COVID-19: What are the Stages and Causes of Death?
What are the signs, symptoms and stages of COVID-19, and what causes death in COVID-19? How long do you spend in the ICU with COVID-19? How long do you have COVID-19 before you die?
What are the stages and symptoms of COVID-19?
- Day 1: The symptoms usually start with a fever, a dry cough and mild breathing issues which may get worse over the next week. You also may have symptoms of a sore throat, coughing up mucus, diarrhea, nausea, body aches and joint pain.
- Day 7: Breathing may become difficult or laboured. This is called dyspnoea.
- Day 9: Sepsis may start, this is the body's extreme response to an infection that can lead to organ failure or injury.
- Day 10-12: People who have mild COVID-19 start to have an improvement in their fever and cough, but in serious cases their fever and cough continues.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) starts to be diagnosed, this is a respiratory problem when there is widespread inflammation in the lungs.
- Day 12: This is the median day to be admitted into the intensive care unit (ICU).
- Day 15: Acute kidney and cardiac injury becomes evident.
- Day 18.5: The median time it takes from the first symptoms of COVID-19 to death is 18.5 days.
- Day 22: This is the median amount of days it takes for COVID-19 survivors to be released from hospital
A study published in The Lancet studied the patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and compared details of the patients who passed away and patients that survived.
This figure below shows the progression and duration of the major symptoms of COVID-19 in survivors and non-survivors for hospitalized patients in the study.
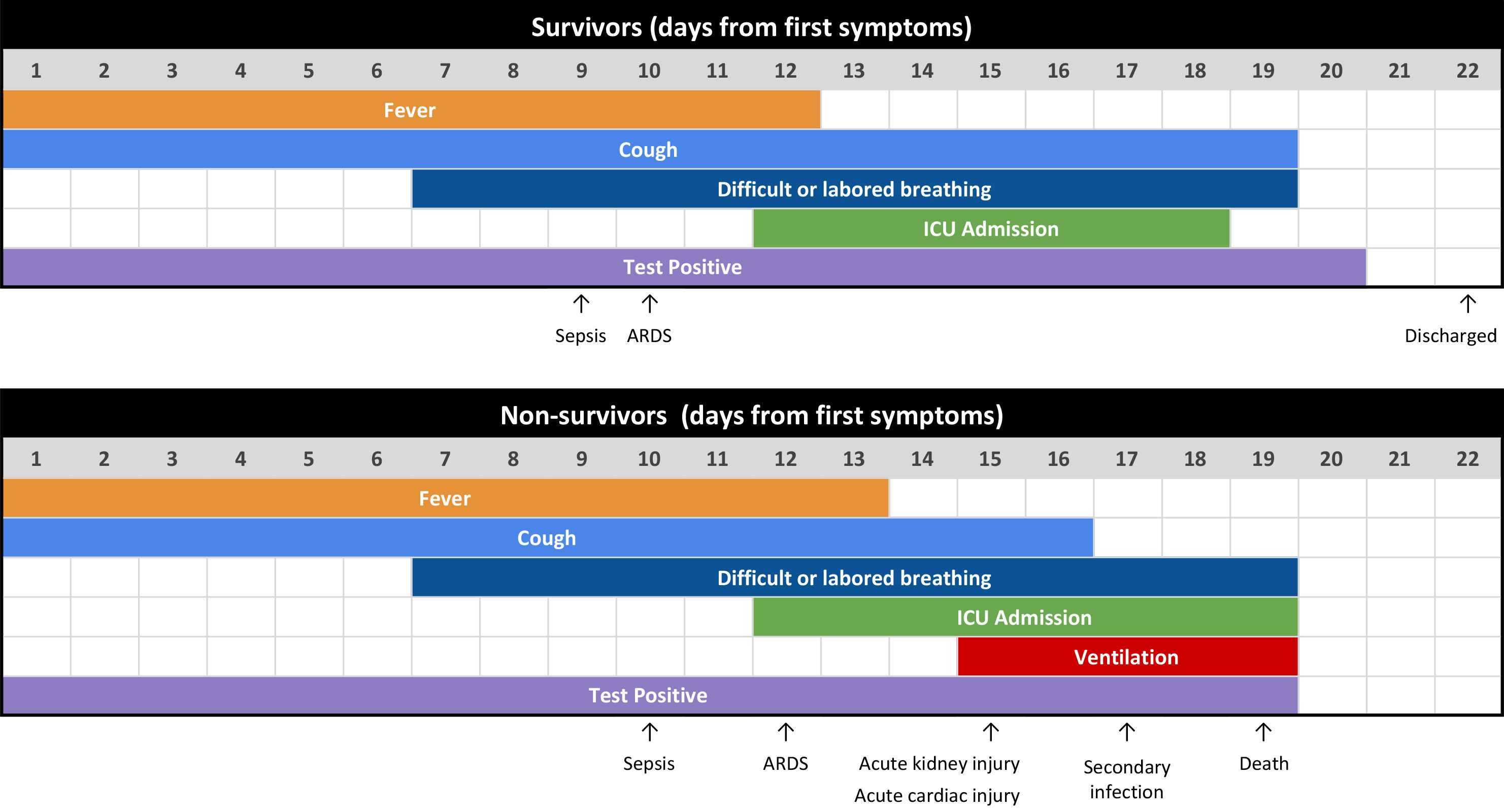
Figure 1. Clinical courses of major symptoms and outcomes and duration of viral shedding from illness onset in patients hospitalised with COVID-19. Reprinted from “Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study,” by X. Yang, Y. Yu, J. Xu, H. Shu, et al., 2020, The Lancet, 395(10229), p. 1056. Copyright 2020 by Elsevier Ltd.
Facts and figures of patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19
Figures from the above study show:
- 191 people hospitalized with COVID 19
- 28% (54) patients died from COVID-19
