Shoulder Arthroplasty
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Shoulder arthroplasty
is surgery to replace part or all of your shoulder joint. Your joint may need to be replaced because of disease or injury.
 |
How to prepare for a shoulder arthroplasty:
- You may need to have x-rays, a CT, or an MRI before your surgery. You may need to stop taking blood thinning medicines and NSAIDs weeks before your surgery. Make arrangements for someone to drive you home when you are discharged. Ask them to stay with you for a few days after you get home.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you not to eat or drink after midnight on the day of your surgery. He or she will tell you what medicines to take or not take on the morning of surgery. You will receive IV antibiotics to help prevent an infection during your surgery.
What will happen during a shoulder arthroplasty:
- You will be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and pain free during your surgery. You may instead be given regional anesthesia. Regional anesthesia blocks pain in the area of your surgery, but, you remain awake. It also helps to decrease pain and increase mobility after surgery. You may be given both types of anesthesia. Your anesthesiologist will discuss what anesthesia is best for you.
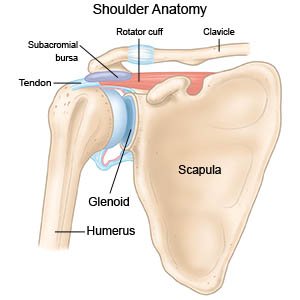
- Your healthcare provider will make an incision on the front of your shoulder. The head (ball) of your humerus and the glenoid fossa (socket) of your shoulder blade will be removed. A shoulder implant will replace the bones that were removed. Your healthcare provider may use medical cement to secure the implant parts. He or she may instead use an implant that has a porous surface. This surface allows your own bone to grow and fill the pores of the implant. Your healthcare provider may use both cement to hold the ball in place, and a porous socket implant.
- A drain may be placed to remove extra blood and fluids from the surgery area. Your incision will be closed with stitches, staples, or glue and covered with a bandage. A sling or splint may be placed to keep your shoulder joint from moving.
What will happen after a shoulder arthroplasty:
- You are taken to a room where your heart and breathing will be monitored. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. When healthcare providers see that you are okay, you will be taken to a hospital room. You will stay in the hospital 1 or 2 days.
- The day after surgery, a physical therapist will come to move your arm for you. You will need to go to physical therapy for several weeks after your surgery. Do not remove the sling or brace until your healthcare provider says it is okay.
Risks of shoulder arthroplasty:
The parts of the new joint may loosen. Your shoulder may become unstable. The bones around the parts may break. You may get an infection. You may have damage to the nerves, blood vessels, or muscles around your shoulder. You may have damage to the ligaments and tendons around your shoulder. You may develop blood clots in your arm. You may not be able to lift your arm. You may need more surgeries to fix any problems.
Call 911 for any of the following:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You have a severe headache or a seizure.
- You have chest pain or shortness of breath.
- You fall and injure your shoulder.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your arm feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Any part of your arm is numb, tingly, cool to the touch, blue, or pale.
- Your surgery site is swollen, red, or has pus coming from it.
- Your stitches come apart.
Contact your surgeon if:
- You have a fever.
- You have chills, a cough, or feel weak and achy.
- You have pain and swelling in your shoulder even after you take your pain medicine.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or has a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may be given any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. You may need to take this medicine before physical therapy. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for yourself at home:
- Wear your sling or brace at all times, for as long as directed. This helps to remind you not to use the arm. It also allows your shoulder to heal and decreases pain.
- Apply ice on your shoulder for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Place a small pillow or towel behind your elbow when you lie on your back. This keeps your shoulder in proper position. You may need to sleep in an upright position if you cannot sleep on your back. Place 2 to 3 pillows lengthwise behind your back when in bed. Make sure the pillows do not move your shoulder forward. Instead, you can sleep in a reclining chair.
- Avoid moving your shoulder. Do not stretch or shrug your shoulder. Do not do exercises on your own until your healthcare provider says it is okay.
- Do not lift with your hand on your surgery side. You put pressure on your shoulder muscles when you lift.
- Do not lean on the hand of your surgery side. Pressure will cause pain and may cause damage to your shoulder.
- Do not drive until your healthcare provider says it is okay.
Shoulder bandage care:
Keep your dressing clean and dry. Your healthcare provider will tell you when it is okay to take a bath or shower. Once you are able, let soap and water run over your surgery area. Do not scrub the area. Pat the area dry and put on a clean bandage as directed.
Physical therapy:
A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. At first, your therapist will move your arm for you. This is called passive range of motion (PROM). He or she may teach someone close to you how to properly move your arm. PROM exercises can be done at home.
Follow up with your surgeon as directed:
You will need to have your drain removed. You may need x-rays to show how your shoulder is healing. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
