Screening for A-Fib (Atrial Fibrillation)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 7, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about screening for atrial fibrillation (A-fib):
Screening means you are checked for A-fib even if you do not have signs or symptoms. Screening can find problems early so treatment can begin. Early treatment can save your life. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the benefits and risks of screening. Screening may be recommended starting at age 50. You may need regular screenings if you stay at high risk for A-fib.
What you need to know about A-fib:
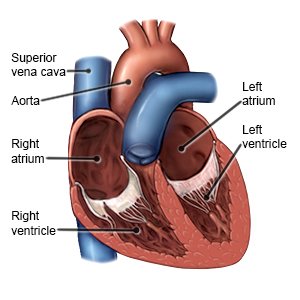
A-fib is an irregular heartbeat. It reduces your heart's ability to pump blood through your body. A-fib may come and go, or it may be a long-term condition. A-fib can cause life-threatening blood clots, stroke, or heart failure. It is important to treat and manage a-fib to help prevent these problems.
 |
Any of the following increases your risk for A-fib:
- High blood pressure, heart failure, or heart valve disease
- Smoking
- COPD, sleep apnea, a blood clot in your lung, or other lung diseases
- Diabetes, obesity, or thyroid disease
- Heavy alcohol use or large amounts of caffeine
- Age 65 or older
- A family history of A-fib or other heart problems
- Certain medicines, such as some antidepressants, bronchodilators, and cancer medicines
Signs and symptoms of A-fib:
- A heartbeat that races, pounds, or flutters
- Weakness, severe tiredness, or confusion
- Feeling lightheaded, sweaty, dizzy, or faint
- Shortness of breath or anxiety
- Chest pain or pressure
Treatment for A-fib:
Your healthcare provider can give you more information about possible treatments for A-fib. Treatment may include any of the following:
- Medicines may be used to help control your heart rate or rhythm. Blood thinners or other medicines may be used to prevent a blood clot or stroke.
- Procedures or surgery may be used to return your heart rate and rhythm to normal, control your heartbeat. Certain electrical signals that cause A-fib may be blocked.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
You are a good candidate for screening if the following are true:
- You have one or more risk factors for A-fib.
- You do not have any signs or symptoms of A-fib.
- You have not had a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
How screening for A-fib is done:
- An EKG may be used to check your heart rhythm and how fast your heart beats.
- A Holter monitor is a portable EKG machine you wear at home while you do your usual activities. You may be asked to wear it for several days.
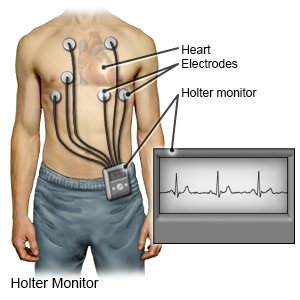
- A smart watch or smart phone may be used to check for an irregular heartbeat at home.
Risks of A-fib screening:
- A false-negative result can happen. The result can delay treatment because no A-fib was found. It may cause you to not seek treatment even when you have symptoms.
- A false-positive result can happen. This result can cause you to have more tests. It can also cause you to feel anxious if you think you have A-fib. Medicines such as blood thinners may be prescribed even though you do not need them. Blood thinners increase your risk for bleeding and bruising.
Before you decide to have A-fib screening,
ask your healthcare provider the following:
- How high is my risk for A-fib?
- Can I have A-fib screening while I am pregnant?
- Will my insurance cover screening?
- Where is the screening done?
- Do I need to do anything to get ready to have screening?
- When and how do I get the results of my screening?
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Screening for A-Fib
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
