Peripheral Neuropathy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Peripheral neuropathy (PN)
is a type of nerve damage that can develop when your peripheral nerves are damaged. Peripheral nerves are located outside of the brain and spinal cord. These nerves send information from your brain and spinal cord to the rest of your body. Damage to these nerves can slow or stop their ability to send signals. PN is most common in the hands and feet. It can also affect body functions, such as urination or digestion.
Common signs and symptoms:
Your symptoms depend on the types of nerves damaged and where they are located. The following are some of the most common signs and symptoms:
- Pain or tingling in your legs, feet, arms, or hands that may feel sharp, stabbing, or burning
- Trouble walking or keeping your balance
- Weakness or trouble holding things
- Loss of your sense of touch or numbness
- Bruising easily
- Trouble controlling your bladder or bowels or having sex
Seek care immediately if:
- You are injured from a fall.
- Your legs or feet start to turn blue or black.
- You have severe trouble walking.
- You have a wound that does not heal or is red, swollen, or draining fluid.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
L-Carnitine
L-Carnitine is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Carnitor
Carnitor is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Carnitor SF
Carnitor SF is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Phenytoin
Phenytoin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. Learn about side effects ...
Capsaicin topical
Capsaicin information from Drugs.com, includes Capsaicin side effects, interactions and indications.
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is used to treat epileptic seizures and nerve pain such as trigeminal neuralgia ...
Levocarnitine
Levocarnitine systemic is used for carnitine deficiency, peripheral neuropathy
Pregabalin
Pregabalin may be used to treat certain types of pain and used in combination with other ...
Call your doctor or neurologist if:
- Your pain is severe.
- You cannot control your bladder.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment:
- Medicines:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Seizure medicines and antidepressants may help relieve nerve pain. These medicines change how your nerves and brain communicate pain.
- Topical treatments, such as creams or patches may also help decrease pain.
- A physical therapist teaches you movements and exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease nerve pain.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) stimulates your nerves and may decrease your pain. Pads are attached to your skin and a mild gentle current is given.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage PN:
- Treatment of underlying conditions is the best way to manage your PN. This may include treating conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or an infection. This may also include healing of an injury or trauma.
- Check your skin daily. Look for redness and swelling, and feel for warmth. Sores can form where your skin makes contact with objects or other body parts. They also can form under splints.
- Be physically active at least 30 minutes, 5 days a week. Ask your healthcare provider about the best activity plan for you. Use caution when you exercise if you have decreased feeling in your feet.

- Limit alcohol as directed. Alcohol can cause high blood sugar levels and weight gain if you drink too much. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor. Your healthcare provider can tell you how many drinks are okay to have within 24 hours and within 1 week.
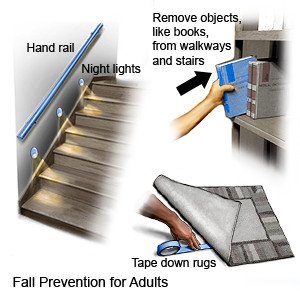
- Prevent falls. Move with care, and stand up slowly. Wear shoes that support your feet, and do not go barefoot. Ask about walking aids, such as a cane or walker. You may want to install railings or nonslip pads in your home, especially in the bathroom. Ask for more information on how to prevent falls.
Follow up with your doctor or neurologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Peripheral Neuropathy
Treatment options
- Medications for Autonomic Neuropathy
- Medications for Peripheral Neuropathy
- Medications for Refsum's Disease
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
