The originating document has been archived. We cannot confirm the completeness, accuracy, or currency of the content.
LASIK
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 21, 2025.
What is LASIK?

LASIK is a form of eye surgery that uses a laser to reshape the cornea. LASIK stands for "laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis."
The cornea is the clear, round "window" of tissue that allows light to enter the front of the eye. By reshaping the cornea, the surgeon adjusts the focus of light on the retina. (The retina is the layer at the back of the eye responsible for sight.)
LASIK surgery often improves vision in people who have nearsightedness, farsightedness or certain other vision problems.
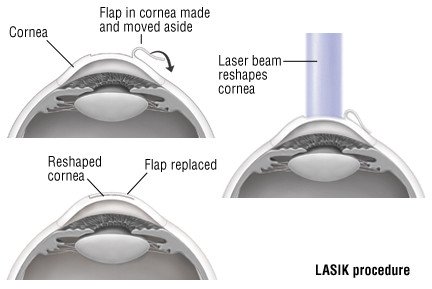
In LASIK, the eye surgeon first cuts a small, hinged flap of tissue from the front of the cornea. This is done with an instrument called a microkeratome. Once this flap is moved out of the way, a laser is used to reshape the underlying protein fibers (collagen) of the cornea.
This reshaping is based on precise measurements made by the eye doctor during the presurgery exam. When the laser reshaping is done, the corneal flap is moved back into place.
The cornea heals quickly. As a result, many people who have LASIK surgery notice dramatic improvements in vision almost immediately.
|
|
LASIK is an outpatient procedure. This means there is no overnight stay in a hospital. Typically eye surgeons work on both the right and left eyes at one sitting. It generally takes 10 to 15 minutes for each eye.
LASIK is the most common surgical treatment to correct nearsightedness in the United States. The technique has been used successfully in the U.S. since 1991.
In addition, most health insurance policies do not cover LASIK surgery. People must pay the entire cost of the procedure themselves.
What It's Used For
LASIK can be used to treat the following vision problems:
- Nearsightedness (myopia). Distant objects appear blurry.
- Farsightedness (hyperopia). Nearby objects appear blurry.
- Astigmatism. Blurred vision is caused by an irregularly shaped cornea.
If you have one of these vision problems, your eye doctor can help determine whether LASIK surgery is appropriate for you.
LASIK may not be an option for you if:
- You are less than 18 years old.
- Your eyeglass or contact lens prescription has changed in the past 12 months. (Pregnancy and breastfeeding can change your prescription temporarily.)
- Your career will be threatened. (Some employers and professional societies do not approve of LASIK surgery. For example, U.S. military has a very cautious view of LASIK, especially for service related to aviation or diving.)
- You have:
- A chronic autoimmune disease (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Any illness that can alter wound healing
- You are taking a medication that affects vision or slows wound healing:
- Retinoic acid (Renova, others)
- Steroids
- Drugs that suppress the immune system
- You play sports (boxing, martial arts, wrestling) in which eye impacts are common.
- You have had a serious eye inflammation, such as uveitis or iritis.
- You have had a herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles) eye infection.
- You have glaucoma or any other condition that changes the pressure inside your eye.
- You have an unusually thin cornea
- You have an eye disorder where the middle of the cornea thins and bulges outward (keratoconus).
- Your cornea has been damaged by trauma or altered by previous eye surgery.
- Your pupils are extraordinarily large.
- You have severely dry eyes.
Preparation
Once you decide to have LASIK eye surgery, your doctor will schedule an eye evaluation prior to surgery. If you wear contact lenses, you must switch to eyeglasses for a few weeks before this evaluation. This will allow your cornea to resume its natural shape.
At your presurgery eye evaluation, your eye doctor will review your medical history and eye history. To confirm that your vision is stable, he or she may ask to see your eye prescription records. Bring those with you to the examination.
Also, make a list of any medications you take. The list should include any over-the-counter drugs and herbal remedies. Your doctor will need to review this list.
After using eye drops to widen (dilate) your pupils, the doctor will examine your eyes thoroughly. This examination will include:
- A test for glaucoma
- An examination of your retina
- A check of how well you can see
Your doctor will take precise measurements of your eyes. These will include measurements of the shape and thickness of your cornea.
