Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: ophthalmic ointment
Drug class: Mydriatics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 29, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ATROPINE SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ATROPINE SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION.
ATROPINE SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, 1%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval 1960
Indications and Usage for Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Ophthalmic solution: 1% atropine sulfate (10mg/mL) (3)
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity or allergic reaction to any ingredient in the formulation (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions that have been reported are eye pain and stinging on administration, blurred vision, photophobia, superficial keratitis, decreased lacrimation, drowsiness, increased heart rate and blood pressure. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alcon Laboratories, Inc., at 1-800-757-9195 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
The use of atropine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) is generally not recommended because of the potential to precipitate hypertensive crisis. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% is indicated for:
2. Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment Dosage and Administration
In individuals from three (3) months of age or greater, 1 drop topically to the cul-de-sac of the conjunctiva, forty minutes prior to the intended maximal dilation time.
In individuals 3 years of age or greater, doses may be repeated up to twice daily as needed.
4. Contraindications
Atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution should not be used in anyone who has demonstrated a previous hypersensitivity or known allergic reaction to any ingredient of the formulation because it may recur.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Photophobia and Blurred Vision
Photophobia and blurred vision due to pupil unresponsiveness and cycloplegia may last up to 2 weeks.
5.2 Elevation of Blood Pressure
Elevation in blood pressure from systemic absorption has been reported following conjunctival instillation of recommended doses of atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution, 1%.
5.3 Increased Adverse Drug Reaction Susceptibility with Certain Central Nervous System Conditions
Individuals with Down syndrome, spastic paralysis, or brain damage are particularly susceptible to central nervous system disturbances, cardiopulmonary, and gastrointestinal toxicity from systemic absorption of atropine.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Photophobia and Blurred Vision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Elevation in Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased Adverse Drug Reaction Susceptibility with Certain Central Nervous System Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
The following adverse reactions have been identified following use of atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
6.1 Ocular Adverse Reactions
Eye pain and stinging occurs upon instillation of atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution. Other commonly occurring adverse reactions include blurred vision, photophobia, superficial keratitis and decreased lacrimation. Allergic reactions such as papillary conjunctivitis, contact dermatitis, and eyelid edema may also occur less commonly.
6.2 Systemic Adverse Reactions
Systemic effects of atropine are related to its anti-muscarinic activity. Systemic adverse events reported include dryness of skin, mouth, and throat from decreased secretions from mucus membranes; drowsiness; restlessness, irritability or delirium from stimulation of the central nervous system; tachycardia; flushed skin of the face and neck.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% administration in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Adequate animal development and reproduction studies have not been conducted with atropine sulfate. In humans, 1% atropine sulfate is systemically bioavailable following topical ocular administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.2 Lactation
There is no information to inform risk regarding the presence of atropine in human milk following ocular administration of Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% to the mother. The effects on breastfed infants and the effects on milk production are also unknown. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Due to the potential for systemic absorption of atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution the use of Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% in children under the age of 3 months is not recommended and the use in children under 3 years of age should be limited to no more than one drop per eye per day. Safety and efficacy in children above the age of 3 months has been established in adequate and well controlled trials.
10. Overdosage
In the event of accidental ingestion or toxic overdosage with atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution supportive care may include a short acting barbiturate or diazepam as needed to control marked excitement and convulsions. Large doses for sedation should be avoided because central depressant action may coincide with the depression occurring late in atropine poisoning. Central stimulants are not recommended.
Physostigmine, given by slow intravenous injection of 1 to 4 mg (0.5 to 1 mg in pediatric populations), rapidly abolishes delirium and coma caused by large doses of atropine. Since physostigmine is rapidly destroyed, the patient may again lapse into coma after one to two hours, and repeated doses may be required.
Artificial respiration with oxygen may be necessary. Cooling measures may be needed to help to reduce fever, especially in pediatric populations.
The fatal pediatric and adult doses of atropine are not known.
11. Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment Description
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% is a sterile topical ophthalmic solution. Each mL of Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% contains 10 mg of atropine sulfate monohydrate equivalent to 9.7 mg/mL of atropine sulfate or 8.3 mg of atropine. Atropine sulfate monohydrate is designated chemically as benzeneacetic acid, α-(hydroxymethyl)-,8-methyl-8-aza-bicyclo-[3.2.1]oct-3-yl ester, endo-(+)-, sulfate(2:1) (salt), monohydrate. Its molecular formula is (C17H23NO3)2 • H2SO4 • H2O and it is represented by the chemical structure:
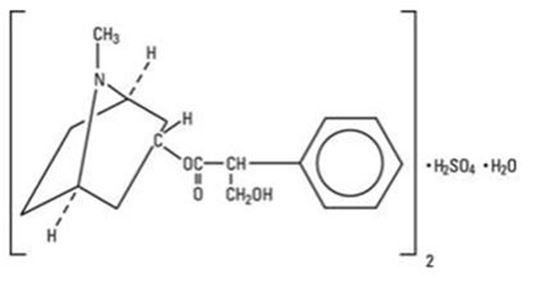
Atropine sulfate monohydrate is colorless crystals or white crystalline powder and has a molecular weight of 694.83.
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% has a pH of 3.5 to 6.0.
Active ingredient: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%
Inactive ingredients: hypromellose, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
12. Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Atropine acts as a competitive antagonist of the parasympathetic (and sympathetic) acetylcholine muscarinic receptors. Topical atropine on the eye induces mydriasis by inhibiting contraction of the circular pupillary sphincter muscle normally stimulated by acetylcholine. This inhibition allows the countering radial pupillary dilator muscle to contract which results in dilation of the pupil. Additionally, atropine induces cycloplegia by paralysis of the ciliary muscle which controls accommodation while viewing objects.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The onset of action after administration of Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% generally occurs in minutes with maximal effect seen in hours and the effect can last multiple days [see Clinical Studies(14)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a study of healthy subjects, after topical ocular administration of 30 μL of atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution, 1%, the mean (± SD) systemic bioavailability of l-hyoscyamine was reported to be approximately 64 ± 29% (range 19% to 95%) as compared to intravenous administration of atropine sulfate. The mean (± SD) time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was approximately 28 ± 27 minutes (range 3 to 60 minutes), and the mean (±SD) peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of l-hyoscyamine was 288 ± 73 pg/mL. The mean (±SD) plasma half-life was reported to be approximately 2.5 ± 0.8 hours.
In a separate study of patients undergoing ocular surgery, after topical ocular administration of 40 μL of atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution, 1%, the mean (± SD) plasma Cmax of l-hyoscyamine was 860 ± 402 pg/mL.
14. Clinical Studies
Topical administration of Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% results in mydriasis and/or cycloplegia, with efficacy demonstrated in both adults and children. The maximum effect for mydriasis is achieved in about 30–40 minutes after administration, with recovery after approximately 7–10 days. The maximum effect for cycloplegia is achieved within 60–180 minutes after administration, with recovery after approximately 7–12 days.
16. How is Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment supplied
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% is supplied sterile in low-density polyethylene plastic DROP-TAINER® dispensers with low-density polyethylene tips and red polypropylene caps as follows:
- 2 mL filled in 4-mL bottles NDC 0065-0817-02
- 5 mL filled in 8-mL bottles NDC 0065-0817-01
Storage: Store Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1% at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). After opening, Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution 1% can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
17. Patient Counseling Information
- Advise patients not to drive or engage in other hazardous activities while pupils are dilated.
- Advise patient that they may experience blurry vision and sensitivity to light and should protect their eyes in bright illumination during dilation. These effects may last up to a couple weeks.
- Advise patients that they may experience drowsiness.
- Advise patients not to touch the dispenser tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
Alcon
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
© 2022 Alcon Inc.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0065-0817-02
For Topical Ophthalmic Use
Alcon
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%
2 mL Sterile
Rx Only
INGREDIENTS: Each mL contains: Active: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%.
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%.
Inactives: hypromellose 0.5%, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing Information.
PRECAUTION: Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
STORAGE: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Read enclosed insert. After opening, Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution 1% can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
Alcon
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
Product of India
300055337-0722
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0065-0817-02
For Topical Ophthalmic Use
Alcon
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%
2 mL Sterile
Rx Only
INGREDIENTS: Each mL contains: Active: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%.
