexafungerp is not an inducer of CYP3A4.
The effect of coadministration of drugs on the pharmacokinetics of ibrexafungerp and the effect of ibrexafungerp on the pharmacokinetics of coadministered drugs were studied in healthy subjects.
Effect of Coadministered Drugs on Ibrexafungerp Pharmacokinetics
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Ketoconazole (400 mg once daily for 15 days), a strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitor, increased the ibrexafungerp AUC by 5.8-fold and C max by 2.5-fold [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Diltiazem (240 mg once daily for 15 days) increased the ibrexafungerp AUC by 2.5-fold and C max by 2.2-fold. This exposure change is not considered clinically significant at the approved recommended dosage for VVC.
Proton Pump Inhibitor: Pantoprazole (40 mg once daily for 5 days) decreased ibrexafungerp AUC by approximately 25% and C max by 22%. This exposure change is not considered clinically significant at the approved recommended dosage for VVC.
Effect of Ibrexafungerp on the Pharmacokinetics of Coadministered Drugs
The effects of ibrexafungerp on substrates of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, P-gp, and OATP1B3 transporters were evaluated in studies that included loading doses of ibrexafungerp of 1250 to 1500 mg (2.1 to 2.5 times the approved recommended daily dose) for two days followed by 750 mg (1.25 times the approved recommended daily dose) once daily for 3-7 days.
CYP2C8 substrates: Ibrexafungerp did not increase the AUC 0-inf or C max of rosiglitazone, a moderate sensitive CYP2C8 substrate.
CYP3A4 substrates: Ibrexafungerp resulted in 1.4-fold increase in the AUC 0-inf and no effect on the C max of the sensitive CYP3A4 and P-gp substrate tacrolimus.
P-gp substrates: Ibrexafungerp resulted in a 1.4-fold increase in the AUC 0-48 and a 1.25-fold increase in the C max of the P-gp substrate dabigatran.
OATP1B3 transporters: Ibrexafungerp resulted in a 2.8-fold increase in the AUC 0-24 and a 3.5 fold increase in the C max of the OATP1B3 transporter substrate pravastatin.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Ibrexafungerp, a triterpenoid antifungal agent, inhibits glucan synthase, an enzyme involved in the formation of 1,3-β-D-glucan, an essential component of the fungal cell wall.
Ibrexafungerp has concentration-dependent fungicidal activity against Candida species as measured by time kill studies. Ibrexafungerp retains in vitro antifungal activity when tested at pH 4.5 (the normal vaginal pH).
Resistance
The potential for resistance to ibrexafungerp has been evaluated in vitro and is associated with mutations of the fks-2 gene; the clinical relevance of these findings is unknown. Ibrexafungerp retains activity against most fluconazole resistant Candida spp. No resistance development was observed after monthly BREXAFEMME dosing in patients with RVVC.
Interaction with Other Antifungals
In vitro studies have not demonstrated antagonism between ibrexafungerp and azoles or echinocandins.
Antimicrobial Activity
Ibrexafungerp has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganism both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)]:
Candida albicans
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. Ibrexafungerp has in vitro activity against most isolates of the following microorganisms:
Candida auris
Candida dubliniensis
Candida glabrata
Candida guilliermondii
Candida keyfr
Candida krusei
Candida lusitaniae
Candida parapsilosis
Candida tropicalis
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Two-year carcinogenicity studies of ibrexafungerp have not been performed.
Mutagenesis
No mutagenic or clastogenic effects were detected in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay, and an in vivo bone marrow micronucleus assay in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
In a male and female fertility study in rats, ibrexafungerp was administered to male rats by oral gavage in doses of 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg/day for 28 days before mating and throughout mating and to female rats for 15 days before mating, during mating, and until gestation day (GD) 6. Ibrexafungerp did not impair fertility in either sex at any dose up to the highest dose of 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the RHD based on AUC comparison).
