Sciatica
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
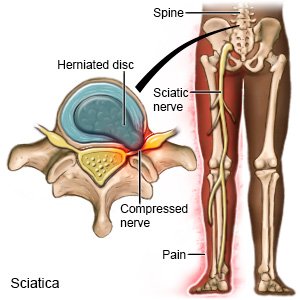
What is sciatica?
Sciatica is a condition that causes pain along your sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve runs from your spine through both sides of your buttocks. It then runs down the back of your thigh, into your lower leg and foot. Any place along your sciatic nerve may be compressed, inflamed, irritated, or stretched.
 |
What causes sciatica?
Sciatica may be related to certain activities, poor posture, and physical or psychological stress. Any of the following may cause or increase your risk for sciatica:
- A slipped disc or narrowed spinal column that presses on the sciatic nerve
- Muscle injury after you twist or lift a heavy object
- Swelling from sprained or irritated muscles that press on the sciatic nerve
- Extra body weight that increases pressure on your back and legs
- A direct blow on the buttocks, thighs, or legs, car accidents, or falls that injure the sciatic nerve
- A disease of the spine, such as arthritis, osteoporosis, or cancer
What are the signs and symptoms of sciatica?
The symptoms of sciatica may be short-term or long-term:
- Pain that goes from the lower back into your buttocks and down the back of your thigh
- Numbness or tingling in your buttocks and legs
- Muscle weakness, difficulty moving or controlling your leg or foot
- Leg pain that increases with standing, sitting, or squatting
How is sciatica diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about other health conditions you may have. Tell your provider about your job, history of back pain, diseases, or surgeries you have had. Your provider will examine you and move your legs to see what increases pain. You may also need any of the following:
- X-rays of your back, hip, thigh, or leg may show other problems, such as fractures (broken bones).
- A CT scan or MRI may show your sciatic nerve, muscles, and blood vessels. You may be given contrast liquid to help the area show up better in pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- An electromyography (EMG) test measures the electrical activity of your muscles at rest and with movement.
- Nerve conduction tests check how surface nerves and related muscles respond to stimulation. Electrodes with wires or tiny needles are placed on certain areas, such as the buttocks and legs.
How is sciatica treated?
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Muscle relaxers help decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Ultrasound therapy is a machine that uses sound waves to decrease pain. Topical medicines may be added to help decrease pain and inflammation.
- Epidural steroid medicine may include both an anesthetic (numbing medicine) and a steroid. A steroid may decrease swelling and relieve pain. It is given as a shot close to the spine in the area where you have pain.
- Chemonucleolysis is an injection given into the damaged disc to soften or shrink the disc.
- Surgery may be done to correct problems such as a damaged disc or a tumor in your spine. Surgery may be done to decrease the pressure on the sciatic nerve. Healthcare providers may also release the muscle that may be pressing into your sciatic nerve.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I help manage sciatica?
- Physical or occupational therapy may be recommended. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. An occupational therapist teaches you skills to help with your daily activities.
- Assistive devices may make you more comfortable or relieve pressure in the area. You may need back support, such as a back brace. You may need crutches, a cane, or a walker to decrease stress on your lower back and leg muscles. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about assistive devices and how to use them correctly.
How can sciatica be prevented?
- Avoid pressure on your back and legs. Do not lift heavy objects, or stand or sit for long periods of time.
- Lift objects safely. Keep your back straight and bend your knees when you pick up an object. Do not bend or twist your back when you lift.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a weight loss plan, if needed.
- Exercise as directed. Ask your healthcare provider about the best stretching, warmup, and exercise plan for you.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
L-Carnitine
L-Carnitine is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Carnitor
Carnitor is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Carnitor SF
Carnitor SF is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Phenytoin
Phenytoin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. Learn about side effects ...
Capsaicin topical
Capsaicin information from Drugs.com, includes Capsaicin side effects, interactions and indications.
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is used to treat epileptic seizures and nerve pain such as trigeminal neuralgia ...
Levocarnitine
Levocarnitine systemic is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Pregabalin
Pregabalin may be used to treat certain types of pain and used in combination with other ...
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have trouble controlling your urine or bowel movements.
- You have weakness in both legs.
- You have numbness in your groin or buttocks.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have pain in your lower back at night or when resting.
- You have pain in your lower back with numbness below the knee.
- You have weakness in one leg only.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Sciatica
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
