Spermatocelectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about a spermatocelectomy:
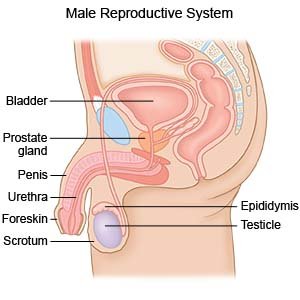
A spermatocelectomy is surgery to remove a spermatocele. A spermatocele is a cyst (sac of fluid) that contains sperm. It forms inside your scrotum on the outside of your testicle. The cyst is most often attached to the epididymis. The epididymis is a tube that stores sperm.
 |
How to prepare for surgery:
- Your surgeon will tell you how to prepare. Arrange to have someone drive you home when you are discharged. You may be told not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of surgery.
- Tell your surgeon about all medicines you currently take. Your surgeon will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for surgery, and when to stop. Your surgeon will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of surgery.
- You may need an ultrasound of your scrotum and testicle. Talk to your surgeon about this or other tests you may need.
What will happen during surgery:
- You may be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery. You may instead be given spinal or local anesthesia to numb the surgery area. With spinal or local anesthesia, you may still feel pressure or pushing during surgery, but you should not feel any pain.
- Your surgeon will make a small incision in your scrotum. Your surgeon will open the membrane that covers your testicle and the spermatocele. The spermatocele will be divided from your testicle and removed.
- The incision will be closed with stitches or medical tape. A small tube may be used to drain extra blood or fluid for a short time.
What to expect after surgery:
You will be taken to a room to rest until you are fully awake. Healthcare providers will monitor you closely for any problems. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. When your healthcare provider sees that you are okay, you will be able to go home or be taken to your hospital room.
- An athletic supporter may be used to decrease swelling and pain, and hold bandages on your scrotum.
- Healthcare providers will place an ice pack on your scrotum every hour for 15 to 20 minutes. Ice helps decrease swelling and pain.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe to ask for more medicine.
Risks of a spermatocelectomy:
You may bleed more than expected or get an infection. Your epididymis may be injured or blocked. This may cause infertility. A blood clot may form inside your scrotum. The spermatocele may come back. Your blood vessels may be injured. This can cause your testicle to shrink. Sperm may leak into your scrotum.
Seek care immediately if:
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- You have severe, sudden pain in your scrotum or testicle.
Call your surgeon or urologist if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- Your wound is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- You have swelling in your testicle that is getting worse.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Wear an athletic supporter as directed. This device helps decrease swelling and pain, and holds bandages on your scrotum.
- Apply ice on your scrotum for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Ask about activities that are okay while you heal. Ask your healthcare provider when it is okay to have sex. Limit heavy activity for 2 weeks after your surgery, or for as long as directed. Heavy activity includes lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercise.
Follow up with your surgeon or urologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
