Tonsillectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2024.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW:
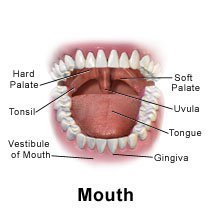
A tonsillectomy is surgery to remove your tonsils. The tonsils are 2 large lumps of tissue in the back of your throat. An adenoidectomy is surgery to remove your adenoids. Adenoids are small lumps of tissue on the top of your throat. Tonsils and adenoids fight infection. Sometimes only your tonsils are removed. Your adenoids may be taken out at the same time if they are large or infected.
 |
INSTRUCTIONS:
Medicines:
- Pain medicine: You may be given medicine to take away or decrease pain. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you take your medicine. If you have pain when you eat, take pain medicine before you start. Do not take aspirin . This may increase your risk of bleeding.
- Antibiotics: This medicine will help prevent an infection. Take your antibiotics until they are gone, even if you feel better.
- Take your medicine as directed: Call your primary healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell them if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Bleeding:
Some people have bleeding after a tonsillectomy. Usually it happens 4 to 8 days after surgery, but it can occur any time up until about 3 weeks after your surgery.
- If you have bleeding:
- Small amount of bleeding: Drink ice water and sit down and rest.
- Large amount of bleeding or bleeding that does not stop: Return to the emergency department immediately .
- Prevent bleeding: Do the following to prevent or reduce the risk of bleeding from your tonsil areas:
- Do not smoke or go to smoky areas after your surgery while your throat is healing. Smoke may cause your throat to start bleeding heavily.
- Wrap a bag of crushed ice in a towel and place it on your neck as directed.
- Avoid using very hot water when taking a shower or bath, or washing your face.
- Avoid drinking liquids or eating foods that are hot, spicy, or have sharp edges (such as chips).
- Avoid harsh gargling or tooth brushing. Gently brush your teeth and rinse your mouth as directed.
- Try not to cough, sneeze, or blow your nose. Tell your primary healthcare provider if you have a cold or allergies. He may suggest medicine to treat sneezing or allergies.
Food and drink:
It is important that you drink enough liquids . Do this to improve your healing, reduce the risk of bleeding, and prevent fluid loss.
- You will need to follow a liquid diet or soft food diet for several days after surgery. Eat popsicles and drink cool liquids often, such as water, apple or grape juice, and soft drinks. Do not drink orange juice or grapefruit juice. Citrus may hurt your throat. You may eat soft, plain foods such as gelatin, applesauce, ice cream, and mashed potatoes if your stomach is not upset. You may slowly begin to eat solid foods after you can eat soft foods easily. Cold liquids and foods help soothe your throat. Avoid hot, spicy, or sharp foods, such as chips, that can hurt your tonsil areas. Avoid milk and dairy foods if you have problems with thick mucus in your throat. This can cause you to cough, which could hurt your surgery areas.
Self care:
- Use a cool humidifier in your home to help moisten the air and soothe your throat.
- Rest and limit your activity for 7 to 10 days after surgery. It may take 2 to 3 weeks for you to recover completely.
- Stay away from people who have colds, sore throats, or the flu. You may get sick more easily after surgery.
- Ask your primary healthcare provider when you can drive again, or return to work.
Follow up with your surgeon in 1 to 2 days or as directed:
Write down any questions you have so you remember to ask them during your visits.
Contact your surgeon or primary healthcare provider if:
- You have severe throat pain or an earache that worsens.
- You have a high fever. Ask your primary healthcare provider what temperatures are a concern.
- Your neck and face is more red or swollen over time.
- You have itchy skin or a rash. This may mean you are allergic to your medicine.
- You have any questions or concerns about your medicine or care.
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have bright red bleeding from your nose or mouth, or bleeding that is worse than what you were told to expect.
- You feel weak, dizzy, or like you might faint when you sit up or stand.
- You are not able to drink or are passing very little urine.
- You have pus or blood draining down your throat.
- You have bad throat pain with drooling or voice changes.
- Your neck is stiff and painful.
- You have swelling or pain in your face or neck.
- You have back or chest pain.
- You have trouble breathing or swallowing.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Tonsillectomy
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Copyright © 2012. Thomson Reuters. All rights reserved. Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
