Tendon Laceration
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
A tendon laceration
is a tear or break in your tendon. A tendon is a string of tissue that connects muscle to bone. Tendons help muscles make bones move. A tendon laceration may be caused by too much pressure or force to a joint or body part. It may also be caused by deep cut. A tendon laceration is most commonly caused by deep cut to your hand, finger, wrist, foot, or toes.
Common signs and symptoms include the following:
The location of signs and symptoms may depend on where in your body your tendon is lacerated. You may have any of the following:
- A deep cut or wound in the skin that covers the tendon
- Trouble straightening or bending the body part with the tendon laceration
- Pain
- Swelling or bruising
Seek care immediately if:
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Your stitches come apart.
- Your hand, fingers, foot, or toes closest to your injury are pale, numb, or cold.
- You hear or feel a sudden snap, pop, or crack where your tendon is lacerated.
- You have sudden severe pain where your tendon is lacerated.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever.
- Your wound is swollen, red, or draining pus.
- Your pain does not get better after you take your medicine or gets worse.
- Your splint or cast falls off.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for a tendon laceration
may include a splint or cast to prevent your tendon from moving. You may need wound care or a tetanus shot if you also have an open wound. You may need surgery to repair your tendon. You may also need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Antibiotics help prevent a bacterial infection.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
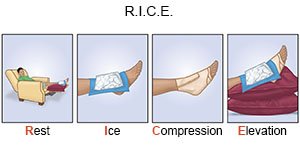 |
- Rest your arm or leg to help it heal.
- Apply ice on your arm or leg for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Elevate your arm or leg above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your injured body part on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably.
- Wear your splint as directed. A splint will keep your tendon straight and prevent movement. This will help your tendon heal. Check your skin under your splint for redness, swelling or open skin. You may need to change your splint when it gets wet or dirty. Ask your healthcare provider how to change your splint.
- Perform range of motion exercises (ROM) as directed. ROM exercises are gentle movements of your joint. ROM exercises will prevent stiffness in your arm or leg and help build strength. Do not do ROM exercises unless your healthcare provider says it is okay.
If you or your child has a cast:
Do not get your cast wet or put pressure on your cast. Do not put sharp items under your cast to scratch your skin. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on how to care for your cast.
Care for your wound as directed:
Ask your healthcare provider when your wound can get wet. Carefully wash around the wound with soap and water. Let soap and water run over your wound. Dry the area and put on new, clean bandages as directed. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty. Check your wound every day for redness, swelling, or pus.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need to return to have stitches removed from your skin. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Tendon Laceration
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