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%.
Inactives: hypromellose 0.5%, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing Information.
PRECAUTION: Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
STORAGE: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Read enclosed insert. After opening, Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution 1% can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
Alcon
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
Product of Germany
300053026-0722
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%
NDC 0065-0817-02
Rx Only
STORAGE: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F).
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
2 mL Sterile
INGREDIENTS: Each mL contains: Active: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%.
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%.
Inactives: hypromellose 0.5%, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing information. FOR TOPICAL OPHTHALMIC USE

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0065-0817-01
For Topical Ophthalmic Use
Alcon
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%
5 mL Sterile
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing Information.
PRECAUTION: Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
STORAGE: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Read enclosed insert. After opening, Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution 1% can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
Rx Only
INGREDIENTS: Each mL contains: Active: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%.
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%.
Inactives: hypromellose 0.5%, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
Alcon
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
Product of Germany
300057551-0722
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0065-0817-01
For Topical Ophthalmic Use
Alcon
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%
5 mL Sterile
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing Information.
PRECAUTION: Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
STORAGE: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Read enclosed insert. After opening, Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution 1% can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
Rx Only
INGREDIENTS: Each mL contains: Active: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%.
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%.
Inactives: hypromellose 0.5%, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
Alcon
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
Product of India
300057552-0722
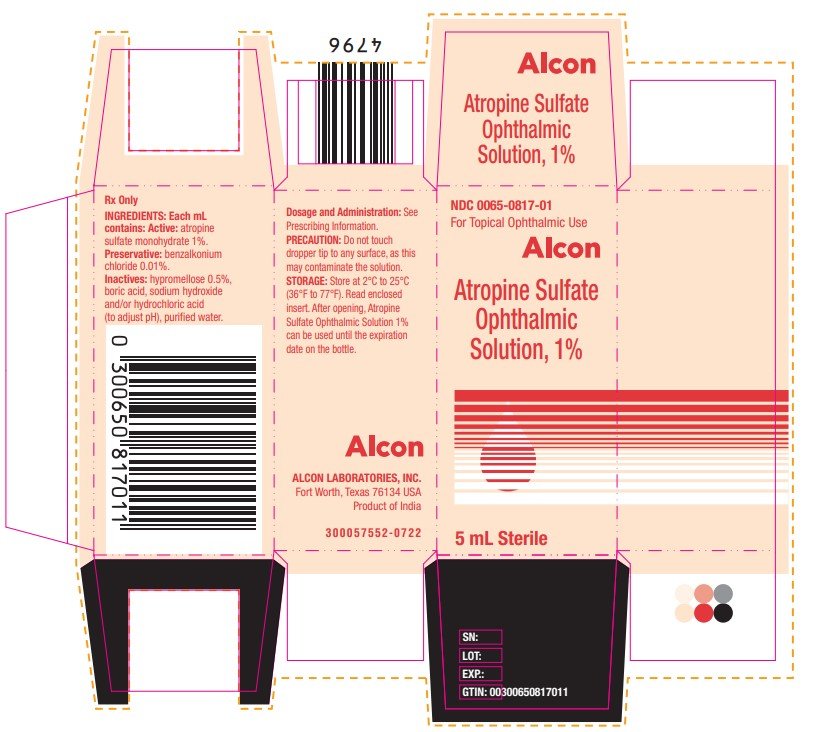
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Atropine Sulfate Ophthalmic Solution, 1%
NDC 0065-0817-01
Sterile 5 mL
Rx Only
INGREDIENTS: Each mL contains: Active: atropine sulfate monohydrate 1%.
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%.
Inactives: hypromellose 0.5%, boric acid, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), purified water.
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing information. FOR TOPICAL OPHTHALMIC USE
STORAGE: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F).
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
300058444-0722

| ATROPINE SULFATE
atropine sulfate solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Alcon Laboratories, Inc. (008018525) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG | 551147440 | api manufacture(0065-0817) , analysis(0065-0817) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laurus Labs Limited | 650751774 | api manufacture(0065-0817) , analysis(0065-0817) | |
More about atropine ophthalmic
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: mydriatics
- Breastfeeding
- En español