13.2 Animal Toxicity and/or Pharmacology
Daily administration of oral ibrexafungerp for 26 weeks in rats, at the highest dose of 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the RHD based on AUC comparison), was associated with marked, but reversible, phospholipidosis and foamy histiocytes in alveolar tissue in the lung and labored breathing, marked irritation and metaplasia in gastric mucosa, and peripheral nerve degeneration accompanied by hind-limb paralysis.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Treatment of VVC
Two randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials (Trial 1, NCT03734991 and Trial 2, NCT03987620) with a similar design were conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a single day of BREXAFEMME 600 mg (two 150 mg tablets per dose, administered 12 hours apart) for the treatment of VVC. Non-pregnant post-menarchal females with a diagnosis of VVC were eligible. A diagnosis of VVC was defined as (a) minimum composite vulvovaginal signs and symptoms (VSS) score of ≥4 with at least two signs or symptoms having a score of 2 (moderate) or greater; (b) positive microscopic examination with 10% KOH in a vaginal sample revealing yeast forms (hyphae/pseudohyphae) or budding yeasts, and (c) normal vaginal pH (≤4.5). The total composite VSS score was based on the vulvovaginal signs (erythema, edema, excoriation) and vulvovaginal symptoms (itching, burning, or irritation) where each was scored as 0= absent, 1= mild, 2= moderate, or 3= severe. Study visits included the test of cure (TOC, Day 8 to 14) visit and a follow-up (Day 21 to 29) visit. The modified intent to treat (MITT) population included randomized subjects with a baseline culture positive for Candida species who took at least 1 dose of study medication.
Trial 1 was conducted in the United States. The MITT population consisted of 190 patients treated with BREXAFEMME and 100 patients treated with placebo. The average age was 34 years (range 17-67 years), with 91% less than 50 years. Fifty-four percent (54%) were White and 40% were Black or African American, 26% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The average BMI was 30 and 9% had a history of diabetes. The median VSS score at baseline was 9 (range 4-18). The majority (92%) of the subjects were culture-positive with C. albicans.
Trial 2 was conducted in the United States (39%) and Bulgaria (61%). The MITT population consisted of 189 patients treated with BREXAFEMME and 89 patients treated with placebo. The average age was 34 years (range 18-65 years), with 92% less than 50 years. Eighty-one percent (81%) were White and 19% were Black or African American, 10% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The average BMI was 26 and 5% had a history of diabetes. The median VSS score at baseline was 10 (range 4-18). The majority (89%) of the subjects were culture-positive with C. albicans.
Efficacy was assessed by clinical outcome at the TOC visit. A complete clinical response was defined as the complete resolution of signs and symptoms (VSS score of 0). Additional endpoints included a negative culture for Candida spp. at the TOC visit, and clinical outcome at the follow-up visit.
Statistically significantly greater percentages of patients experienced a complete clinical response at TOC, negative culture at TOC, and complete clinical response at follow-up with treatment with BREXAFEMME compared to placebo. The results for the clinical and mycological responses are presented in Table 4.
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||
| BREXAFEMME N = 190
n (%) | Placebo
N = 100 n (%) | BREXAFEMME N = 189
n (%) | Placebo
N = 89 n (%) |
|
| Complete Clinical Response at TOC1 | 95 (50.0) | 28 (28.0) | 120 (63.5) | 40 (44.9) |
| Difference (95% CI)
P-value | 22.0 (10.2, 32.8)
0.001 | 18.6 (6.0, 30.6)
0.009 |
||
| Negative Culture at TOC | 94 (49.5) | 19 (19.0) | 111 (58.7) | 26 (29.2) |
| Difference (95% CI)
P-value | 30.5 (19.4, 40.3)
< 0.001 | 29.5 (17.2, 40.6)
< 0.001 |
||
| Complete Clinical Response at follow-up2 | 113 (59.5) | 44 (44.0) | 137 (72.5) | 44 (49.4) |
| Difference (95% CI)
P-value | 15.5 (3.4, 27.1)
0.007 | 23.1 (10.8, 35.0)
0.006 |
||
1Absence of signs and symptoms (VSS Score of 0) without need for additional antifungal therapy or topical drug therapy for the treatment of vulvovaginal symptoms at test of cure (TOC) visit.