- 72% (137) patients survived COVID-19
- 26% (50) of patients went into intensive care unit (ICU)
- 78% (39) patients who went into ICU passed away
- 22% (11) patients who went to ICU survived
- 8 days was the median length of stay in ICU
- 11 days was the median total length of stay in hospital
- 22 days was the time from first symptom until discharge from hospital for survivors
- 18.5 days from first symptoms until death for non-survivors
- 20 days median length of time for viral shedding, starting at first day of symptoms
- 52 years old median age for survivor
- 69 years old median age for non-survivor
What health complications of COVID-19 cause you to die?
COVID-19 is well known for breathing problems, but other health complications also contribute towards the death from COVID-19. It is often a combination of these health problems that cause the body to fail and ultimately result in death.
| COVID-19 Deaths (n=54) | COVID-19 Survivors (n=137) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sepsis | 100% (54) | 42% (58) |
| Respiratory failure | 98% (53) | 36% (50) |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) | 93% (50) | 7% (9) |
| Heart failure | 52% (28) | 12% (16) |
| Septic shock | 70% (38) | 0 |
| Blood coagulation issues | 50% (27) | 7% (10) |
| Acute cardiac injury | 59% (32) | 0.7% (1) |
| Acute kidney injury | 50% (27) | 0.7% (1) |
| Secondary infection | 50% (27) | 0.7% (1) |
| Low protein blood levels | 37% (20) | 1.5% (2) |
| Acidosis (body fluids are too acid) | 30% (16) | 0.7% (1) |
Related questions
- Can you have Covid without a fever?
- Which breathing techniques help with COVID-19?
- How effective is Lagevrio (molnupiravir) for COVID-19?
Can blood tests be used to help determine the severity level of COVID-19 illness?
Lymphocyte levels: In COVID-19 survivors the blood lymphocyte counts are high and increase after day 7, when compared to patients that pass away who have severely low lymphocyte counts
D-dimer, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I, serum ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase, and IL-6 levels: These were all clearly elevated in non-survivors compared to the survivors. These levels in non-survivors all increased dramatically after approximately 2 weeks.
