Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Placement for Hydrocephalus in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement?
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement is surgery to help remove extra cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in your child's brain.
 |
How do I prepare my child for surgery?
Your child's healthcare provider will talk to you about how to prepare your child for surgery. He or she may tell you not to let your child eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of surgery. He or she will tell you what medicines to give or not give on the day of your child's surgery.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Acetazolamide
Acetazolamide systemic is used for edema, epilepsy, glaucoma, hydrocephalus, hypokalemic periodic ...
What will happen during my child's surgery?
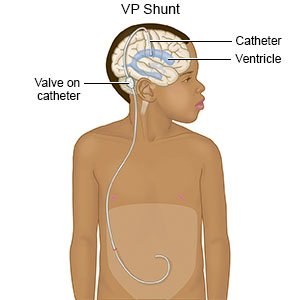
- General anesthesia will keep your child asleep during the surgery. A small area of hair on your child's head will be cut or shaved. Two small incisions will be made. One incision will be in your child's head and the other in his or her abdomen. One end of a shunt will be placed into your child's brain. This end of the shunt will be connected to a valve that controls the amount of CSF that goes through the shunt. Near the valve is a reservoir or pump. This pump that lies right under his or her scalp. This pump can be pressed by healthcare providers to check how the shunt is working.
- Connected to the valve on the shunt is a catheter (tube). This catheter is tunneled under your child's skin, from his or her head to the abdomen. The extra CSF will empty into his or her abdomen. It will be quickly absorbed into his or her blood. Some teenagers or tall children may need a small third incision made near the collarbone. Your child's incisions may be closed with staples or stitches. Bandages may be placed over the incisions.
What are the risks of surgery?
Your child's tube may become blocked or move out of place, and he or she may need another surgery. Your child could have bleeding into his or her brain, and he or she may need surgery to treat it. He or she may get an infection at the incision site or a more serious infection in his or her brain.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Placement for Hydrocephalus
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
