Scalp Contusion in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 7, 2024.
What is a scalp contusion?
A scalp contusion is a bruise that appears on your child's skin after an injury. A bruise happens when small blood vessels tear but skin does not. Blood leaks into nearby tissue, such as soft tissue or muscle.
What increases my child's risk for a scalp contusion?
- A disorder that makes your child bleed more easily
- Kidney or liver disease, or an infection
- Medicines such as blood thinners or certain over-the-counter medicines and herbal medicines
- Weakened skin and muscles from nutrition problems
What are the signs and symptoms of a scalp contusion?
- An area that may be black, blue, red, or darker than the skin around it
- Pain, tenderness, swelling, or a lump at the site of the bruise or near it
How is a scalp contusion diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider may ask about any injuries, infections, or bleeding problems your child has had. The provider will check the skin over the injured area. Your child may also need any of the following:
- Blood tests may be used to check for blood disorders or to see how long it takes for your child's blood to clot.
- Ultrasound pictures may show how deep the bruise is and if your child has any other injury.
- MRI pictures may show if a hematoma (pooling of blood) has started to form. Your child may be given contrast liquid to help the pictures show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not let your child enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI machine uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has any metal in or on his or her body.
How is a scalp contusion treated?
A scalp contusion may heal without any treatment. The bruise may become lighter or change to green or yellow as it heals. Your child may need any of the following if the contusion is severe or does not heal easily:
- Medicine may be needed to treat or prevent pain or swelling.
- Aspiration is a procedure to drain pooled blood to prevent pressure from building up.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to manage my child's scalp contusion?
- Stay with your child for 24 to 48 hours after the injury. Watch for signs of serious injury, such as a seizure or trouble moving. Your child will need immediate care if he or she develops any of the signs.
- Apply ice to decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel and place it on your child's bruise. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour, or as directed.
- Do not massage the area or put heating pads on the bruise right after the injury. Heat and massage may slow healing. Your child's healthcare provider may tell you to apply heat after several days. At that time, heat will start to help the injury heal.
How can I help my child prevent a scalp contusion?
- Use safety belts and child restraints in the car.

- Have your child use a helmet when he or she rides a bicycle.
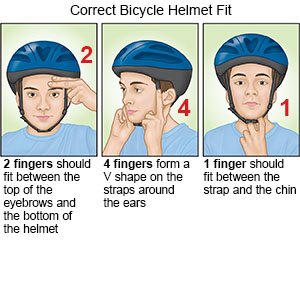
- Have your child use a mouth and face guard during sports.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has a seizure.
- Your child is hard to wake or cannot be woken.
- Your child is having trouble speaking, keeping his or her balance, or walking.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child's breathing is too slow, too fast, or different than usual.
- Your child has blood or clear fluid coming out of his or her nose, ears, or mouth.
- Your child has vomited 2 to 3 times within 24 hours.
- Your child's pupils are not the same size.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child has a headache or neck pain.
- Your child is irritable, will not stop crying, or cannot be consoled.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Scalp Contusion
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