2Absence of signs and symptoms (VSS Score of 0) without need for further antifungal treatment or topical drug therapy for the treatment of vulvovaginal symptoms prior to follow-up visit.
14.2 Reduction in the Incidence of RVVC
A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial (Trial 3, NCT04029116) was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of BREXAFEMME 300 mg (two 150 mg tablets) administered approximately 12 hours apart (e.g., in the morning and in the evening) for one day, for a total daily dosage of 600 mg (four 150 mg tablets) administered once monthly for six months. Trial 3 was conducted in the United States (33%), Bulgaria (28%), Poland (12%), and Russia (28%). Non-pregnant post-menarchal females presenting with a symptomatic VVC episode and a history of recurrent VVC (at least 3 episodes of VVC in the previous 12 months) were eligible. The symptomatic episode at Screening was treated with 3 doses of fluconazole 150 mg 3 days apart.
To be randomized, patients had to have a culture-confirmed VVC episode at Screening and had to achieve significant resolution of their vulvovaginal signs and symptoms (defined as a total composite score ≤ 2 on the VSS Scale) after fluconazole treatment. Patients were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive double-blind BREXAFEMME or placebo administered as a single-day treatment repeated every 4 weeks for a total of 6 single-day treatments. Study visits included the test of cure (TOC) at Week 24 (4 weeks after the last dose) and a follow-up visit at Week 36. The intent to treat (ITT) population was all randomized patients.
The ITT population consisted of 130 patients treated with BREXAFEMME and 130 patients treated with placebo. The average age was 34 years (range 18-65 years) with 95% less than 50 years. Ninety percent (90%) of patients were White, 8% were Black or African American, and 2% were Asian and other race. Eight percent (8%) of patients were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The average BMI of the patient population was 25 and 16.5% were obese (BMI >30).
Efficacy was assessed as the percentage of patients with Clinical Success, defined as subjects with No Culture Proven, Presumed or Suspected Recurrence of VVC requiring antifungal therapy up to TOC at Week 24. Clinical success was also assessed at the Week 36 Follow-up visit.
Statistically significantly greater percentages of patients experienced Clinical Success at TOC compared to placebo. The clinical success rate at TOC was lower for patients in the United States when compared to patients outside the United States (ex-US) for both BREXAFEMME and placebo groups. In both regions, the BREXAFEMME group had a higher clinical success rate compared to placebo (US: 33% vs 23% and ex-US: 81% vs 68% in BREXAFEMME vs placebo arms, respectively) and the difference between the treatment groups was consistent [US: 10.1% (-9.0, 29.1) and ex-US: 12.9% (0.04, 25.7)]. Clinical Success at Week 36 was also greater for BREXAFEMME compared to placebo. The results for clinical success and reasons for clinical failure are presented in Table 5.
| Trial 3 | |||
| BREXAFEMME
N = 130 n (%) | Placebo
N = 130 n (%) | Difference (95% CI)
P-value |
|
| Clinical success at TOC (Week 24) | 85 (65.4) | 69 (53.1) | 12.7 (2.2, 23.1)
0.020 |
| Reasons For Clinical Failure at TOC
Mycologically Proven Recurrence Presumed Recurrence Suspected Recurrence Imputed Recurrence 1 | 30 (23.1)
7 (5.4) 2 (1.5) 6 (4.6) | 47 (36.2)
3 (2.3) 4 (3.1) 7 (5.4) | |
| Clinical success at Week 36 Follow Up Visit | 75 (57.7) | 60 (46.2) | 11.9 (1.1, 22.6)
0.034 |
| Reasons For Clinical Failure at Week-36 Follow-up Visit
Mycologically Proven Recurrence Presumed Recurrence Suspected Recurrence Imputed Recurrence 1 | 37 (28.5)
8 (6.2) 4 (3.1) 6 (4.6) | 51 (39.2)
5 (3.8) 5 (3.8) 9 (6.9) | |
Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; TOC = test of cure.
1Imputed recurrences are subjects whose clinical outcome cannot be determined due to early termination or missing critical efficacy assessment at TOC.
