Cipro Dosage
Generic name: CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE 250mg
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Drug class: Quinolones and fluoroquinolones
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 20, 2024.
CIPRO Tablets and Oral Suspension should be administered orally as described in the appropriate Dosage Guidelines tables.
Dosage in Adults
The determination of dosage and duration for any particular patient must take into consideration the severity and nature of the infection, the susceptibility of the causative microorganism, the integrity of the patient’s host-defense mechanisms, and the status of renal and hepatic function. CIPRO Tablets or CIPRO for Oral Suspension may be administered to adult patients when clinically indicated at the discretion of the physician. Administer CIPRO for Oral Suspension using the co-packaged graduated spoon.
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conversion of IV to Oral Dosing in Adults
Patients whose therapy is started with CIPRO IV may be switched to CIPRO Tablets or Oral Suspension when clinically indicated at the discretion of the physician (Table 2).
|
CIPRO Oral Dosage |
Equivalent CIPRO IV Dosage |
|
250 mg Tablet every 12 hours |
200 mg intravenous every 12 hours |
|
500 mg Tablet every 12 hours |
400 mg intravenous every 12 hours |
|
750 mg Tablet every 12 hours |
400 mg intravenous every 8 hours |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients
Dosing and initial route of therapy (that is, IV or oral) for cUTI or pyelonephritis should be determined by the severity of the infection. CIPRO should be administered as described in Table 3. Administer CIPRO for Oral Suspension using the co-packaged graduated spoon.
| Infection | Dose | Frequency | Total Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Complicated Urinary Tract or Pyelonephritis (patients from 1 to 17 years of age) |
10 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg (maximum 750 mg per dose; not to be exceeded even in patients weighing more than 51 kg) |
Every 12 hours |
10–21 days1 |
|
Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure)2 |
15 mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) |
Every 12 hours |
60 days |
|
Plague2,3 |
15 mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) |
Every 8 to 12 hours |
|
1 The total duration of therapy for cUTI and pyelonephritis in the clinical trial was determined by the physician. The mean duration of treatment was 11 days (range 10 to 21 days).
2Begin drug administration as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure.
3Begin drug administration as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure to Y. pestis.
Dosage Modifications in Patients with Renal Impairment
Ciprofloxacin is eliminated primarily by renal excretion; however, the drug is also metabolized and partially cleared through the biliary system of the liver and through the intestine. These alternative pathways of drug elimination appear to compensate for the reduced renal excretion in patients with renal impairment. Nonetheless, some modification of dosage is recommended, particularly for patients with severe renal dysfunction. Dosage guidelines for use in patients with renal impairment are shown in Table 4.
|
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) |
Dose |
|
> 50 |
See Usual Dosage. |
|
30–50 |
250–500 mg every 12 hours |
|
5–29 |
250–500 mg every 18 hours |
|
Patients on hemodialysis or Peritoneal dialysis |
250–500 mg every 24 hours (after dialysis) |
When only the serum creatinine concentration is known, the following formulas may be used to estimate creatinine clearance:
|
Men - Creatinine clearance (mL/min) = Weight (kg) x (140–age) |
|
|
72 x serum creatinine (mg/dL) |
|
|
Women - 0.85 x the value calculated for men. |
|
The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function.
In patients with severe infections and severe renal impairment, a unit dose of 750 mg may be administered at the intervals noted above. Patients should be carefully monitored.
Pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency were excluded from the clinical trial of cUTI and pyelonephritis. No information is available on dosing adjustments necessary for pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency (that is, creatinine clearance of < 50 mL/min/1.73m2).
Important Administration Instructions
With Multivalent Cations
Administer CIPRO at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after magnesium/aluminum antacids; polymeric phosphate binders (for example, sevelamer, lanthanum carbonate) or sucralfate; Videx® (didanosine) chewable/buffered tablets or pediatric powder for oral solution; other highly buffered drugs; or other products containing calcium, iron or zinc.
With Dairy Products
Concomitant administration of CIPRO with dairy products (like milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone should be avoided since decreased absorption is possible; however, CIPRO may be taken with a meal that contains these products.
Hydration of Patients Receiving CIPRO
Assure adequate hydration of patients receiving CIPRO to prevent the formation of highly concentrated urine. Crystalluria has been reported with quinolones.
Instruct the patient of the appropriate CIPRO administration.
Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, it should be taken anytime but not later than 6 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. If less than 6 hours remain before the next dose, the missed dose should not be taken and treatment should be continued as prescribed with the next scheduled dose. Double doses should not be taken to compensate for a missed dose.
Directions for Reconstitution of the CIPRO Microcapsules for Oral Suspension
CIPRO Oral Suspension is supplied in 5% (5 g ciprofloxacin in 100 mL) and 10% (10 g ciprofloxacin in 100 mL) strengths. CIPRO oral suspension is composed of two components (microcapsules and diluent) that must be combined prior to dispensing.
|
Dose |
5% (250 mg/5 mL) |
10% (500 mg/5 mL) |
|
250 mg |
5 mL |
2.5 mL |
|
500 mg |
10 mL |
5 mL |
|
750 mg |
15 mL |
7.5 mL |
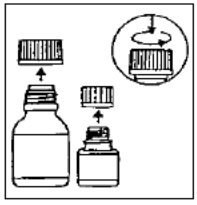
Preparation of the suspension:
Step 5: Write the expiration date of the re-constituted oral suspension on the bottle label.
Reconstituted product may be stored below 30°C (86°F) for 14 days. Protect from freezing.
