Uterine Prolapse
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
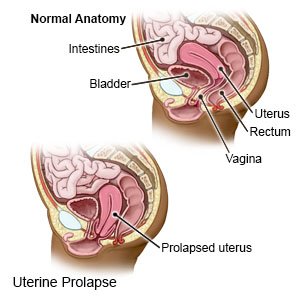
A uterine prolapse is a condition that causes your uterus to slip down into your vagina. Prolapse can happen if the tissues and muscles supporting your uterus become weak or damaged.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have bleeding from your vagina that does not stop.
- You have a mass coming out of your vagina that you cannot push back in.
- You are unable to urinate or have a bowel movement.
- You have severe abdominal pain.
Call your doctor or gynecologist if:
- You are leaking urine or bowel movement.
- You have a fever.
- You have foul-smelling fluid coming from your vagina.
- You see blood coming from your vagina that is not from your monthly period.
- You have questions about your condition or care.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Myrbetriq
Myrbetriq (mirabegron) is used to treat overactive bladder with symptoms of frequent or urgent ...
Botox
Botox is used to treat chronic migraines, excessive sweating, bladder conditions, eye muscle ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
VESIcare
Vesicare is used to treat symptoms of overactive bladder such as incontinence and frequent ...
OnabotulinumtoxinA
OnabotulinumtoxinA information from Drugs.com, includes OnabotulinumtoxinA side effects ...
Darifenacin
Darifenacin systemic is used for overactive bladder, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence
Solifenacin
Solifenacin systemic is used for neurogenic bladder, neurogenic detrusor overactivity, overactive ...
Tolterodine
Tolterodine systemic is used for overactive bladder, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence
Medicines:
- Estrogen may help strengthen the pelvic muscles and keep the prolapse from getting worse. This may be taken as a pill, applied as a cream, or inserted into your vagina.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Pessary care:
A pessary is a rubber device shaped like a donut. It helps to hold your uterus in place. If your gynecologist fits you for a pessary, you will need to remove and clean it regularly. You will be taught when and how to clean the pessary.
Manage your symptoms:
- Sit with your legs elevated. This can help relieve pain or discomfort. Put pillows or blankets under your ankles to elevate your entire legs.
- Do Kegel exercises. These exercises strengthen the muscles that hold your uterus in place. They also tighten the muscles you use when you urinate or have a bowel movement. Tighten muscles in your pelvis (muscles you use to stop urinating). Hold the muscles tight for 5 seconds, then relax for 5 seconds. Gradually work up to holding the muscles contracted for 10 seconds. Do at least 3 sets of 10 repetitions a day.
- Do not strain. Do not lift heavy objects, stand for long periods of time, or strain to have a bowel movement. Prevent constipation by drinking plenty of liquids and eating foods high in fiber. Ask how much liquid to drink every day. High-fiber foods include fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider for a healthy weight for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight. He or she can also help you create an exercise program. Exercise helps your bowels work better and decreases pressure inside your colon.

Follow up with your doctor or gynecologist as directed:
You may need to return regularly to have your pessary checked. You may also need to see your gynecologist for possible surgery. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