Summary
- What is the death rate for people hospitalized with COVID-19? 28%
- What is the survival rate for people hospitalized with COVID-19? 72%
- What rate of hospitalized COVID-19 patients go into the intensive care unit (ICU)? 26%
- What percentage of COVID-19 patients who go into the ICU die? 78%
- What percentage of COVID-19 patients who go into the ICU survive? 22%
- How many days from onset of first symptoms of COVID-19 until ICU admission? 12 days (median)
- What is the median length of stay in ICU for COVID-19 patients? 8 day (median)
- How many days is the median hospital stay for COVID-19 patients? 11 days
- How long does it take from the first COVID-19 symptoms until hospital discharge? 22 days (median)
- How long is viral shedding in COVID-19 patients, starting from the first day of symptoms? Until death or in survivors it is 20 days (median)
- What is the average age of a hospitalized COVID-19 survivor? 52 years old
- What is the average age of a hospitalized COVID-19 who dies? 69 years old
- How many days from first COVID-19 symptoms until death for hospitalized patients? 18.5 days
References
Read next
Can you become immune to COVID-19?
Patients who recover from COVID-19 make antibodies to the virus that may impart immunity for at least 6 months; however, breakthrough infections do occur and may be more likely with newly circulating variants of the virus. Immunizing with the latest recommended COVID-19 vaccine can help to extend your immunity and prevent disease. Continue reading
Is obesity a major risk factor for Covid-19?
Obesity is a major risk factor for covid-19 and people who are obese are more likely than those who are not obese to contract Covid-19 at a younger age, develop severe Covid-19, require hospitalization, oxygen, mechanical ventilation, intubation, or admission into ICU, end up in hospital sooner, or die from Covid-19. Continue reading
COVID-19 vaccines and variants: What you should know
As of May 2025, the top 5 variants circulating in the U.S. are all lineages of the Omicron variant are: LP.8.1 (73%), XFC (10%), XEC (4%), LF.7.7.2 (3%), and LF.7 (2%), as estimated by the CDC on the COVID Data Tracker.
Continue readingSee also:
Related medical questions
- Is Omicron worse than Delta?
- Should I wear a face mask to protect myself from COVID-19?
- COVID-19: Why is social distancing so important?
- Why do more men die from coronavirus?
- Can ivermectin be used to treat COVID-19?
- Can you take Ibuprofen if you have COVID-19 (coronavirus)?
- What is the difference between Spikevax and mNEXSPIKE?
- What antibiotics kill Covid-19 (coronavirus)?
- What's the difference between Bacteria and Viruses?
- Does Zinc protect you from Covid-19 or boost your immune system?
- How do I Treat Nasal Congestion with COVID-19?
- Does Losartan block COVID-19 Coronavirus Receptors?
- An Update: Is hydroxychloroquine effective for COVID-19?
- Does Paxlovid make you less contagious?
- Where can I buy an at-home test kit for COVID-19?
- Can you take Paxlovid twice if COVID rebounds?
- Does Tamiflu (oseltamivir) work on COVID-19?
- Can vitamin C prevent or treat COVID-19 (coronavirus)?
- Does Mucinex help with Covid?
- Should I take Paxlovid after a Positive COVID-19 Test?
- Can I take NyQuil with COVID or after the COVID vaccine?
- How long does COVID-19 last? and other COVID-19 FAQ
- How effective is Paxlovid for COVID-19?
- What are the best antibiotics for pneumonia?
- Can pneumonia go away on its own?
- Can a cold or bronchitis turn into pneumonia? How can you tell?
- Can you have pneumonia without a cough?
- How long does it take to recover from pneumonia?
- Is walking pneumonia contagious?
- What are the common side effects of antibiotics?
Related support groups
- COVID-19 (104 questions, 91 members)
- Pneumonia (58 questions, 112 members)
- Fever (106 questions, 176 members)
- Viral Infection (31 questions, 13 members)
- Respiratory Failure (2 questions, 9 members)
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (1 questions, 6 members)