No additions should be made to the mixed final ciprofloxacin suspension. CIPRO Oral Suspension should not be administered through feeding or NG (nasogastric) tubes due to its physical characteristics.
Administration Instructions for CIPRO for Oral Suspension After Reconstitution
- •
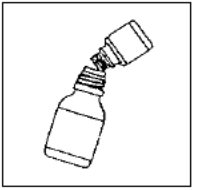
- Shake CIPRO Oral Suspension vigorously each time before use for approximately 15 seconds.
- •
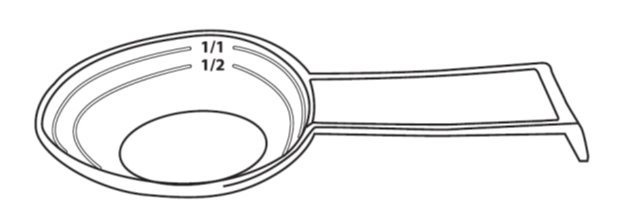
- Administer CIPRO Oral Suspension using the co-packaged graduated teaspoon provided for the patient (see Figure 1)
The Co-packaged graduated teaspoon (5mL) is provided, with markings for 1/2 (2.5 mL) and 1/1 (5 mL)
- •
- After use, clean the graduated teaspoon under running water with dish detergent and dry thoroughly.
- •
- Do Not chew the microcapsules in the CIPRO Oral Suspension, instead swallow them whole.
- •
- Water may be taken afterwards.
- •
- Reclose the bottle properly after each use according to instructions on the cap.
- •
- After treatment has been completed, CIPRO Oral Suspension should not be reused.
Dosing of CIPRO for Oral Suspension using the Co-Packaged Spoon in Adults and Pediatric Patients
Table 6: 5% Cipro for Oral Suspension: 250 mg ciprofloxacin per 5 mL after reconstitution
|
Infection |
Body weight (kg) |
Dose by Measuring Spoonful(s) using Co-Packed Spoon* |
Dose Strength (mg) |
|
Complicated Urinary Tract or Pyelonephritis (patients from 1 to 17 years of age)1 and Plague2 |
9 kg to 12 kg |
½ teaspoonful (2.5 mL) |
125 mg |
|
13 kg to 18 kg |
1 teaspoonful (5 mL) |
250 mg |
|
|
19 kg to 24 kg |
1 to 1 ½ teaspoonful(s) (5 mL to 7.5 mL) |
250 mg to 375 mg |
|
|
25 kg to 31 kg |
1 ½ to 2 teaspoonfuls (7.5 mL to 10 mL) |
375 mg to 500 mg |
|
|
32 kg to 37 kg |
1 ½ to 2 ½ teaspoonfuls (7.5 mL to 12.5 mL) |
375 mg to 625 mg |
|
|
38 kg or more |
2 to 3 teaspoonfuls (10 mL to 15 mL) |
500 mg to 750 mg |
|
|
Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure)3 |
9 kg to 12 kg |
½ teaspoonful (2.5 mL) |
125 mg |
|
13 kg to 18 kg |
1 teaspoonful (5 mL) |
250 mg |
|
|
19 kg to 24 kg |
1 to 1 ½ teaspoonful(s) (5 mL to 7.5 mL) |
250 mg to 375 mg |
|
|
25 kg or more |
2 teaspoonfuls (10 mL) |
500 mg |
* A graduated teaspoon (5mL) with markings 1/2 (2.5) mL and 1/1 (5 mL) is provided for the patient.
1Administer every 12 hours for 10-21 days
2Administer every 8-12 hours for 10-21 days for Pediatric patients; for adults administer every 12 hours for 14 days
3Administer every 12 hours for 60 days
|
Infection |
Body weight (kg) |
Dose by Measuring Spoonful(s) using Co-Packed Spoon* (teaspoonful (s) (volume (mL)) |
Dose Strength (mg) |
|
Complicated Urinary Tract or Pyelonephritis (patients from 1 to 17 years of age)1 and Plague2 |
13 kg to 24 kg |
½ teaspoonful (2.5 mL) |
250 mg |
|
25 kg |
½ to 1 teaspoonful (2.5 mL to 5 mL) |
250 mg to 500 mg |
|
|
26 kg to 37 kg |
1 teaspoonful (5 mL) |
500 mg |
|
|
38 kg or more |
1 to 1½ teaspoonful(s) (5 mL to 7.5 mL) |
500 mg to maximum dose of 750 mg |
|
|
Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure)3 |
13 kg to 24 kg |
½ teaspoonful (2.5 mL) |
250 mg |
|
25 kg or more |
1 teaspoonful (5 mL) |
500 mg |
* A graduated teaspoon (5mL) with markings 1/2 (2.5) mL and 1/1 (5 mL) is provided for the patient.
1Administer every 12 hours for 10-21 days
2Administer every 8-12 hours for 10-21 days for Pediatric patients; for adults administer every 12 hours for 14 days
3Administer every 12 hours for 60 days
Frequently asked questions
- How long does Cipro take to work?
- What types of infections does Cipro treat?
- How long does ciprofloxacin stay in your system when finished?
- Can I use Cipro to treat a bacterial vaginitis infection?
- Ciprofloxacin - can you crush Cipro 500 tablets and mix with food?
- What is the best antibiotic to treat a sinus infection?
- What medications can affect your taste or smell?
More about Cipro (ciprofloxacin)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (319)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Patient tips
- During pregnancy
- Generic availability
- Support group
- Drug class: quinolones and fluoroquinolones
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Other brands
Professional resources
Other formulations
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.