Screening for Hypertension
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about screening for hypertension?
Screening means your blood pressure (BP) is checked for hypertension, even if you do not have signs or symptoms. Regular screening can find problems early and treatment can begin. Early treatment can save your life. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the benefits and risks of screening. Screening is recommended every year starting at age 40. Screening may be recommended every 3 to 5 years from ages 18 to 39. If you are pregnant, screening will be done at each prenatal visit.
What do I need to know about hypertension?
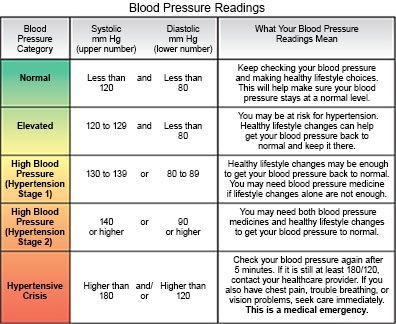
- Blood pressure is the force of your blood pressing against the walls of your arteries. Blood pressure readings are shown with a top number and a bottom number. The top number (systolic pressure) shows the pressure in your arteries while your heart contracts. The bottom number (diastolic pressure) shows the pressure in between heartbeats.
- Normal BP is 119/79 or lower.
- Prehypertension is 120/80 to 129/80.
- Stage 1 hypertension is 130/80 to 139/89.
- Stage 2 hypertension is 140/90 to 180/120.
- A hypertensive crisis is 181/121 or higher.
- You may have hypertension and not know it until serious health effects develop. This can cause a delay in treatment.
- Hypertension can be life-threatening if it is not treated. Even with treatment, hypertension can damage your blood vessels.
- Possible treatment includes medicines to lower your BP. If your BP is elevated, your healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle changes before medicines. Changes include losing weight if you are overweight, having less sodium (salt), and getting more physical activity.
What increases my risk for hypertension?
- Age older than 55 years (males) or 65 (females)
- Pregnancy
- Stress, or a family history of hypertension or heart disease
- Obesity, sleep apnea, lack of exercise, or too many high-sodium foods
- Use of tobacco, alcohol, or illegal drugs
- A medical condition, such as diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid disease, or adrenal gland disorder
- Certain medicines, such as steroids or birth control pills
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Valsartan
Valsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) that may be used to treat high blood pressure ...
Hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril
Hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril systemic is used for heart failure, high blood pressure
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Cozaar
Cozaar (losartan) is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). Includes Cozaar side ...
Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat fluid retention and high blood pressure by increasing ...
Clonidine
Clonidine lowers blood pressure by decreasing the levels of certain chemicals in your blood. It is ...
Carvedilol
Carvedilol (Coreg) is used to treat heart failure and hypertension (high blood pressure). Includes ...
Toprol-XL
Toprol-XL (metoprolol) is a beta-blocker used to treat angina and high blood pressure. Includes ...
Atenolol
Atenolol is used to treat angina (chest pain) and hypertension (high blood pressure). Learn about ...
Am I a good candidate for hypertension screening?
You are a good candidate if you are at least 18 years old and either of the following is true:
- You are at risk for hypertension, but you do not have any signs or symptoms.
- You have a family history of hypertension.
How is screening for hypertension done?
- Your healthcare provider will check your BP. Your provider may check your BP a few times during your office visit. This helps make sure the reading is accurate. BP can rise if a person is nervous about being in a doctor's office.
- Your BP will be checked again after you leave your provider's office. The following are ways your BP may be checked:
- A device you wear gives BP readings automatically. The readings are taken every 20 to 30 minutes for 12 to 24 hours. You will be able to do your normal daily activities and sleep during this time.
- You may be shown how to check your BP with a machine. You will strap a cuff to your upper arm. The cuff tightens as the machine starts. You will need to check your BP regularly. Your healthcare provider will tell you when and how often to check.

What are the risks of hypertension screening?
- A false-negative result can happen. The result can delay treatment because no hypertension was found. It may cause you to not seek treatment even when you have symptoms.
- A false-positive result can happen. This result can cause you to have more tests. It can also cause you to feel anxious if you think you have hypertension.
What should I ask my healthcare provider before I decide to have hypertension screening?
- How high is my risk for hypertension?
- Will my insurance cover screening?
- Where is the screening done?
- Do I need to do anything to get ready to have screening?
- When and how do I get the results of my screening?
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
