Wound Healing and your Diet
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
Your body uses nutrients from healthy foods to heal wounds caused by injury, surgery, or pressure injuries. There is no special diet that will heal your wound, but a healthy meal plan can help your wound heal faster. Nutrients that are important for healing are protein, zinc, and vitamin C. Liquids are also important for wound healing.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Follow a healthy meal plan:
- Eat a variety of foods from each food group every day. Eat regular meals and snacks to help you get enough calories and nutrients. If you have trouble eating 3 meals each day, eat 5 to 6 small meals throughout the day instead. Include good sources of protein, zinc, and vitamin C each day.

- Drink liquids as directed. Drink plenty of liquids during and between meals, unless your healthcare provider has told you to limit liquids. Ask your healthcare provider or dietitian how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Limit unhealthy foods, such as those that are high in fat, sugar, and salt. Examples include doughnuts, cookies, fried foods, candy, and regular soda. These kinds of foods are low in nutrients that are important for healing.
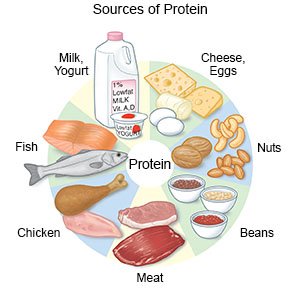
Good sources of protein:
Your dietitian will tell you how much protein and how many calories you need each day. The average amount of protein in foods is listed below in grams (g). To find the exact amount of protein in a food, read the food labels on packaged items.
- Dairy:
- 1 cup of any type of milk (8 g)
- ½ cup of evaporated canned milk (9 g)
- ¼ cup of nonfat dry milk (11 g)
- 1 ounce of semi-hard or solid cheese (7 g)
- ¼ cup of parmesan cheese (8 g)
- ½ cup of cottage cheese (14 g)
- ½ cup of pudding (4 g)
- 1 cup of plain or fruit yogurt (8 g)
- Meats and meat substitutes:
- 3 ounces of cooked freshwater fish (21 g)
- 3 ounces of cooked shellfish (19 g)
- ½ cup of canned tuna (14 g)
- 3 ounces of cooked chicken, turkey, or other poultry (24 g)
- 3 ounces of cooked beef, pork, lamb, or other red meat (21 g)
- 1 large egg (6 g)
- ¼ cup of fat-free egg substitute (5 g)
- ½ cup of tofu or tempeh (10 g)
- 1 cup of cooked dried beans, such as pinto, kidney, or navy (15 g)
- Nuts and seeds:
- 2 tablespoons of almonds, cashews, sunflower seeds, or walnuts (5 g)
- 2 tablespoons of peanuts (7 g)
- 2 tablespoons of peanut butter (8 g)
 |
How to add extra protein:
- Add powdered milk to milk, cereals, scrambled eggs, soups, and casseroles.
- Add cheese to sauces, soups, or vegetables.
- Add eggs to tuna, salads, sauces, or casseroles.
- Add nutrition supplements and breakfast drink mixes to milk or shakes.
- Add nuts to foods or eat them as snacks.
- Add meat (beef, chicken, or pork) to soups, casseroles, pasta dishes, or vegetables.
- Add beans, peas, and other legumes to salads.
- Eat cottage cheese or yogurt with fruit.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
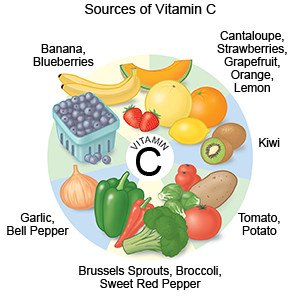
Good sources of vitamin C:
Vitamin C is found in fruits and vegetables. Fruits such as oranges, strawberries, grapefruit, cantaloupe, and tangerines are good sources of vitamin C. Red and green bell peppers, broccoli, potatoes, tomatoes, and cabbage are also high in vitamin C.
 |
Good sources of zinc:
Good sources of zinc are beef, liver, and crab. Smaller amounts of zinc are found in sunflower seeds, almonds, peanut butter, eggs, and milk. Other foods that contain zinc include wheat germ, black-eyed peas, and whole-grain products.
How to add extra calories to foods:
Your dietitian may recommend that you add extra calories to your meals if you are not eating enough. You can increase calories by adding butter, margarine, sugar, or jam to foods. Work with your dietitian if you have other medical conditions and need to follow a special diet.
What else you should know about nutrients and wound healing:
Your healthcare provider or dietitian may recommend vitamin and nutrition supplements if your body is low in certain nutrients. If your dietitian recommends a liquid nutrition supplement, take it between meals. Ask your healthcare provider which supplements are right for you.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
