Acular: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: ketorolac tromethamine
Dosage form: ophthalmic solution
Drug class: Ophthalmic anti-inflammatory agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 1, 2025.
On This Page
Highlights of Prescribing Information
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ACULAR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ACULAR.
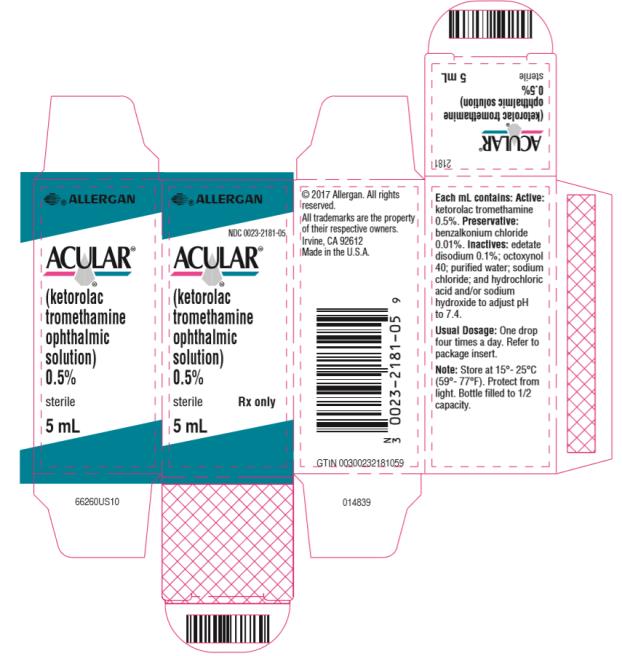
ACULAR® (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) 0.5%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1991
Recent Major Changes
Warnings and Precautions (5.5) 3/2025
Indications and Usage for Acular
Acular Dosage and Administration
- For temporary relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, apply one drop of ACULAR to the affected eye(s) four times a day.
- For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction, apply one drop of ACULAR to the affected eye four times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Ophthalmic solution containing 0.5% (5 mg/mL) ketorolac tromethamine. (3)
- 10 mL size bottle filled with 5 mL of solution
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any component of this product. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most frequent adverse reactions reported by up to 40% of patients participating in clinical trials have been transient stinging and burning on instillation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Acular
ACULAR is indicated for the temporary relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. ACULAR is also indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction.
2. Acular Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Temporary Relief of Ocular Itching Due to Seasonal Allergic Conjunctivitis
The recommended dosage of ACULAR is one drop four times a day to the affected eye(s) for the temporary relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
Treatment of Postoperative Inflammation in Patients Who Have Undergone Cataract Extraction
Apply one drop of ACULAR to the affected eye four times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period for the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction.
2.2 Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
ACULAR has been safely administered in conjunction with other ophthalmic medications such as antibiotics, alpha-agonists, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics. Drops should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
10 mL size bottle filled with 5 mL of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution, 0.5% (5 mg/mL).
4. Contraindications
ACULAR solution is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formulation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Delayed Healing
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
5.2 Cross-Sensitivity or Hypersensitivity
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other NSAIDs. There have been reports of bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma associated with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution in patients who have either a known hypersensitivity to aspirin/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or a past medical history of asthma. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
5.3 Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that ACULAR be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications, which may prolong bleeding time.
5.4 Corneal Effects
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration, or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 1 day prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post-surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
5.5 Risk of Contamination
Avoid allowing the tip of the bottle to contact the eye or surrounding structures because this could cause the tip to become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Delayed Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cross-Sensitivity or Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased Bleeding Time [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Corneal Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most frequent adverse reactions reported with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions have been transient stinging and burning on instillation. These reactions were reported by up to 40% of patients participating in clinical trials.
Other adverse reactions occurring approximately 1% to 10% of the time during treatment with ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions included allergic reactions (including eye swelling, hyperemia, and pruritus), corneal edema, iritis, ocular inflammation, ocular irritation, ocular pain, superficial keratitis, and superficial ocular infections.
Other adverse reactions reported rarely with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions included: corneal infiltrates, corneal ulcer, eye dryness, headaches, and visual disturbance (blurry vision).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% in clinical practice. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the drug.