16. How is Brexafemme supplied
16.1 How Supplied
BREXAFEMME (ibrexafungerp tablets) are purple, oval, biconvex shaped tablets debossed with 150 on one side and SCYX on the other side. Each tablet contains 150 mg ibrexafungerp (equivalent to 189.5 mg of ibrexafungerp citrate).
Tablets are packaged in polyvinyl/polyvinylidene chloride child-resistant blister packs, four (4) tablets per pack. (NDC 75788-115-04)
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA approved patient labeling ( Medication Guide)
Risk of Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise patients that BREXAFEMME is contraindicated in pregnancy since it may cause fetal harm.
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Inform females of reproductive potential that their healthcare provider will verify that they are no pregnant prior to initiating BREXAFEMME treatment.
- Advise females of reproductive potential that reassessing pregnancy status prior to each is recommended when BREXAFEMME is used monthly for 6 months for reduction in the incidence of RVVC.
- For treatment of VVC, advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception while taking BREXAFEMME and for 4 days after the last dose
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- For reduction in the incidence of RVVC, advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception throughout the 6-month treatment period with BREXAFEMME and for 4 days after the last dose
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise patients who have inadvertently taken BREXAFEMME during pregnancy that there is a pregnancy safety study that monitors pregnancy outcomes. Encourage these patients to report their pregnancy to SCYNEXIS, Inc. at 1-888-982-7299 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Important Administration Instructions
For treatment of VVC, inform the patient that each BREXAFEMME dose consists of two tablets. A total treatment course for VVC is two doses taken approximately 12 hours apart and consists of a total of four tablets.
For reduction in the incidence of RVVC, inform the patients that the total treatment course is for six months. Each dose consists of two tablets taken approximately 12 hours apart for a total daily dosage of four tablets, taken monthly for six months.
If the first two tablets are taken in the morning, the second two tablets should be taken that same day in the evening. If the first two tablets are taken in the afternoon or evening, the second two tablets should be taken the following morning.
Inform the patient that BREXAFEMME can be taken with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise the patient to inform their health care provider if they are taking any other medications as certain medications can increase or decrease blood concentrations of BREXAFEMME or BREXAFEMME may increase or decrease blood concentrations of certain medications [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Manufactured for:
SCYNEXIS, Inc.
Jersey City, NJ
Patent: www.scynexis.com/product/patent
BREXAFEMME ® is a registered trademark of SCYNEXIS, Inc.
Medication Guide
| MEDICATION GUIDE
BREXAFEMME® [brex a fem] (ibrexafungerp tablets) for oral use |
| What is the most important information I should know about BREXAFEMME?
BREXAFEMME may cause serious side effects, including:
See “Do not take BREXAFEMME if you:” |
What is BREXAFEMME?
|
Do not take BREXAFEMME if you:
|
Before you take BREXAFEMME, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
How should I take BREXAFEMME?
|
What are the possible side effects of BREXAFEMME?
These are not all the possible side effects of BREXAFEMME. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
How should I store BREXAFEMME?
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of BREXAFEMME.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use BREXAFEMME for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give BREXAFEMME to other people even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about BREXAFEMME that is written for health professionals. |
| What are the ingredients in BREXAFEMME?
Active ingredient: ibrexafungerp Inactive ingredients: Tablet core: butylated hydroxyanisole, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. Tablet film coating: FD&C Blue #2, FD&C Red #40, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose 2910, talc and titanium dioxide. BREXAFEMME is a registered trademark of SCYNEXIS, Inc. Manufactured for: SCYNEXIS, Inc., Jersey City, New Jersey, 07302 ©2022 SCYNEXIS, Inc. For more information, call 1-888-982-SCYX (7299) or go to www.brexafemme.com |
This Medication Guide -has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 11/2022
| BREXAFEMME
ibrexafungerp tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - SCYNEXIS, INC. (001073530) |
More about Brexafemme (ibrexafungerp)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (3)
- Drug images
- Latest FDA alerts (1)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: miscellaneous antifungals
- Breastfeeding
- En español