Urinary Tract Infection in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
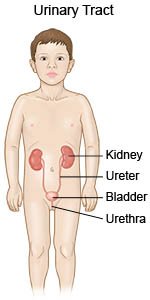
A UTI is caused by bacteria that get inside your child's urinary tract. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most UTIs happen in the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder and urethra.
 |
What increases my child's risk for a UTI?
UTIs are more common in girls because the urethra is shorter. This allows bacteria to enter the urinary tract more easily. The following increase your child's risk for a UTI:
- Girls wiping from back to front after urinating or having a bowel movement
- Not urinating when he or she feels the urge
- Constipation
- Boys not being circumcised
What are the signs and symptoms of a UTI in children younger than 2 years?
- Fever
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Irritability
- Lethargy (less active or sleeping more than usual)
- Poor feeding or slow weight gain
What are the signs and symptoms of a UTI in children older than 2 years?
- Fever and chills
- Nausea
- Abdominal, side, or back pain
- Urine that smells bad
- Urgent need to urinate or urinating more often than normal
- Urinating very little, leaking urine, or bedwetting
- Pain or a burning feeling when urinating
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Macrobid
Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) is an antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections. Includes side ...
Cipro
Cipro (ciprofloxacin) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Learn ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Bactrim
Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim) is an antibiotic used to treat ear infections, urinary ...
Amoxil
Amoxil (amoxicillin) is a penicillin antibiotic used to treat many different types of infections ...
Augmentin
Augmentin is a prescription antibiotic combining amoxicillin and clavulanate to treat bacterial ...
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic used to treat many different bacterial infections such as ...
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that fights bacteria. It is used to treat many types of ...
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim systemic is used for acne, bacterial infection, bacterial skin ...
Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections and prevent ...
How is a UTI diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will ask about your child's signs and symptoms. The provider may press on your child's stomach, sides, and back to check if he or she feels pain. Your child may need any of the following:
- Urinalysis will show infection and your child's overall health.
- Urine cultures may show which germ is causing your child's infection.
- Ultrasounds pictures may be taken of your child's urinary tract if your child is younger than 2 years. These pictures may show if an anatomic problem is causing the infection.
How is a UTI treated?
Antibiotics are used to treat a bacterial infection. Your child may need to get antibiotics through an IV if he or she is very young.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I help prevent my child from getting a UTI?
- Have your child empty his or her bladder often. Make sure your child urinates and empties his or her bladder as soon as needed. Teach your child not to hold urine for long periods of time.
- Encourage your child to drink more liquids. Ask how much liquid your child should drink each day and which liquids are best. Your child may need to drink more liquids than usual to help flush out the bacteria. Do not let your child drink caffeine or citrus juices. These can irritate your child's bladder and increase symptoms. Your child's healthcare provider may recommend cranberry juice to help prevent a UTI.
- Teach your child to wipe from front to back. Your child should wipe from front to back after urinating or having a bowel movement. This will help prevent germs from getting into the urinary tract through the urethra.
- Treat your child's constipation. This may lower his or her UTI risk. Ask your child's healthcare provider how to treat your child's constipation.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child has a high fever with shaking chills.
- Your child has severe pain in his or her abdomen, sides, or back.
- Your child urinates very little or not at all.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child has a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher.
- Your child is not getting better after 2 days of treatment.
- Your child is vomiting.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Urinary Tract Infection
- Antibiotic Resistance: The Top 10 List
- Antibiotics 101: Common Names, Types & Their Uses
- Antibiotics For UTI Treatment - What Are My Options?
- Antibiotics and Birth Control Pill Interactions
- Anticholinergic Drugs to Avoid in the Elderly
- Can You Drink Alcohol with Antibiotics?
- Common Side Effects from Antibiotics, and Allergies and Reactions
- Why Don’t Antibiotics Kill Viruses?
Treatment options
Care guides
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Kidney Infection
- Urinary Tract Infection in Men
- Urinary Tract Infection in Women
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
