Thoracic Disc Herniation
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
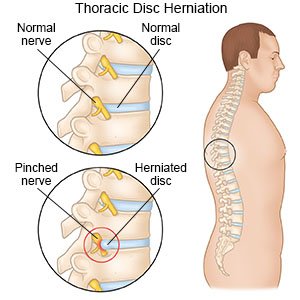
What is thoracic disc herniation (TDH)?
TDH occurs when a disc bulges out from between your vertebrae. Discs are spongy cushions between the vertebrae in your spine. Thoracic discs are located between the base of your neck and your lower back. The herniated disc may press on your nerves or spinal cord.
 |
What causes or increases my risk for a TDH?
- Cracked vertebrae that cause the disc to bulge out
- Weakened discs from decreased gel-like material inside the disc
- Aged 30 to 50 years
- A back injury
- Pressure from scar tissue that builds up between discs and the spinal cord covering
What are the signs and symptoms of a TDH?
Mild herniation may not cause any signs or symptoms. You may have any of the following if the herniated disc presses against your nerves or spinal cord:
- Pain in the upper or middle part of your back or your chest
- Pain radiating to the forearm
- Band-like pain travelling from the back to the abdomen/chest on one or both sides of the body
- Headaches when you sit or lie in certain positions
- Numbness, tingling, or a burning feeling in your legs
- Trouble walking or moving your legs
- Weakness in your arms or legs
- Trouble urinating or having a bowel movement
How is a TDH diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and any health problems you have. Tell your provider if you have had any recent injuries. Your provider may look at your spine and feel for any abnormal areas. Tell your provider if any area on your spine is painful when touched. Tests may be used to check the movement and feeling in your legs. You may also need any of the following:
- An x-ray, MRI, or CT scan may show a bulging disc or abnormal areas of your spine. You may be given contrast liquid to help the bulging disc or spine show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Myelography is an x-ray of your spinal cord. Contrast liquid will be injected into the area around your spinal cord before the pictures are taken.
- An electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks for damage to the nerves that control your muscles.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Tylenol
Tylenol is a pain reliever and a fever reducer used to treat many conditions such as headaches ...
Dilaudid
Dilaudid (hydromorphone) is a narcotic pain reliever used to treat moderate to severe pain ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
OxyContin
OxyContin (oxycodone) is an opioid pain reliever used to treat moderate to severe pain. Includes ...
Percocet
Percocet (acetaminophen and oxycodone) is used to relieve moderate to severe pain. Includes ...
Acetaminophen/hydrocodone
The combination of hydrocodone and acetaminophen is used to relieve moderate to severe pain ...
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone (Hysingla ER and Zohydro ER) is used for around-the-clock treatment of severe pain ...
Oxycodone
Oxycodone is an opioid analgesic used to treat moderate to severe pain; it has a high potential for ...
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is a widely used pain reliever and fever reducer for conditions like headaches ...
How is a TDH treated?
Your healthcare provider may have you rest in bed for a few days. You may also need any of the following:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Muscle relaxers decrease pain from muscle spasms.
- A steroid injection may be given to reduce inflammation. Steroid medicine is injected into the epidural space. The epidural space is between your spinal cord and vertebrae. You may be given pain medicine along with the steroids.
- Physical therapy may be recommended by your healthcare provider. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. A physical therapist can teach you safe ways to bend, lift, sit, and stand to help relieve back pain.
- Surgery to remove the disc may be needed if other treatments do not work. You may also need surgery if you have new or worsening nerve problems.
How can I manage pain from a TDH?
- Apply heat on your back for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours for as many days as directed. Heat helps decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Apply ice on your back for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you apply it to your skin. Ice decreases swelling and pain.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have new and sudden chest pain.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are not able to move one or both of your legs.
- You have severe headaches when you hold your head in certain positions.
When should I call my doctor?
- You begin leaking urine or bowel movement.
- Your pain worsens even after you take medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