After this eye examination is finished, your doctor will discuss LASIK as an option for you. This discussion should include:
- Your expectations
- Potential risks and complications of surgery
- Other treatment options
- Frank answers to your questions
At the end of this discussion, your doctor probably will ask to you sign an informed consent form. This gives the doctor permission to do the surgery.
How It's Done
Your doctor will ask you to stop wearing makeup, lotions and perfumes for a day or two before surgery. You will not be able to drive after your LASIK procedure. Make arrangements for someone to drive you home.
On the day of the procedure, your doctor may give you a mild sedative to help you relax. You will enter the operating room and lie down in a reclining chair.
The area around your eye will be cleaned with an antiseptic solution. Next, numbing eye drops will be placed in your eye so that you will not feel pain or discomfort during the procedure. An instrument called a lid speculum will be inserted into your eye to keep your eyelids open. The doctor will use special ink to mark the surgical area on your cornea.
Next, a ringlike suction device will be placed on the front of your eyes to hold your cornea in place during the procedure. This suction ring will cause a sensation of pressure, but no pain.
Then, a delicate cutting instrument called a microkeratome or a special cutting laser will be used to slice a tiny, hinged flap of tissue from the front of your cornea. You will not see or feel the microkeratome cutting your cornea.
Once the cutting is done, the surgeon will remove the suction ring from your eye, and fold back the hinged flap of cornea. Next, the laser will be moved into position, and you will be asked to stare at a light. Staring fixes your gaze and keeps your eye from moving.
Once your eye is steady, the doctor will use the laser to vaporize portions of your cornea. This vaporization is guided by a computer. It is based on precise eye measurements that were made during your presurgery examination. As the laser works, you will hear a clicking sound, and you may notice a smell similar to burning hair. These sounds and smells are normal.
When your laser treatment is finished, the doctor will reposition the hinged flap of cornea. No stitches are necessary. The doctor probably will cover your eye with an eye shield to protect the corneal flap as it heals.
You will be prescribed eye drops, which often include a topical corticosteroid and antibiotic. You likely will need someone to help you with the drops when you first get home. It's important to strictly follow your doctor's instructions.
After your surgery, you must be careful not to touch or press your eye. For a day or two, the pain can be intense. Your doctor will provide information to help with pain relief.
Follow-Up
Your first follow up visit probably will be scheduled for the day after surgery. At this visit, your doctor will:
- Remove the eye patch
- Examine your cornea
- Check your vision
He or she may prescribe antibiotic eye drops and "artificial tears."
Your doctor will tell you when it is safe for you to resume:
- Driving
- Wearing eye makeup
- Playing contact sports
- Using a whirlpool or hot tub
To help protect your healing eye, you probably will need to wear the eye shield at night for about four weeks.
Your doctor may ask you to return for a second follow up visit seven days after surgery. Depending on your progress, a few more eye exams may be necessary in the next six months.
Risks
Potential risks and complications include:
- Malfunctions of the microkeratome, suction device, or laser equipment. This can result in improper cutting of the corneal flap, or improper positioning of the laser beam.
- Infection or scarring of the cornea
- Replacing the corneal flap in the wrong position after surgery
- Glare or decreased vision, especially at night. Some people also complain of seeing "star bursts" or "halos" around objects.
- Dry eye
- A decrease in vision after surgery. In some cases, even eyeglasses or contact lenses may not correct the problem completely.
- Persistent eye discomfort, blurry vision, glare or increased sensitivity to light
- Overcorrection, so that a nearsighted person is made farsighted or a farsighted person is made nearsighted
Surgical complications occur in a small number of LASIK patients. In addition, some people develop complications within the first three months after surgery. A small percent of patients need to return for a second procedure to fine tune vision.
For the majority of people, however, LASIK treatment is successful and uncomplicated. Nearsighted patients usually achieve vision that measures 20/40 or better after LASIK surgery. For farsighted patients, the percentage is somewhat lower, but still quite high. In some cases, vision improves immediately. In others, improvement occurs gradually over three to six months.
When To Call A Professional
Call your doctor immediately if:
- You have redness, pain, or increased discomfort in the eye that had LASIK.
- Your vision continues to get worse.
- You develop any new visual symptoms that you did not have before surgery.
Additional Info
National Eye Institute
https://www.nei.nih.gov/
American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery
https://www.ascrs.org/
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.