Urethral Bulking
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What do I need to know about urethral bulking?
Urethral bulking is used to help control stress incontinence in women. A silicone material is injected into 3 areas of your urethra to bulk up the tissue (make it thicker). This helps narrow your urethra to make it more difficult for urine to leak out. The material will stay in place permanently.
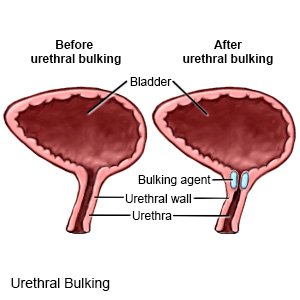 |
How is the material implanted?
The material is implanted in your healthcare provider's office or an outpatient facility. The procedure usually takes about 30 minutes.
- You will be given antibiotics to help prevent a bacterial infection. You may be given local anesthesia to numb the area. You may instead be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain. Your bladder will be filled halfway with liquid to make the implantation area easier to see.
- Your healthcare provider may insert a cystoscope. This is a long, thin tube with a light and camera on the end. The scope will help your provider find the implantation areas in your urethra. Your provider may instead use an implantation device made for this procedure. A needle will be inserted in your urethra to inject the material.
- Your provider will check to make sure you can urinate before you go home. You should be able to return to your usual activities within a day of the procedure.
Related medications
How can I manage stress incontinence?
- Do pelvic muscle exercises often. Your pelvic muscles help you stop leaking urine. Squeeze these muscles tight for 5 seconds, then relax for 5 seconds. Gradually work up to squeezing for 10 seconds. Do 3 sets of 15 repetitions a day, or as directed. This will help strengthen your pelvic muscles and improve bladder control.
- Keep a symptom record. Write down how often you leak urine and how much you leak. Make a note of what you were doing when you leaked urine.
- Train your bladder. Go to the bathroom at set times, such as every 2 hours, even if you do not feel the urge to go. You can also try to hold your urine when you feel the urge to go. For example, hold your urine for 5 minutes when you feel the urge to go. As that becomes easier, hold your urine for 10 minutes.
- Drink liquids as directed. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. You may need to limit the amount of liquid you drink to help control your urine leakage. Do not drink any liquid right before you go to bed. Limit or do not have drinks that contain caffeine or alcohol.
- Prevent constipation. Eat a variety of high-fiber foods. Good examples are high-fiber cereals, beans, vegetables, and whole-grain breads. Prune juice may help make your bowel movement softer. Walking is the best way to trigger your intestines to have a bowel movement.

- Reach or maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a safe weight loss plan, if needed. Your provider can also help you create a physical activity plan. A healthy weight and physical activity help decrease pressure on your bladder.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are urinating very little or not at all.
- You have a high fever with shaking chills.
- You have side or back pain that gets worse.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You see blood in your urine.
- You have pain when you urinate.
- Your mouth feels dry or you have vision changes.
- Your urine is cloudy or smells bad.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