Eye Disorders: corneal erosion, corneal perforation, corneal thinning, and epithelial breakdown.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma.
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with ACULAR in pregnant women. No evidence of teratogenicity has been observed in rats or rabbits with ACULAR at clinically relevant doses.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Because of the known effects of prostaglandin-inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of the ductus arteriosus), the use of ACULAR during late pregnancy should be avoided.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether ketorolac when given topically is present in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ACULAR is administered to a nursing woman.
11. Acular Description
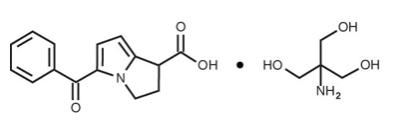
ACULAR (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a member of the pyrrolo-pyrrole group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for topical ophthalmic use. Its chemical name is (±)-5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid, compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (1:1) and it has the following structure:
ACULAR ophthalmic solution is supplied as a sterile isotonic aqueous 0.5% solution, with a pH of 7.4. ACULAR ophthalmic solution contains a racemic mixture of R-(+) and S-(-)- ketorolac tromethamine. Ketorolac tromethamine may exist in three crystal forms. All forms are equally soluble in water. The pKa of ketorolac is 3.5. This white to off-white crystalline substance discolors on prolonged exposure to light. The molecular weight of ketorolac tromethamine is 376.41. The osmolality of ACULAR ophthalmic solution is 290 mOsmol/kg.
Each mL of ACULAR ophthalmic solution contains: Active: ketorolac tromethamine 0.5%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%. Inactives: edetate disodium 0.1%; octoxynol 40; purified water; sodium chloride; hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
12. Acular - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ketorolac tromethamine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug which, when administered systemically, has demonstrated analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-pyretic activity. The mechanism of its action is thought to be due to its ability to inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Two drops of 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution instilled into the eyes of patients 12 hours and 1 hour prior to cataract extraction achieved a mean ketorolac concentration of 95 ng/mL in the aqueous humor of 8 of 9 eyes tested (range 40 to 170 ng/mL).
One drop of 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution was instilled into 1 eye and 1 drop of vehicle into the other eye TID in 26 healthy subjects. Five (5) of 26 subjects had detectable concentrations of ketorolac in their plasma (range 11 to 23 ng/mL) at Day 10 during topical ocular treatment. The range of concentrations following TID dosing of 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution are approximately 4 to 8% of the steady state mean minimum plasma concentration observed following four times daily oral administration of 10 mg ketorolac in humans (290 ± 70 ng/mL).
14. Clinical Studies
Two controlled clinical studies showed that ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution was significantly more effective than its vehicle in relieving ocular itching caused by seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
Two controlled clinical studies showed that patients treated for two weeks with ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution were less likely to have measurable signs of inflammation (cell and flare) than patients treated with its vehicle.
Results from clinical studies indicate that ketorolac tromethamine has no significant effect upon intraocular pressure; however, changes in intraocular pressure may occur following cataract surgery.
16. How is Acular supplied
ACULAR (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is supplied sterile, in white opaque plastic (LDPE) bottles with white droppers, with gray high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
5 mL in 10 mL bottle NDC 0023-2181-05
Storage: Store at 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Protect from light.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Slow or Delayed Healing
Advise patients of the possibility that slow or delayed healing may occur while using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Avoiding Contamination of the Product
Instruct patients to avoid allowing the tip of the bottle to contact the eye or surrounding structures because this could cause the tip to become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
Contact Lens Wear
Advise patients that ACULAR should not be administered while wearing contact lenses.
Intercurrent Ocular Conditions
Advise patients that if they develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection) or have ocular surgery, they should immediately seek their physician’s advice concerning the continued use of ACULAR.
Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
Advise patients that if more than one topical ophthalmic medication is being used, the medicines should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
Distributed by:
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064
© 2025 AbbVie. All rights reserved.
ACULAR and its design are trademarks of Allergan, Inc., an AbbVie company.
20091161
| ACULAR
ketorolac tromethamine solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |
More about Acular (ketorolac ophthalmic)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Generic availability
- Drug class: ophthalmic anti-inflammatory agents
- Breastfeeding
- En español